Vorion: A RISC-V GPU with Hardware-Accelerated 3D Gaussian Rendering and Training
By Yipeng Wang, Mengtian Yang, Chieh-pu Lo, and Jaydeep P. Kulkarni
University of Texas at Austin Austin, TX
Abstract
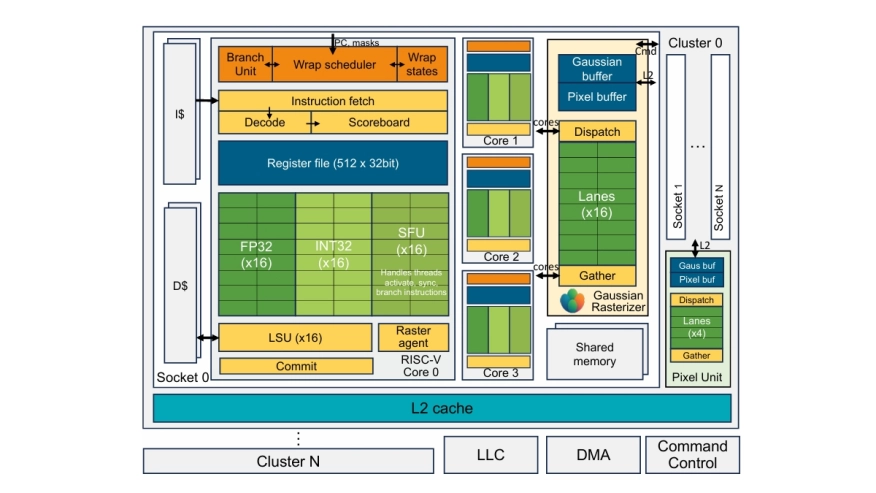
 3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently emerged as a foundational technique for real-time neural rendering, 3D scene generation, volumetric video (4D) capture. However, its rendering and training impose massive computation, making real-time rendering on edge devices and real-time 4D reconstruction on workstations currently infeasible. Given its fixed-function nature and similarity with traditional rasterization, 3DGS presents a strong case for dedicated hardware in the graphics pipeline of next-generation GPUs. This work, Vorion, presents the first GPGPU prototype with hardware-accelerated 3DGS rendering and training. Vorion features scalable architecture, minimal hardware change to traditional rasterizers, z-tiling to increase parallelism, and Gaussian/pixel-centric hybrid dataflow. We prototype the minimal system (8 SIMT cores, 2 Gaussian rasterizer) using TSMC 16nm FinFET technology, which achieves 19 FPS for rendering. The scaled design with 16 rasterizers achieves 38.6 iterations/s for training.
3D Gaussian Splatting (3DGS) has recently emerged as a foundational technique for real-time neural rendering, 3D scene generation, volumetric video (4D) capture. However, its rendering and training impose massive computation, making real-time rendering on edge devices and real-time 4D reconstruction on workstations currently infeasible. Given its fixed-function nature and similarity with traditional rasterization, 3DGS presents a strong case for dedicated hardware in the graphics pipeline of next-generation GPUs. This work, Vorion, presents the first GPGPU prototype with hardware-accelerated 3DGS rendering and training. Vorion features scalable architecture, minimal hardware change to traditional rasterizers, z-tiling to increase parallelism, and Gaussian/pixel-centric hybrid dataflow. We prototype the minimal system (8 SIMT cores, 2 Gaussian rasterizer) using TSMC 16nm FinFET technology, which achieves 19 FPS for rendering. The scaled design with 16 rasterizers achieves 38.6 iterations/s for training.
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- Compact Embedded RISC-V Processor
- Highly configurable HW PQC acceleration with RISC-V processor for full CPU offload
- Vector-Capable Embedded RISC-V Processor
- Tiny, Ultra-Low-Power Embedded RISC-V Processor
- Enhanced-Processing Embedded RISC-V Processor
Related Articles
- A RISC-V Multicore and GPU SoC Platform with a Qualifiable Software Stack for Safety Critical Systems
- An Open-Source Approach to Developing a RISC-V Chip with XiangShan and Mulan PSL v2
- Lyra: A Hardware-Accelerated RISC-V Verification Framework with Generative Model-Based Processor Fuzzing
- ElfCore: A 28nm Neural Processor Enabling Dynamic Structured Sparse Training and Online Self-Supervised Learning with Activity-Dependent Weight Update
Latest Articles
- GenAI for Systems: Recurring Challenges and Design Principles from Software to Silicon
- Creating a Frequency Plan for a System using a PLL
- RISCover: Automatic Discovery of User-exploitable Architectural Security Vulnerabilities in Closed-Source RISC-V CPUs
- MING: An Automated CNN-to-Edge MLIR HLS framework
- Fault Tolerant Design of IGZO-based Binary Search ADCs