Video Codec IP
Video codec IP cores encode and decode digital video signals in real-time. These cores are designed to offload the computationally intensive tasks of video compression and decompression from a general-purpose processor. By supporting various video standards such as H.264, HEVC, VP9, and AV1, video codec IP cores enable efficient video streaming, storage, and playback. They offer high performance, low power consumption, and flexibility, ensuring high-quality video experiences across a wide range of applications.
All offers in
Video Codec IP
Filter
Compare
315
Video Codec IP
from
69
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
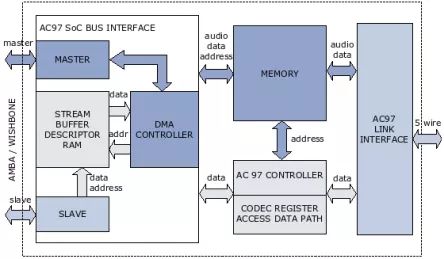
AC97 Audio Controller
- Fixed 48kHz audio support
- Hardware variable sample rate support from 8kHz to 48kHz (up to 96kHz with Double Rate Audio enabled)
- Double Rate Audio support for Left, Right and Center channels
- 16 bit sample size support (18 and 20 bit support planned in future)
-
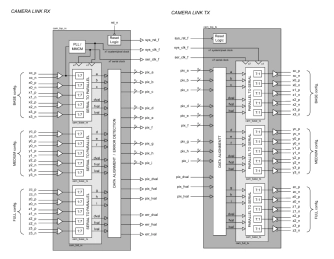
Camera Link Interface
- The Camera Link® IP Core is a high-speed LVDS transmitter / receiver pair that conforms to the standard Camera Link protocol originally developed by National Semiconductor Corp®.
- The design is comprised of an independent transmitter and receiver that may be implemented separately or together as a single transceiver unit. The IP Core may be used in either the BASE, MEDIUM or FULL configurations as defined in the Camera Link specification.
-
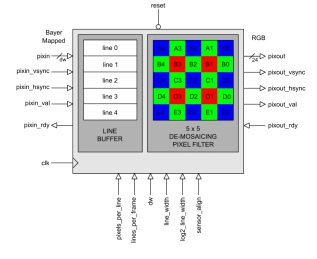
Bayer to RGB Converter
- BAYER_TO_RGB is a fully pipelined Bayer-mapped to RGB converter IP Core.
- The IP Core may be used to process the raw pixels from an image sensor or Colour Filter Array (CFA).
- These pixels are typically organized as a bayer pattern of discrete Red, Green and Blue values which must be interpolated to recover the original image - a process that is commonly known as de-mosaicing.
-
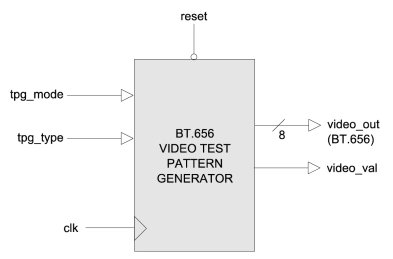
BT656 Test Pattern Generator
- Test patterns as industry standard ITU-R BT.656
- Supports PAL (576i) and NTSC (480i) formats
- Choice of various test pattern outputs
- All signals synchronous with pixel clock
-
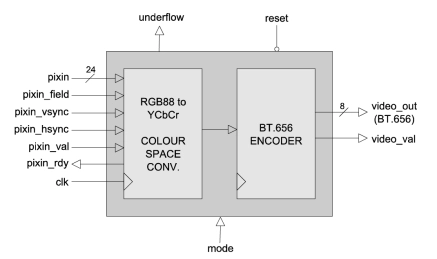
BT656 Encoder with Colour-Space Converter
- BT_656_ENCODER is a digital video encoder with integrated colour-space converter. The encoder accepts 24-bit RGB pixels from sequential odd and even fields.
- These pixels are then mapped to the YCbCr colour-space and formatted correctly into a BT.656 output stream.
-
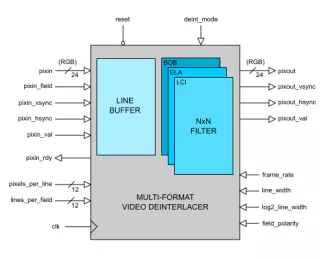
Multi-format Video Deinterlacer
- The DEINTERLACER IP Core is a high quality 24-bit RGB video deinterlacer capable of generating progressive output video at up to 4096x4096 pixels in resolution.
- The design is fully customizable, supporting any desired interlaced video format.
-
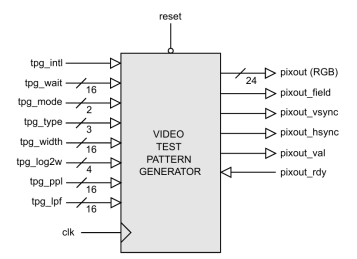
Video Test Pattern Generator
- Pixels and syncs are generated on a rising clock-edge when pixout_val is high and pixout_rdy is high.
- The signal pixout_vsync is active high when the first pixel of a frame is output.
- The signal pixout_hsync is active high when the first pixel of a line is output.
- The pixout_field flag indicates either an odd or even field when interlaced mode is enabled.
-
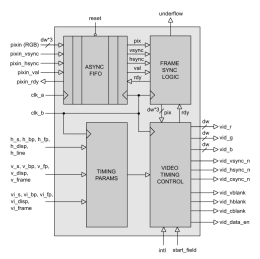
Video Timing Generator
- The VID_TIMING_GEN IP Core is a fully configurable video timing generator with the ability to support any video resolution up to 216 x 216 pixels in size.
- The module is compatible with a wide range of video DACs, encoders and transmitters and provides a flexible solution for displaying digital or analogue video on an external TV, monitor or flat panel display.
- The module is capable of clock speeds in excess of 400 MHz on some FPGA platforms, making it ideal for the latest generation HD and UHD video solutions.
-
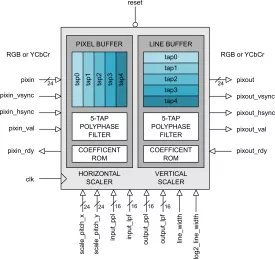
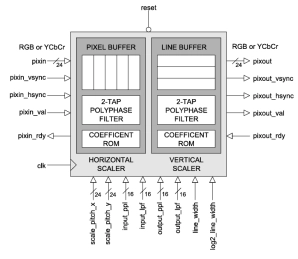
Bilinear Video Scaling Engine
- XY2_SCALER is a very high quality video scaler capable of generating interpolated output images from 16x16 up to 216 x 216 pixels in resolution.
- The architecture permits seamless scaling (either up or down) depending on the chosen scale factor.
- Internally, the scaler uses a 24-bit accumulator and a bank of polyphase FIR filters with 16 phases or interpolation points.
- All filter coefficients are programmable, allowing the user to define a wide range of filter characteristics.
-
Digital Video Scaler
- 24-bit RGB video in/out
- Independent vertical and horizontal scaling
- Resolutions from 16x16 to 4095x4095 pixels