RISC-V Processor IP
Welcome to the ultimate RISC-V Processor IP hub! Explore our vast directory of RISC-V Processor IP.
RISC-V is an open-source instruction set architecture used to develop custom processors for a variety of applications, from embedded designs to supercomputers.
Unlike proprietary processor architectures, RISC-V is an open-source instruction set architecture (ISA) used for the development of custom processors targeting a variety of end applications.
All offers in
RISC-V Processor IP
Filter
Compare
150
RISC-V Processor IP
from
34
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
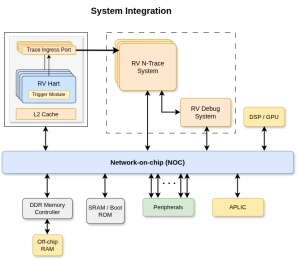
RISC-V Debug & Trace IP
- 10xEngineers Debug & N-Trace IP delivers a unified Debug + Trace solution that provides full-system visibility with low overhead and multi-hart awareness.
- Standards-compliant debug, real-time trace, and flexible triggering significantly reduce bring-up time and simplify system integration.
-
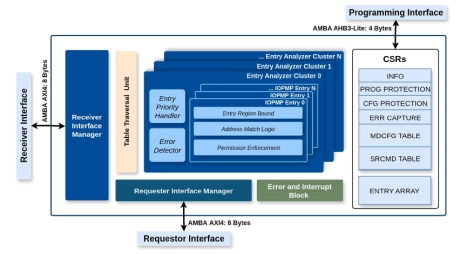
RISC-V IOPMP IP
- The I/O Physical Memory Protection (IOPMP) unit is a hardware-based access control mechanism designed to safeguard memory regions in RISC-V SoCs.
- It ensures only authorized devices and masters can access sensitive memory areas, enabling secure and reliable system operation.
-
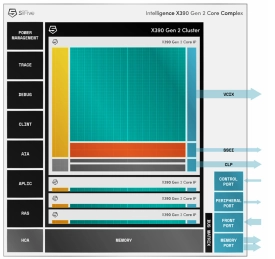
Gen#2 of 64-bit RISC-V core with out-of-order pipeline based complex
- Gen#2 of 64-bit RISC-V core with out-of-order pipeline based complex. Designed for a range of applications requiring maximum single thread performance in Linux-capable devices. Improved performance compared with Gen#1.
-
64-bit RISC-V core with in-order single issue pipeline. Tiny Linux-capable processor for IoT applications.
- 64-bit RISC-V core with in-order single issue pipeline based complex.
- Tiny Linux-capable processor optimized for low power and small area.
- Ideally fits IoT applications requiring Linux.
-
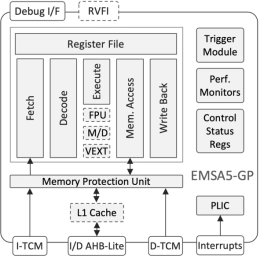
Vector-Capable Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The EMSA5-GP is a highly-featured 32-bit RISC-V embedded processor IP core optimized for processing-demanding applications.
- It is equipped with floating-point and vector-processing units, cache memories, and is suitable for concurrent execution in a multi-processor environment.
-
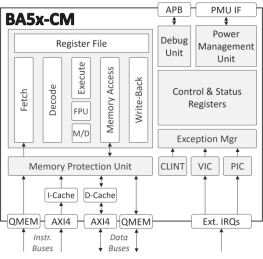
Compact Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The BA5x-CM is a feature-rich 32-bit deeply embedded processor.
- Equipped with a floating-point unit and an instruction cache memory and supporting concurrent execution in a multiprocessor environment, it is well-suited to a wide range of edge IoT and similar applications.
-
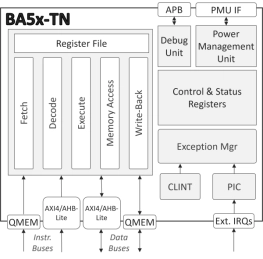
Tiny, Ultra-Low-Power Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The BA5x-TN is a compact, ultra-low power, 32-bit, deeply embedded processor IP core.
- With a two-stage execution pipeline, the processor implements the Embedded variant of the base RV32 ISA (RV32E).
- It uses just 16 general-purpose compressed instructions and omits other resource-demanding extensions.
-
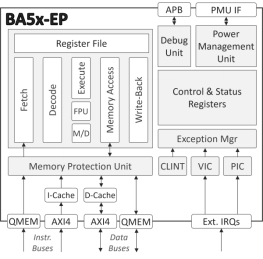
Enhanced-Processing Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The BA5x-EP is a highly-featured 32-bit RISC-V embedded processor IP core optimized for complex, processing-demanding applications.
- It is equipped with a floating-point unit and cache memories, supports hardware-level virtualization, and is suitable for concurrent execution in a multi-processor environment.
-
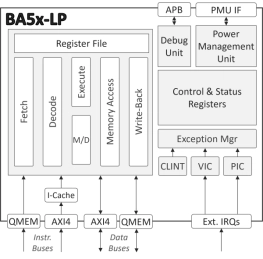
Low-Power Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The BA5x-LP is a highly efficient, low-power, 32-bit, deeply embedded processor IP core.
- The two-stage pipeline processor implements either the RV32I or RV32E instruction set.
- It comes pre-configured with the Multiply/Divide (M) and Compressed Instruction (C) extensions, providing a more flexible and capable platform without a significant increase in area or power.
-
8-stage dual issue, in-order, superscalar processor with dual vector processing units (1024-bit VLEN/512-bit DLEN)
- New RVA23 support
- New RVV1.0 512-bit vector engine
- New SSCI interface added alongside VCIX
- New instructions and extensions
- New improved memory subsystem