AMBA AHB / APB/ AXI IP
Welcome to the ultimate AMBA AHB / APB/ AXI IP hub! Explore our vast directory of AMBA AHB / APB/ AXI IP
All offers in
AMBA AHB / APB/ AXI IP
Filter
Compare
337
AMBA AHB / APB/ AXI IP
from
38
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
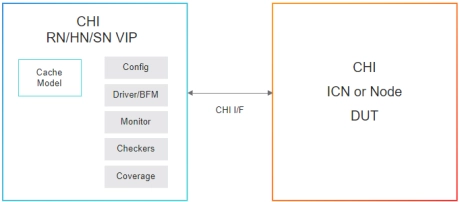
Simulation VIP for AMBA CHI
- Support testbench language interfaces for SystemVerilog, UVM, OVM, e, and SystemC
- Generates constrained-random bus traffic with predefined error injection
- Callbacks access at multiple queue points for scoreboarding and data manipulation
- Provides comprehensive checking and coverage model
-
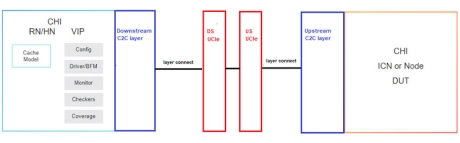
Simulation VIP for AMBA CHI-C2C
- Incorporating the latest protocol updates, the Cadence Verification IP for CHI-C2C provides a complete bus functional model (BFM), integrated automatic protocol checks, and a coverage model.
- Designed for easy integration in testbenches at IP, systems with multiple CPUs, accelerators, or other device chiplets, the VIP for CHI-C2C provides a highly capable compliance verification solution that supports simulation, formal analysis, and hardware acceleration platforms.
-
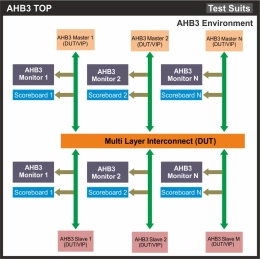
AMBA AHB 3 Lite Verification IP
- The AMBA 3 AHB-Lite Verification IP provides an effective & efficient way to verify the components interfacing with AMBA®3 AHB-Lite bus of an IP or SoC.
- The AMBA 3 AHB-Lite VIP is fully compliant with standard AMBA 3 AHB-Lite specification from ARM.
- This VIP is a light weight VIP with easy plug-andplay interface so that there is no hit on the design cycle time.
-
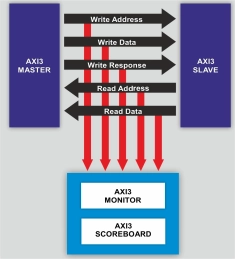
AMBA AXI3 Verification IP
- The AMBA AXI3 Verification IP provides an effective & efficient way to verify the components interfacing with AMBA® AXI3 bus of an IP or SoC.
- The AMBA AXI3 VIP is fully compliant with standard AMBA® AXI3 specification from ARM.
- This VIP is a light weight VIP with easy plug-and-play interface so that there is no hit on the design cycle time.
-
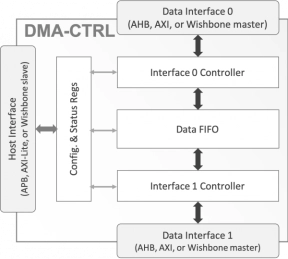
AHB/AXI/Wishbone DMA Controller
- The AXI4-SGDMA IP core implements a Host-to-Peripheral (H2P), or a Peripheral-to-Host (P2H) Direct Memory Access (DMA) engine, which interfaces the host system with an AXI4 Memory-Mapped master port and the peripheral with either a slave or a master AXI4-Stream port.
- The core operates in either Scatter-Gather (SG) Mode, reading descriptors from a run-time defined memory mapped-location, or in Direct Mode, transferring data according to a descriptor stored in local registers.
-
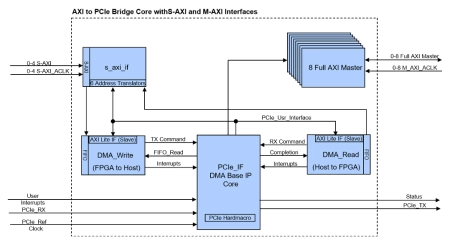
AXI Bridge for PCIe IP Core
- The AXI Bridge for PCIe IP core is the IP solution with a powerful mix of multiple industry standard memory mapped AXI Interfaces.
- The AXI Bridge IP core translates the AXI4 memory read or writes to PCI-Express Transaction Layer Packets and translates PCIe memory read and write requests to AXI4 transactions.
- All interfaces support fully parallel operation without any interferences. Interfaces that are not required can be turned off individually and do not occupy logic resources.
-
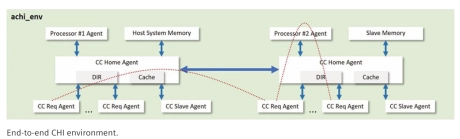
Verification IP for AMBA
- AMBA® ACE and CHI coherent interconnect technologies enable an entirely new class of high-performance datacenter applications in areas of machine learning, network processing, storage off-load, in-memory database, and 4G/5G wireless technology.
- Processor architectures and accelerators can now seamlessly operate over cache coherent intercon nects using the right combination of general-purpose processors and heterogeneous acceleration devices, such as FPGAs, GPUs, network/ storage adapters, intelligent networks, and custom ASICs.
-
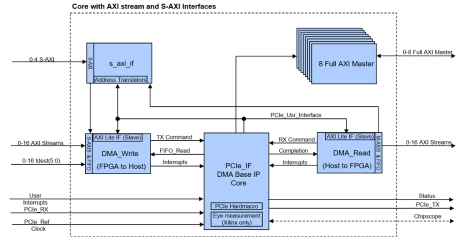
AXI Bridge with DMA for PCIe IP Core
- The AXI Bridge with DMA IP core is the ultimate PCIe DMA IP solution with a powerful mix of multiple industry standard AXI Interfaces.
- AXI Stream interfaces allow continuous data streaming from FPGA to Host or from Host to FPGA. S-AXI Memory mapped interfaces allow easy data access of remote memories in order to realize shared memory access or per to peer applications.
-
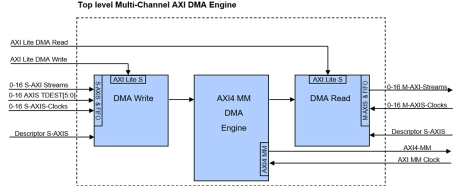
Multi-Channel AXI DMA Engine
- The Multi-Channel AXI DMA engine IP Core for AXI4 is a powerful programmable AXI Stream to AXI memory mapped bridge with sophisticated data addressing options.
- These features allow data accesses on a tile basis in order to address regions of interest (ROI) based applications like stereo cameras, 2D picture compression algorithms and others.
-
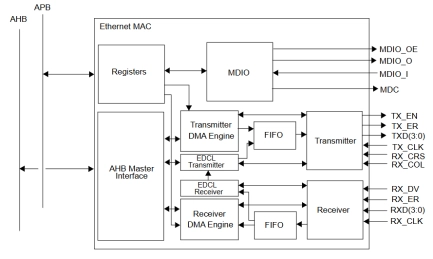
10/100 Mbit Ethernet MAC
- The GRETH core implements a 10/100 Mbit/s Ethernet Media Access Controller (MAC) with AMBA host interface.
- The core implements the 802.3-2002 Ethernet standard. Receive and transmit data is autonomously transferred between the Ethernet MAC and the AMBA AHB bus using DMA transfers.