CAN IP
CAN controller IP cores provide a standardized communication interface, ensuring compatibility and interoperability between ECUs within the vehicle. It allows for seamless data exchange, enabling efficient coordination and control of various automotive systems.
Explore our vast directory of CAN IP Cores
All offers in
CAN IP
Filter
Compare
41
CAN IP
from
24
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
3.3V CAN Transceiver
- The TS_CAN_3V3_X8 is a 3.3V CAN transceiver, which supports data rates up to 1Mbps and is compatible with ISO 11898-2 compliant CAN transceivers.
- It supports a standby mode with wake up via wake-up pattern.
- The TS_CAN_3V3_X8 provides a symmetrical output signal on CANL/CANH and incorporates slope-control to improve EMI performance.
-
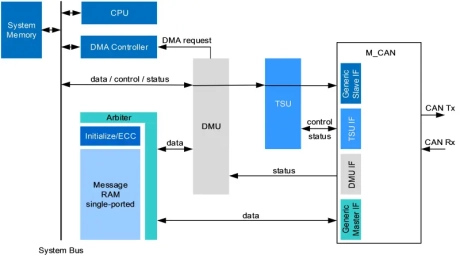
Timestamping unit
- Supports DMA transfers between M_CAN Message RAM and System Memory
- Up to sixteen 32-bit timestamps supported by TSU
- On reception or transmission of sync messages by the attached M_CAN, the TSU captures the actual value of its internal 32-bit timestamp counter and stores it to one of its timestamp registers.
-
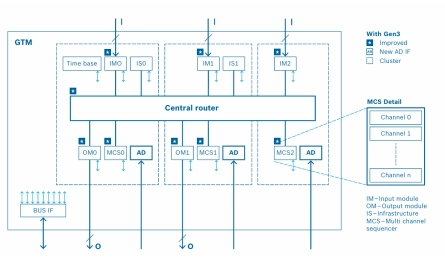
Generic timer IP
- Enables real-time control loops
- Deterministic multi-threaded architecture (8 threads per RISC unit)
- Programmability (special purpose RISC/ALU)
- Scalable and configurable architecture
-
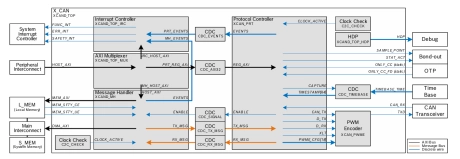
Protocol controller IP for Classical CAN / CAN FD / CAN XL
- The X_CAN is the new CAN Communication Controller IP supporting CAN XL protocol.
- It can be integrated as part of a SoC. It is described in VHDL on RTL level, prepared for synthesis.
- The X_CAN performs communication according to ISO11898-1:2015 and CiA610-1.
-
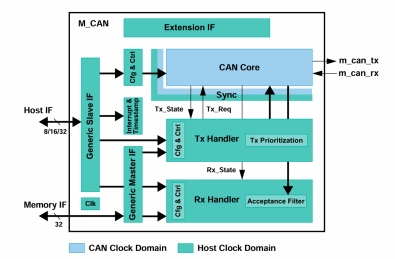
Protocol controller IP for CAN / CAN FD
- The M_CAN module is the new CAN Communication Controller IP-module that can be integrated as stand-alone device or as part of an ASIC.
- It is described in VHDL on RTL level, prepared for synthesis. The M_CAN performs communication according to ISO 11898-1:2015. Additional transceiver hardware is required for connection to the physical layer.
-
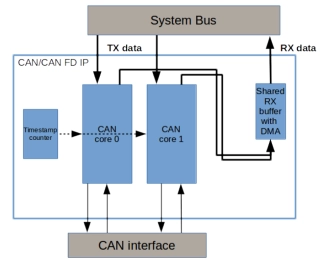
CAN 2.0/CAN FD IP core
- The IP is compliant to the new ISO 11898-1:2015 standard, supporting both standard CAN and CAN FD.
- The IP is available for most Xilinx, Altera, Lattice and Microsemi FPGA devices, supporting native bus interfaces like AXI, Avalon and APB. Processor integration is available for SOC type of FPGAs.
-
CAN FD LIGHT BUS CONTROLLER IP
- The Controller Area Network – Flexible Data-Light (CAN-FD Light) Controller IP implements the CAN FD-Light (CIA 604-1) protocol.
- It can be integrated into devices that require CAN-FD-Light connectivity commonly used in sensors and actuators for the automotive and industrial applications.
-
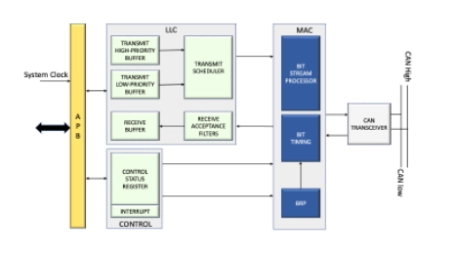
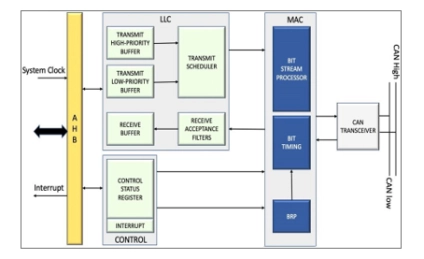
CAN 2.0 Bus Controller IP
- The CAN IP Controller Core performs serial communication as per CAN IP 2.0 Specifications. It supports full CAN IP 2.0 (both CAN IP 2.0A and 2.0B).
- The design implements the BOSCH CAN IP Message Transfer Protocols 2.0A (which is equivalent to CAN IP 1.2 and covers standard message formats with 11-bit identifiers); and 2.0B which covers both standard and extended message formats (both 11-bit and 29-bit identifiers).
-
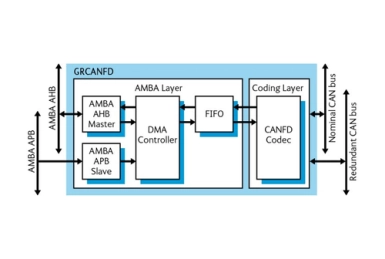
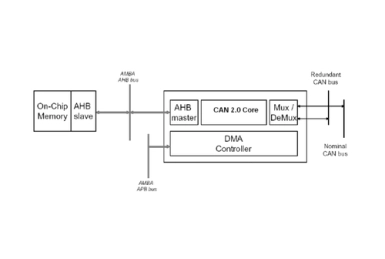
CAN 2.0 Controller with DMA
- GRCAN is a CAN 2.0 IP core that implements an internal CAN controller and an AHB DMA backend.
- The APB bus is used for configuration, control and status handling and the AHB bus is used for retrieving and storing CAN messages via the DMA engine.
-
CAN FD controller compatible with both CAN 2.0 and CAN FD
- Compatible with both CAN 2.0B and CAN-FD
- Fully compliant with ISO 11898-1:2015