MIPI IP
MIPI IP cores enable seamless communication between processors, sensors, and peripherals in mobile, automotive, and consumer electronics applications. Two key components of MIPI IP cores are the MIPI Controller IP and MIPI PHY IP. The MIPI Controller IP manages the data transfer process, ensuring efficient and reliable communication between devices, while the MIPI PHY IP handles the physical layer of the interface, ensuring high-speed, noise-resistant signal transmission.
Explore our vast directory of MIPI IP cores below.
All offers in
MIPI IP
Filter
Compare
695
MIPI IP
from
52
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
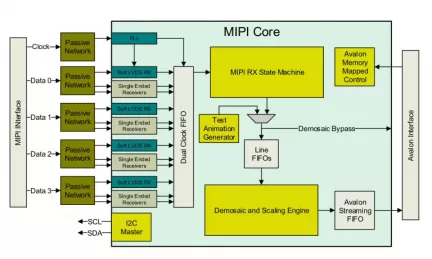
MIPI CSI2 Receiver
- Provides Compatible MIPI D-Phy v1.1 physical layer using FPGA LVDS/LVCMOS IO and passive network
- Supports CSI-2 protocol for unidirectional data transfer
- Compatible with D-PHY Configured for 1 clock and 4 data lanes
- Intended for per-lane clocks rates up to 1 Gbps, depending on device speed grade
-
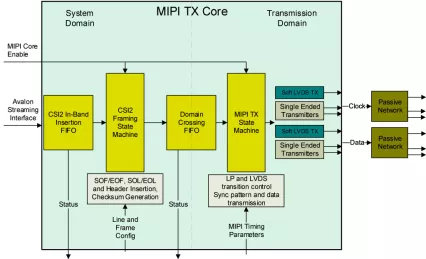
MIPI CSI2 Transceiver
- Provides Compatible MIPI D-Phy v1.1 physical layer using FPGA LVDS/LVCMOS IO and passive network
- Supports CSI-2 protocol for unidirectional data transfer
- Compatible with D-PHY Configured for 1 clock and 1 data lane
- Intended for per-lane clocks rates up to 1 Gbps, depending on device speed grade
-
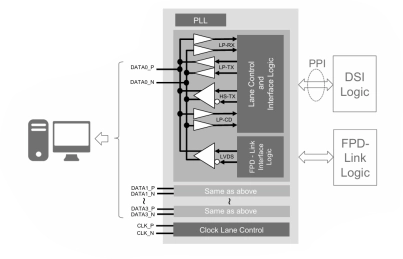
MIPI D-PHY and FPD-Link (LVDS) Combinational Transmitter for TSMC 22nm ULP
- Technology is TSMC 22nm ULP 1p10M.
- Supply voltage can be applied 1.0V for core voltage, 1.8V for IO voltage.
- Maximum data rate of each channel is 1.5Gbps at High-speed mode for MIPI D-PHY Transmitter.
- Data rate of each channel is 609Mbps for FPD-Link(LVDS).
-
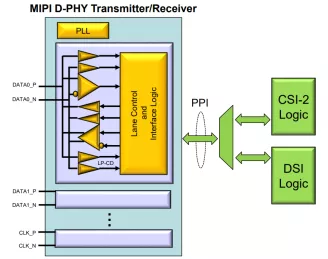
MIPI D-PHY Transmitter/Receiver for DSI/CSI-2 on Samsung 28nm FD-SOI
- Technology is Samsung 28nm FD-SOI 8M (6U1x_2T8x_LB).
- Supply voltage can be applied 1.1V for core voltage, 1.8V for IO voltage.
- Maximum data rate of each channel is 1.5Gbps at High-speed mode.
-
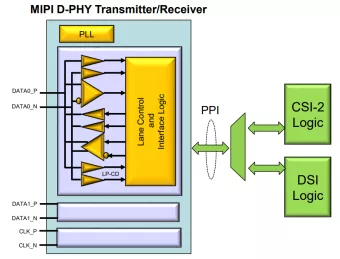
MIPI D-PHY Transmitter/Receiver for TSMC 40nm LP
- Renesas MIPI D-PHY Transmitter/Receiver can be used for analog Transmitter/Receiver of following interface.
- Technology is TSMC 40nm LP 1p6M (4x1z) .
- Supply voltage can be applied 1.1V for core voltage, 1.8V for IO voltage.
-
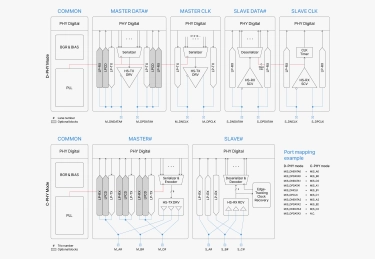
MIPI C/D-PHY Combo IP
- Compliant to MIPI D-PHY v3.0, C-PHY v2.1 specification
- Area efficient macro optimized for placement for dense SoC designs
- Support Uni-(TX or RX) and Bi-directional(TX and RX) mode
- Support emphasis architecture over lossy channel for TX
- Support equalize architecture over lossy channel for RX
-
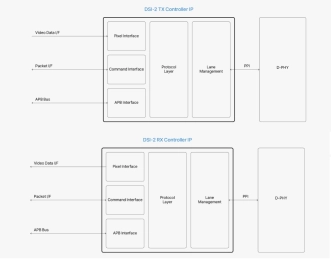
DSI-2 TX/RX Controller
- DSI-2 TX/RX IP supports both transmit and receive functions in line with the DSI-2 v1.1 and D-PHY v2.0 standards.
- Designed for modern SoCs integrating display functionality, it supports high-speed and low-power modes, lane configurability, and robust link features—making it ideal for advanced embedded display applications.
-
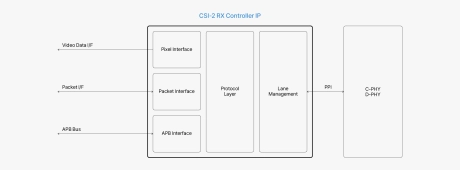
MIPI CSI-2 RX Controller
- Lane merging, virtual channel detection, and programmable data extraction
- Error detection and correction, including packet-level and protocol decoding errors
- Supports all pixel formats defined in the CSI-2 standard
-
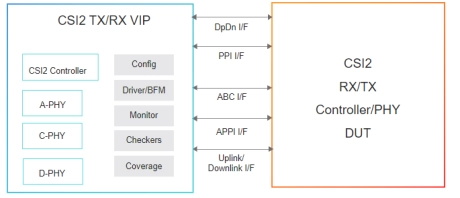
Simulation VIP for MIPI CSI-2
- Support testbench language interfaces for SystemVerilog, UVM, OVM, e, and SystemC
- Generates constrained-random bus traffic with predefined error injection at CSI-2, D-PHY, C-PHY and A-PHY levels
- Callbacks access at multiple TX and RX queue points for scoreboarding and data manipulation
-
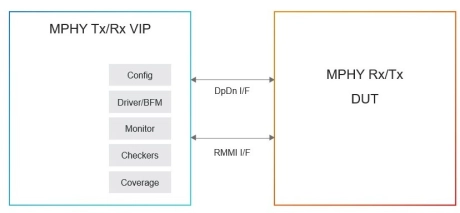
Simulation VIP for MIPI M-PHY
- Specification Compliance
- Complies with MIPI M-PHY 4.0, 4.1 and 5.0 specification
- M-PHY Type 1 and Type 2
- Supports Type 1 and Type 2