UEC-CBFC: Credit-Based Flow Control for Next-Gen Ethernet in AI and HPC
For ages, Ethernet has been the backbone of networking — starting from simple web browsing to cloud computing, data centers, automobiles, and more. Ethernet has enabled countless innovations, and now, it's expanding to meet the demands of AI and HPC.
As the world shifts toward these new technologies, new challenges are emerging. These include increased scale, higher bandwidth density, multi-pathing, and fast congestion response. As existing ethernet and other protocols were not designed to fully address these challenges, UEC steps in to fulfills the requirements introduced by these workloads.
The Ultra Ethernet Consortium is an industry-driven organization focused on establishing the best ethernet based high-performance network for AI and HPC workloads. UEC aims to improve bandwidth, latency, and scalability to meet the demands of future workload and computer architecture. UEC ensures backward compatibility with widely deployed APIs while defining new API.
Traditional flow control methods like IEEE 802.3 PAUSE stops all traffic on a link, which can lead to inefficiency. To improve this, Priority-based Flow Control (PFC) was introduced, which pauses traffic based on broad priority classes, but it still lacks granularity. To address these limitations, the Ultra Ethernet Consortium (UEC) introduced Credit-Based Flow Control (CBFC) which enables fine – grained and efficient control flow.
UEC – Credit-Based Flow Control
CBFC ensures lossless packet delivery by using a credit system to manage buffer space at the receiver. It is link layer flow control mechanism designed for full-duplex and point-to-point Ethernet connections. CBFC serves as an alternative to the IEEE 802.1Q-2022 standard Priority-based Flow Control (PFC).
How CBFC Works
- The receiver allocates available buffer space in the form of credits, where each credit represents unit of storage in buffer.
- The sender sends the packet only when it has enough credits to cover the packet’s size, thus eliminating the buffer overflow at the receiver.
- CBFC uses two cyclic counters to track the credits consumed and freed at sender and receiver, respectively.
UEC PHY
To support advanced features introduced by the UEC, such as Credit-Based Flow Control (CBFC) and Link-Level Retry (LLR), enhancements are required at the physical layer. UEC PHY supports Ethernet PHYs with 100 Gb/s signaling per lane. The PCS decoder/encoder supports UEC data rates ranging from 100G to 800G and includes optional support for Control Ordered Set – a messaging mechanism used by UEC features such as Link-Level Retry (LLR) and Credit-Based Flow Control (CBFC).
To learn more about UEC Link Layer Retry (LLR), please visit the following link: UEC-LLR: The Future of Loss Recovery in Ethernet for AI and HPC
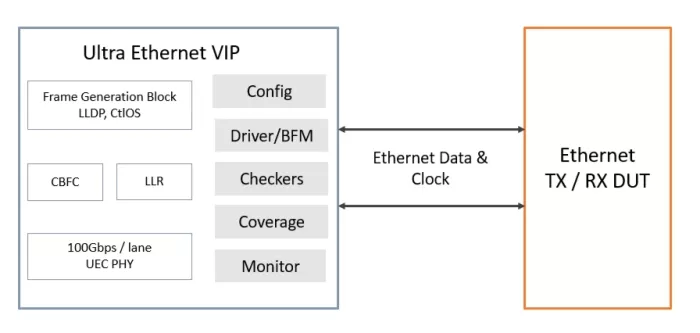
With the availability of the Cadence Verification IP for Ethernet, adopters can start working with these specifications immediately, ensuring compliance with the standard and achieving the fastest path to IP and SoC verification closure. Incorporating the latest protocol updates, the mature and comprehensive Cadence Verification IP (VIP) for the Ethernet protocol provides a complete bus functional model (BFM), integrated automatic protocol checks, and coverage model. Designed for easy integration in test benches at IP, system-on-chip (SoC), and system levels, the VIP for Ethernet helps you reduce the time to test, accelerate verification closure, and ensure end-product quality. The VIP for Ethernet runs on all major simulators and supports System Verilog and e-verification languages and associated methodologies, including the Universal Verification Methodology (UVM). More details are available in the Ethernet Verification IP portfolio.
For more information, reach out to us at talk_to_vip_expert@cadence.com.
Related Semiconductor IP
- Multi-channel Ultra Ethernet TSS Transform Engine
- Verification IP for Ultra Ethernet (UEC)
- Ultra Ethernet Verification IP
- 100G MAC/PCS Ultra Ethernet
- Complete 1.6T Ultra Ethernet IP Solution
Related Blogs
- UEC-LLR: The Future of Loss Recovery in Ethernet for AI and HPC
- Rambus Announces Industry-Leading Ultra Ethernet Security IP Solutions for AI and HPC
- High-Speed Test IO: Addressing High-Performance Data Transmission And Testing Needs For HPC & AI
- UA Link vs Interlaken: What you need to know about the right protocol for AI and HPC interconnect fabrics
Latest Blogs
- Embedded Security explained: Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) for embedded Systems
- Accreditation Without Compromise: Making eFPGA Assurable for Decades
- Synopsys Delivers First Complete UFS 5.0 and M‑PHY v6.0 IP Solution for Next‑Gen Storage
- World First: Synopsys MACsec IP Receives ISO/PAS 8800 Certification for Automotive and Physical AI Security
- Last-level cache has become a critical SoC design element
