Zero ASIC announces release of Platypus heterogeneous eFPGA
October 21, 2025 -- Zero ASIC is pleased to announce advance model access to an expansion of its PlatypusTM product line, the world’s first open-standard eFPGA IP.
The expansion grows Platypus from a brand for a single eFPGA core, the z1000 eFPGA launched in March 2025, into a family of eFPGA cores. Joining the z1000 are five new eFPGA cores. The new offerings give customers the option to select cores that differ from z1000 in one or more of three ways: a larger array size, use of 6-input lookup tables instead of 4-input lookup tables, and inclusion of hardened logic for digital signal processing (DSP blocks) and block memory (BRAM). A CAD model for each core is available now to evaluate using Zero ASIC’s open source RTL-to-bitstream flow, Logik.
Platypus Family Product Table
The complete Platypus product family table mapping all Platypus part names to their features and resource counts is shown below. Like z1000, all parts in the Platypus family are:
- 100% open and standardized FPGA architectures
- 100% open source FPGA bitstream formats
- 100% open source FPGA development tools
| LUT Size | LUTs | Flops | DSPs | BRAMs | IOs | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| z1000 | 4 | 2048 | 2048 | 0 | 0 | 1024 |
| z1002 | 4 | 8192 | 8192 | 0 | 0 | 2048 |
| z1010 | 4 | 1664 | 1664 | 4 | 4 | 1024 |
| z1012 | 4 | 6656 | 6656 | 16 | 16 | 2048 |
| z1060 | 6 | 1664 | 1664 | 4 | 4 | 1024 |
| z1062 | 6 | 6656 | 6656 | 16 | 16 | 2048 |
By offering these additional cores, Zero ASIC takes a step forward in offering customers the ability to select an off-the-shelf, open eFPGA architecture matched to their project needs.
Platypus Evaluation
All Platypus family core CAD models are publicly available via the logiklib repository. CAD model tarballs may be direct-downloaded from this repository release assets for inspection, but are best evaluated via Logik. Launched in 2024, Logik seamlessly integrates logiklib with Silicon Compiler to deliver a flexible, easy-to-adopt Python interface for organizing FPGA projects that use Platypus eFPGA cores. Logik Python API function calls allow users to import their HDL, integrate 3rd party IP, and execute a complete, push-button RTL-to-bitstream flow. Metrics reporting gives users feedback about their design’s resource utilization and performance. Logik’s Documentation and example Python scripts enable users to ramp up and become productive quickly.
To assist users in evaluating CAD flow performance analysis methods, a proxy delay model is used. Delay parameters for this model are chosen as a coarse approximation of eFPGA performance. The delay model does not reflect performance for a specific process technology or a specific physical implementation of the IP core.
Try Platypus Today
Zero ASIC has benchmarked a complete eFPGA architecture and CAD solution by codeveloping new Platypus architectures with concurrently released solutions for logic synthesis and benchmarking Because all the components are now open source, all results shown are reproducible.
A new demo showing how the well-known picrov32 RISC-V core maps to the z1062 architecture is now included with Logik. To run it, simply do the following:
- Install pre-requisites. See Logik documentation for more details.
- Run the following Linux commands:
pip install logik
git clone https://github.com/siliconcompiler/logik
cd examples/picorv32
python3 picorv32
At the end of the run, you will see a summary of all key design metrics printed to the screen.
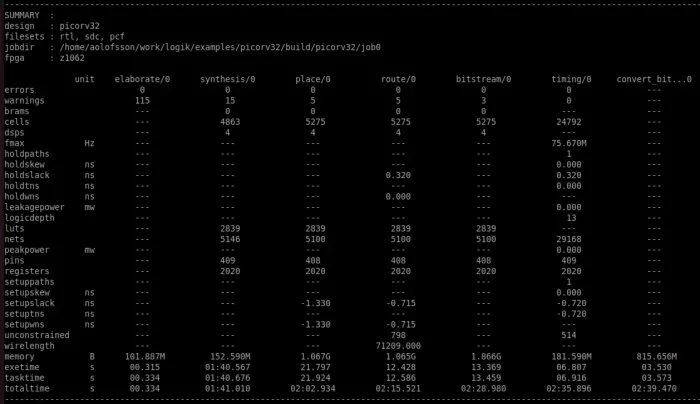
To check out how Logik performs on your own designs, you just need to make a copy of the picorv32.py example and swap out the single file picorv32.v with your own set of files.
About Zero ASIC
Zero ASIC is a semiconductor startup based in Cambridge, Massachusetts. The company mission is to democratize access to silicon through chiplets and design automation. Zero ASIC is building the world’s first composable chiplet platform, enabling billions of unique silicon systems to be assembled in hours from a catalog of off-the-shelf chiplets.
Related Semiconductor IP
- eFPGA on GlobalFoundries GF12LP
- eFPGA IP — Flexible Reconfigurable Logic Acceleration Core
- Heterogeneous eFPGA architecture with LUTs, DSPs, and BRAMs on GlobalFoundries GF12LP
- eFPGA Soft IP
- Radiation-Hardened eFPGA
Related News
- Zero ASIC launches world’s first open standard eFPGA product
- Is the world ready for Platypus, Zero ASIC’s open eFPGA IP? CEO Andreas Olofsson is betting that the answer is “Yes”
- Synapse Design and Flex Logix Tape Out Mutual Customer ASIC on a New Process in Less Than a Year Using Embedded FPGA (eFPGA) Technology
- Global Unichip Corporation and Flex Logix Achieve First-Time Working Silicon on Joint ASIC Development Using EFLX Embedded FPGA (eFPGA) IP
Latest News
- Silvaco Reports Fourth Quarter and Full-Year 2025 Financial Results
- Klepsydra Technologies and BrainChip Announce Strategic Partnership to Deliver Heterogeneous AI Runtime for Akida™ Neuromorphic Processors
- Alchip Reports ASIC-Leading 2nm Developments
- AI Demand Drives 4Q25 Global Top 10 Foundries Revenue Up 2.6% QoQ; Samsung Gains Share and Tower Moves Up in Rankings
- GlobalFoundries Announces Availability of AutoPro150 eMRAM Technology on Enhanced FDX Platform for Advanced Automotive Applications