Pushing the Boundaries of Memory: What’s New with Weebit and AI
Memory Made Smarter: Weebit Nano’s Role in the AI Hardware Revolution
Artificial intelligence is transforming nearly every industry, from autonomous driving to healthcare to connected devices. But as AI models grow more complex, the biggest barrier to progress is no longer the raw compute; it’s the movement of data. Every time information travels between the memory and processor, precious speed and power are lost.
Memory plays a key role in overcoming this barrier. Our advanced Resistive RAM (ReRAM / RRAM) technology is not only a more efficient embedded non-volatile memory (NVM) than flash; it is also the foundation for new computing paradigms that can dramatically accelerate AI.
Smarter Memory for AI SoCs
Next-generation AI systems-on-chips (SoCs) are typically built on 22nm and smaller technologies. Unlike embedded flash, which cannot scale below 28nm, ReRAM continues to scale to advanced nodes. This allows the memory to be placed closer to the processor, a critical advantage for these systems.
By storing neural network weights directly on-chip, embedded ReRAM eliminates the need for external memories, reducing cost, power, size, and security risks. For today’s AI accelerators and microcontrollers, embedding ReRAM closer to processing units is a critical step forward. Near-memory computing (NMC) minimizes data movement by placing memory directly alongside logic. This enables faster access to weights and parameters, cutting latency and improving energy efficiency for AI inference, particularly in edge devices that must process data locally. In automotive and aerospace, ReRAM’s robust reliability, including AEC-Q100 qualification and radiation tolerance, ensures that AI systems can perform consistently even in the most demanding environments.
Above: We’ve already demonstrated the advantages of ReRAM for near-memory computing
The next leap is towards computing inside the memory itself, called in-memory computing (IMC). ReRAM crossbars can perform matrix-vector multiplications (the core operation of neural networks) directly within the memory array.
By reducing the constant back-and-forth between memory and the processing unit, IMC promises significant speed-ups and lower power consumption for AI workloads. Weebit ReRAM is ideal for these architectures, with cost-efficiency, ultra-low power consumption, scaling advantages, analog behavior and ease of fabrication in the back end of the line (BEOL).
Looking even further ahead, Weebit ReRAM is naturally suited for neuromorphic computing, which mimics how the human brain processes information. According to Yole Intelligence, the neuromorphic computing market is expected to grow to $412 million by 2029 and $5.4 billion by 2034. The research firm expects that analog IMC solutions including those with ReRAM will ramp up starting in 2027.
The Weebit ReRAM cell functions similarly to a synapse in the brain, making it a promising solution. ReRAM devices can act as artificial synapses, with analog conductance levels representing synaptic weights. This opens the door to energy-efficient, brain-like chips capable of real-time learning and adaptation.
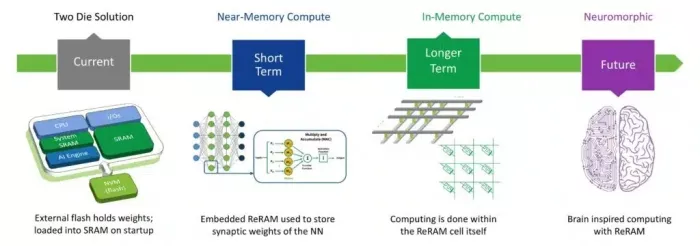
Above: The evolution of NVM as an enabler for AI
Collaborations Drive Innovation
Our partnership with CEA-Leti and collaborations with research institutes around the globe including ongoing neuromorphic studies, position Weebit technology as a building block for future brain-inspired processors.
Weebit is also now a member of the EDGE AI FOUNDATION, bringing our low-power, high-performance ReRAM to a dynamic community focused on uniting industry leaders and researchers to drive innovation, solve global challenges, and democratize edge AI technologies. We will be actively contributing towards this mission.
Above: A brief introduction to the EDGE AI FOUNDATION
In addition, we are collaborating with industry leaders on the development of ultra-low-power neuromorphic processing solutions under the NeMo Consortium, a three-year development program funded by the Israeli Innovation Authority. NeMo brings together research groups from major industry R&D teams and leading academia researchers across Israel. Its goal is to develop a technology infrastructure enabling neuromorphic processing capabilities for various edge products such as medical and security applications, with power consumption three orders of magnitude lower than the state of the art. The system will include dedicated hardware components, advanced AI software modules using spiking neural networks, and algorithms integrated with various sensors to enable ultra-low-power AI applications.
We are also working alongside a large group of companies under the NeAIxt project, which aims to solidify Europe’s position in edge AI and eNVM technology. The group is focused on enhancing AI enablers, evolving embedded NVM for edge applications, and demonstrating AI capabilities at both chip and system levels. The project will integrate advances in NVM technologies with cutting-edge MCU design to enable efficient in-memory computing. NeAIxt will address the entire edge AI value chain, from academia to industry, and from design to end-user applications, building on Europe’s strong technological foundation.
These are just a few of the areas where Weebit is pushing innovation in AI. You can read some of the latest papers in our Resources section.
The Road Ahead
From today’s embedded AI chips to tomorrow’s neuromorphic systems, Weebit is working to ensure that memory is no longer a bottleneck, but a driver of innovation. By making memory smarter, we are helping shape a new era of computing where intelligence is faster, more efficient, and available everywhere.
Related Semiconductor IP
Related Blogs
- The Future of Technology: Transforming Industrial IoT with Edge AI and AR
- Analog Bits Steals the Show with Working IP on TSMC 3nm and 2nm and a New Design Strategy
- Enhancing Edge AI with the Newest Class of Processor: Tensilica NeuroEdge 130 AICP
- The Evolution of AI and ML- Enhanced Advanced Driver Systems
Latest Blogs
- Silicon Insurance: Why eFPGA is Cheaper Than a Respin
- One Bit Error is Not Like Another: Understanding Failure Mechanisms in NVM
- Introducing CoreCollective for the next era of open collaboration for the Arm software ecosystem
- Integrating eFPGA for Hybrid Signal Processing Architectures
- eUSB2V2: Trends and Innovations Shaping the Future of Embedded Connectivity
