RISCover: Automatic Discovery of User-exploitable Architectural Security Vulnerabilities in Closed-Source RISC-V CPUs
By Fabian Thomas, Eric García Arribas, Lorenz Hetterich, Daniel Weber, Lukas Gerlach, Ruiyi Zhang and Michael Schwarz
CISPA Helmholtz Center for Information Security Saarbrücken, Saarland, Germany
Abstract
 The open and extensible RISC-V instruction set has enabled many new CPU vendors and implementations, but most commercial CPUs are closed-source, significantly hindering vulnerability analysis—especially for bugs exploitable from unprivileged user space.
The open and extensible RISC-V instruction set has enabled many new CPU vendors and implementations, but most commercial CPUs are closed-source, significantly hindering vulnerability analysis—especially for bugs exploitable from unprivileged user space.
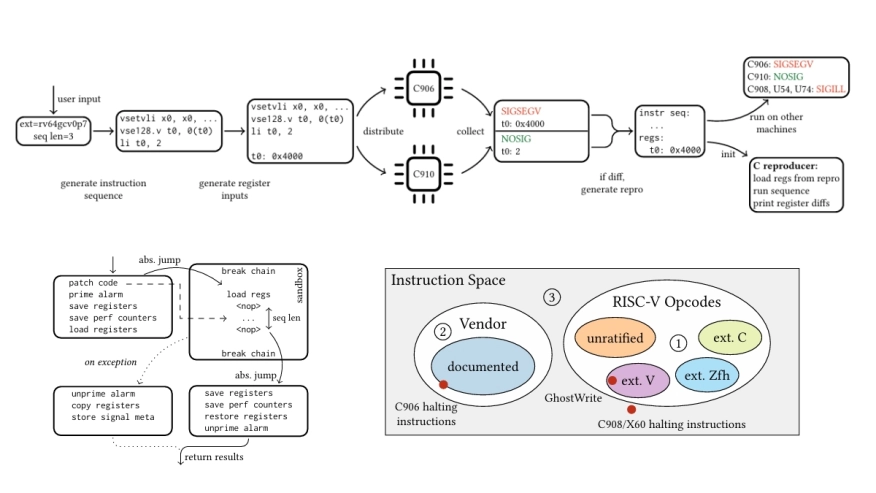
We present RISCover, a user-space framework for detecting architectural vulnerabilities in closed-source RISC-V CPUs. It compares instruction-sequence behavior across CPUs, identifying deviations without source code, hardware changes, or models, and achieving orders-of-magnitude speedups over RTL-based methods. Unlike prior work, RISCover runs user code on Linux directly on real hardware, exposing vulnerabilities exploitable by unprivileged attackers. Evaluated on 8 off-the-shelf CPUs from 3 different vendors, it uncovers 4 previously unknown vulnerabilities.
Notably, GhostWrite lets unprivileged code write chosen bytes to physical memory, enabling arbitrary data leakage and full machine-mode execution, while 3 unprivileged ''halt-and-catch-fire'' bugs halt CPUs and misaligned zero-stores silently corrupt data. Our results highlight the pressing need for post-silicon fuzzing techniques. RISCover complements existing RTL-level fuzzers by enabling rapid and automated security analysis of closed-source CPUs.
Keywords: CPUFuzzing; RISC-V; Architectural CPU Vulnerabilities
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- RISC-V Debug & Trace IP
- Gen#2 of 64-bit RISC-V core with out-of-order pipeline based complex
- Compact Embedded RISC-V Processor
- Multi-core capable 64-bit RISC-V CPU with vector extensions
- 64 bit RISC-V Multicore Processor with 2048-bit VLEN and AMM
Related Articles
- An AUTOSAR-Aligned Architectural Study of Vulnerabilities in Automotive SoC Software
- RISC-V's CPU Verification Challenge
- LLM Inference with Codebook-based Q4X Quantization using the Llama.cpp Framework on RISC-V Vector CPUs
- Reconfiguring Design -> How to extend configurable CPU performance
Latest Articles
- Creating a Frequency Plan for a System using a PLL
- RISCover: Automatic Discovery of User-exploitable Architectural Security Vulnerabilities in Closed-Source RISC-V CPUs
- MING: An Automated CNN-to-Edge MLIR HLS framework
- Fault Tolerant Design of IGZO-based Binary Search ADCs
- A 16 nm 1.60TOPS/W High Utilization DNN Accelerator with 3D Spatial Data Reuse and Efficient Shared Memory Access