cMPI: Using CXL Memory Sharing for MPI One-Sided and Two-Sided Inter-Node Communications
By Xi Wang 1, Bin Ma 1, Jongryool Kim 2, Byungil Koh 2, Hoshik Kim 2, Dong Li 1
1 University of California, Merced, CA, USA
2 SK hynix, San Jose, CA, USA
Abstract
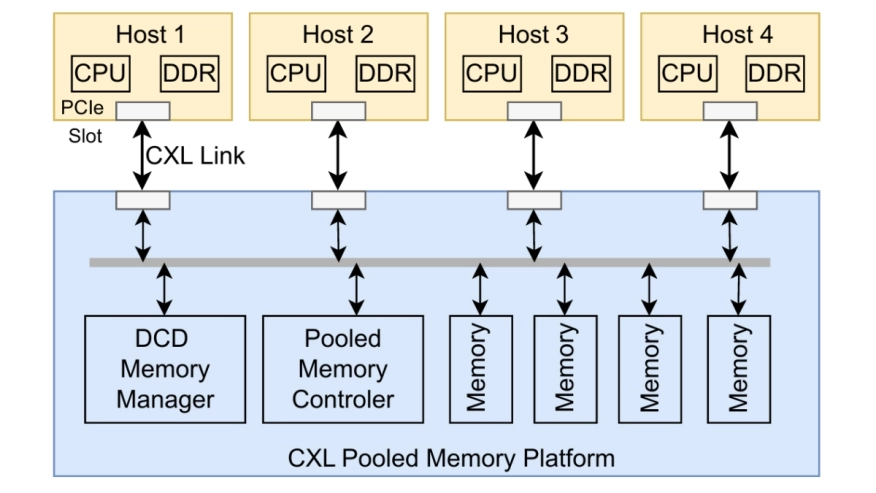
 Message Passing Interface (MPI) is a foundational programming model for high-performance computing. MPI libraries traditionally employ network interconnects (e.g., Ethernet and InfiniBand) and network protocols (e.g., TCP and RoCE) with complex software stacks for cross-node communication. We present cMPI, the first work to optimize MPI point-to-point communication (both one-sided and two-sided) using CXL memory sharing on a real CXL platform, transforming cross-node communication into memory transactions and data copies within CXL memory, bypassing traditional network protocols. We analyze performance across various interconnects and find that CXL memory sharing achieves 7.2x-8.1x lower latency than TCP-based interconnects deployed in small- and medium-scale clusters. We address challenges of CXL memory sharing for MPI communication, including data object management over the dax representation [50], cache coherence, and atomic operations. Overall, cMPI outperforms TCP over standard Ethernet NIC and high-end SmartNIC by up to 49x and 72x in latency and bandwidth, respectively, for small messages.
Message Passing Interface (MPI) is a foundational programming model for high-performance computing. MPI libraries traditionally employ network interconnects (e.g., Ethernet and InfiniBand) and network protocols (e.g., TCP and RoCE) with complex software stacks for cross-node communication. We present cMPI, the first work to optimize MPI point-to-point communication (both one-sided and two-sided) using CXL memory sharing on a real CXL platform, transforming cross-node communication into memory transactions and data copies within CXL memory, bypassing traditional network protocols. We analyze performance across various interconnects and find that CXL memory sharing achieves 7.2x-8.1x lower latency than TCP-based interconnects deployed in small- and medium-scale clusters. We address challenges of CXL memory sharing for MPI communication, including data object management over the dax representation [50], cache coherence, and atomic operations. Overall, cMPI outperforms TCP over standard Ethernet NIC and high-end SmartNIC by up to 49x and 72x in latency and bandwidth, respectively, for small messages.
Keywords: MPI, Compute Express Link (CXL), high-performance computing (HPC), shared memory, interconnection architectures
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- CXL 4 Verification IP
- VIP for Compute Express Link (CXL)
- CXL 3.0 Controller
- CXL Controller IP
- CXL memory expansion
Related Articles
- The Growing Importance of AI Inference and the Implications for Memory Technology
- Accelerating SoC Evolution With NoC Innovations Using NoC Tiling for AI and Machine Learning
- A novel 3D buffer memory for AI and machine learning
- Using non-volatile memory IP in system on chip designs
Latest Articles
- GenAI for Systems: Recurring Challenges and Design Principles from Software to Silicon
- Creating a Frequency Plan for a System using a PLL
- RISCover: Automatic Discovery of User-exploitable Architectural Security Vulnerabilities in Closed-Source RISC-V CPUs
- MING: An Automated CNN-to-Edge MLIR HLS framework
- Fault Tolerant Design of IGZO-based Binary Search ADCs