In-DRAM True Random Number Generation Using Simultaneous Multiple-Row Activation: An Experimental Study of Real DRAM Chips
By Ismail Emir Yüksel §, Geraldo F. Oliveira §, Ataberk Olgun §, F. Nisa Bostancı §, Mohammad Sadrosadati §, Oguzhan Canpolat §, A. Giray Yaglıkçı §Γ, Onur Mutlu §
§ ETH Zürich
Γ CISPA
Abstract
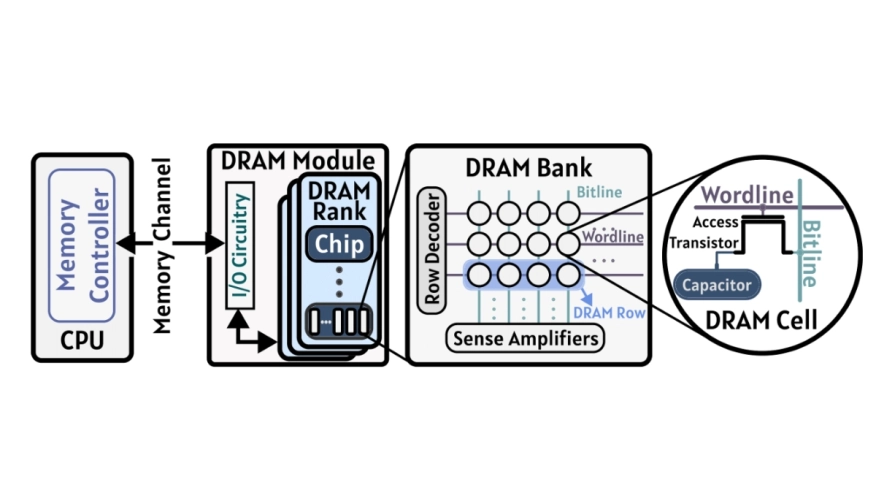
 In this work, we experimentally demonstrate that it is possible to generate true random numbers at high throughput and low latency in commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) DRAM chips by leveraging simultaneous multiple-row activation (SiMRA) via an extensive characterization of 96 DDR4 DRAM chips. We rigorously analyze SiMRA's true random generation potential in terms of entropy, latency, and throughput for varying numbers of simultaneously activated DRAM rows (i.e., 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32), data patterns, temperature levels, and spatial variations. Among our 11 key experimental observations, we highlight four key results. First, we evaluate the quality of our TRNG designs using the commonly-used NIST statistical test suite for randomness and find that all SiMRA-based TRNG designs successfully pass each test. Second, 2-, 8-, 16-, and 32-row activation-based TRNG designs outperform the state-of-theart DRAM-based TRNG in throughput by up to 1.15x, 1.99x, 1.82x, and 1.39x, respectively. Third, SiMRA's entropy tends to increase with the number of simultaneously activated DRAM rows. Fourth, operational parameters and conditions (e.g., data pattern and temperature) significantly affect entropy. For example, for most of the tested modules, the average entropy of 32-row activation is 2.51x higher than that of 2-row activation. For example, increasing the temperature from 50°C to 90°C decreases SiMRA's entropy by 1.53x for 32-row activation. To aid future research and development, we open-source our infrastructure at github.com/CMU-SAFARI/SiMRA-TRNG.
In this work, we experimentally demonstrate that it is possible to generate true random numbers at high throughput and low latency in commercial off-the-shelf (COTS) DRAM chips by leveraging simultaneous multiple-row activation (SiMRA) via an extensive characterization of 96 DDR4 DRAM chips. We rigorously analyze SiMRA's true random generation potential in terms of entropy, latency, and throughput for varying numbers of simultaneously activated DRAM rows (i.e., 2, 4, 8, 16, and 32), data patterns, temperature levels, and spatial variations. Among our 11 key experimental observations, we highlight four key results. First, we evaluate the quality of our TRNG designs using the commonly-used NIST statistical test suite for randomness and find that all SiMRA-based TRNG designs successfully pass each test. Second, 2-, 8-, 16-, and 32-row activation-based TRNG designs outperform the state-of-theart DRAM-based TRNG in throughput by up to 1.15x, 1.99x, 1.82x, and 1.39x, respectively. Third, SiMRA's entropy tends to increase with the number of simultaneously activated DRAM rows. Fourth, operational parameters and conditions (e.g., data pattern and temperature) significantly affect entropy. For example, for most of the tested modules, the average entropy of 32-row activation is 2.51x higher than that of 2-row activation. For example, increasing the temperature from 50°C to 90°C decreases SiMRA's entropy by 1.53x for 32-row activation. To aid future research and development, we open-source our infrastructure at github.com/CMU-SAFARI/SiMRA-TRNG.
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- Multi-channel Ultra Ethernet TSS Transform Engine
- Configurable CPU tailored precisely to your needs
- Ultra high-performance low-power ADC
- HiFi iQ DSP
- CXL 4 Verification IP
Related Articles
- True Random Number Generators for Truly Secure Systems
- Methodology Independent Exhaustive Constraint Solver for Random Verification and Regression Generation
- Paving the way for the next generation audio codec for the True Wireless Stereo (TWS) applications - PART 1 : TWS challenges explained
- Paving the way for the next generation audio codec for True Wireless Stereo (TWS) applications - PART 2 : Increasing play time
Latest Articles
- GenAI for Systems: Recurring Challenges and Design Principles from Software to Silicon
- Creating a Frequency Plan for a System using a PLL
- RISCover: Automatic Discovery of User-exploitable Architectural Security Vulnerabilities in Closed-Source RISC-V CPUs
- MING: An Automated CNN-to-Edge MLIR HLS framework
- Fault Tolerant Design of IGZO-based Binary Search ADCs