Accelerating Post-Quantum Cryptography via LLM-Driven Hardware-Software Co-Design
By Yuchao Liao, Tosiron Adegbija, Roman Lysecky
University of Arizona, Tucson, AZ, USA
Abstract
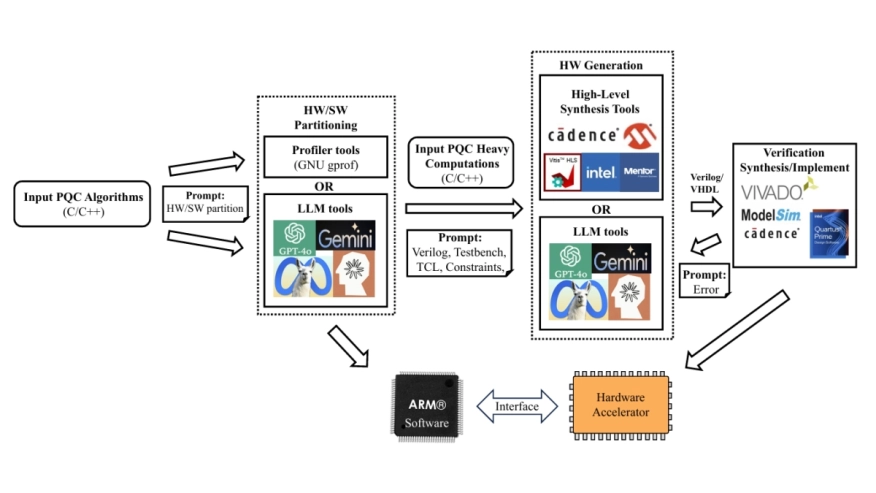
 Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) is crucial for securing data against emerging quantum threats. However, its algorithms are computationally complex and difficult to implement efficiently on hardware. In this paper, we explore the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) to accelerate the hardware-software co-design process for PQC, with a focus on the FALCON digital signature scheme. We present a novel framework that leverages LLMs to analyze PQC algorithms, identify performance-critical components, and generate candidate hardware descriptions for FPGA implementation. We present the first quantitative comparison between LLM-driven synthesis and conventional HLS-based approaches for low-level compute-intensive kernels in FALCON, showing that human-in-the-loop LLM-generated accelerators can achieve up to 2.6x speedup in kernel execution time with shorter critical paths, while highlighting trade-offs in resource utilization and power consumption. Our results suggest that LLMs can minimize design effort and development time by automating FPGA accelerator design iterations for PQC algorithms, offering a promising new direction for rapid and adaptive PQC accelerator design on FPGAs.
Post-quantum cryptography (PQC) is crucial for securing data against emerging quantum threats. However, its algorithms are computationally complex and difficult to implement efficiently on hardware. In this paper, we explore the potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) to accelerate the hardware-software co-design process for PQC, with a focus on the FALCON digital signature scheme. We present a novel framework that leverages LLMs to analyze PQC algorithms, identify performance-critical components, and generate candidate hardware descriptions for FPGA implementation. We present the first quantitative comparison between LLM-driven synthesis and conventional HLS-based approaches for low-level compute-intensive kernels in FALCON, showing that human-in-the-loop LLM-generated accelerators can achieve up to 2.6x speedup in kernel execution time with shorter critical paths, while highlighting trade-offs in resource utilization and power consumption. Our results suggest that LLMs can minimize design effort and development time by automating FPGA accelerator design iterations for PQC algorithms, offering a promising new direction for rapid and adaptive PQC accelerator design on FPGAs.
Index Terms — Post-quantum cryptography, large language models, hardware-software partitioning, hardware acceleration
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Solution
- PQC CRYSTALS core for accelerating NIST FIPS 202 FIPS 203 and FIPS 204
- Highly-optimized PQC implementations, capable of running PQC in under 15kb RAM
- Highly configurable HW PQC acceleration with RISC-V processor for full CPU offload
- xQlave® PQC ML-DSA (Dilithium)
Related Articles
- Hardware/software codesign needs new business model
- Rigorous Framework for Hardware-Software Co-design of Embedded Systems
- An Introduction to Post-Quantum Cryptography Algorithms
- Post-Quantum Cryptography: Why Open Source alone is Not Enough for Secure IP Deployment
Latest Articles
- PDF: PUF-based DNN Fingerprinting for Knowledge Distillation Traceability
- TeraPool: A Physical Design Aware, 1024 RISC-V Cores Shared-L1-Memory Scaled-up Cluster Design with High Bandwidth Main Memory Link
- AutoGNN: End-to-End Hardware-Driven Graph Preprocessing for Enhanced GNN Performance
- LUTstructions: Self-loading FPGA-based Reconfigurable Instructions
- CQ-CiM: Hardware-Aware Embedding Shaping for Robust CiM-Based Retrieval