Interface Security IP
All offers in
Interface Security IP
Filter
Compare
87
Interface Security IP
from
20
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
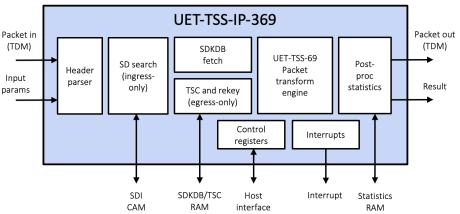
Multi-channel Ultra Ethernet TSS Complete Layer
- The UET-TSS-IP-369 (EIP-369) is an inline, high-performance, multi-channel packet engine that provides the complete TSS layer, bypass/drop and basic crypto processing at rates up to 1.6Tbps.
- The engine is designed for integration into the systems that require TSS processing for one or more ports. The engine is provided as separate ingress and egress data paths.
- The EIP-369 embeds the UET-TSS-IP-69 for the packet transformation.
-
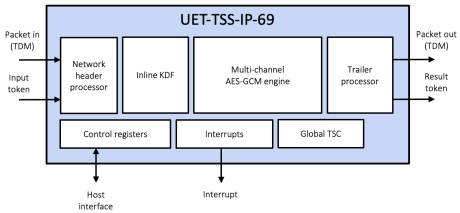
Multi-channel Ultra Ethernet TSS Transform Engine
- The UET-TSS-IP-69 (EIP-69) is a high-performance, multi-channel transform engine that provides the complete TSS packet transformation (including KDF and IP/UDP updates), bypass/drop and basic crypto processing at rates up to 1.6Tbps.
- The engine is designed for integration into the systems that require TSS processing for one or more ports. The engine is provided as separate ingress and egress data paths.
-
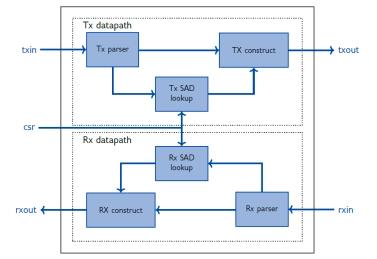
IPSEC AES-256-GCM (Standalone IPsec)
- XIP7213E implements the Internet Protocol Security (IPsec) as standardised in RFC4303 and RFC4305.
- The IPsec protocol defines a security infrastrucure for Layer 3 (as per the OSI model) traffic by assuring that a received packet has been sent by the transmitting station that claimed to send it.
-
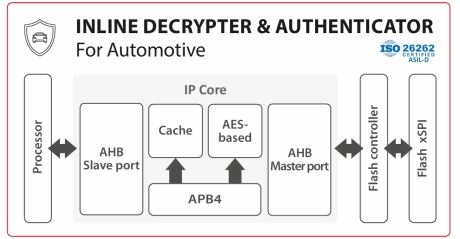
Inline Decrypter & Authenticator IP Core for Automotive
- The Inline Decrypter and Authenticator IP core enables on-the-fly execution of encrypted and signed code from Flash.
- It is used to authenticate and decrypt code located in Flash. In addition it is ISO26262 certified (ASIL-D).
-
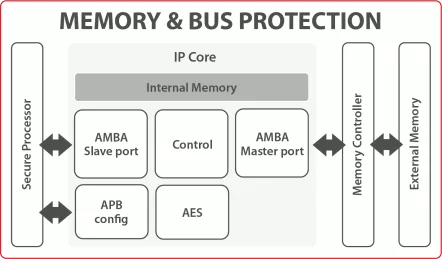
Memory & Bus Protection IP Core
- The Memory & Bus Protection IP Core module enables on-the-fly encryption/decryption and authentication to the external memory.
- It supports AHB/AXI slave/master interfaces, APB port for configuration purpose, and contains a cache.
-
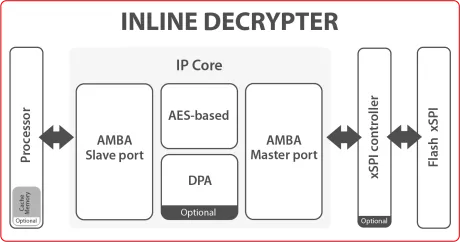
Inline Decrypter IP Core
- The Inline Decrypter IP Core enables on-the-fly execution of encrypted code from Flash.
- It is often used to protect the source code from decompiling or reverse engineering.
-
-
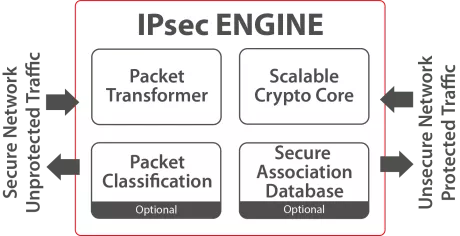
IPsec Engine
-
The IPsec Engine implements RFC4301 and other relevant RFCs, providing confidentiality, connectionless data integrity, data-origin authentication and replay protection on OSI layer 3.
-
-
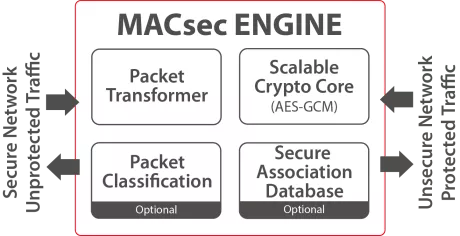
1.6 Tbps MACsec Engine
- Throughput up to 1.5Tb
- ASIC and FPGA
- Multi-channel support for link aggregation or FlexE
-
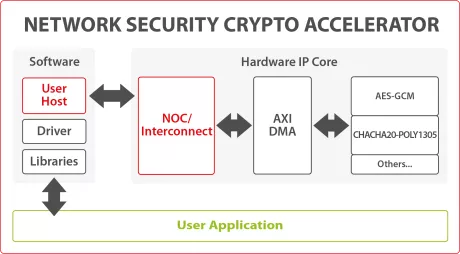
Network Security Crypto Accelerator
- The Network Security Crypto Accelerator is a hardware IP core platform that accelerates cryptographic operations in System-on-Chip (SoC) environment on FPGA or ASIC.
- This IP is used to accelerate/offload MACsec, IPsec, VPN, TLS/SSL, disk encryption, or any other custom application, requiring symmetric cryptography algorithms.