Wide I O IP
Filter
Compare
18
IP
from
11
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
Dual 12-bit 80Msps Low power silicon proven in 28nm ADC IP
- • Differential analog input
- • Small footprint
- • Internal reference generator (no
- external component)
-
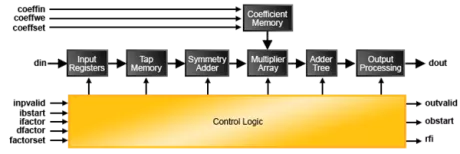
FIR Filter Generator
- Direct Form 64-Tap FIR Filter: In the direct form FIR filter, the input samples are shifted into a shift register queue and each shift register is connected to a multiplier. The products from the multipliers are added together to get the FIR filter’s output sample. This example shows a 64-tap FIR filter using 16 sysDSP blocks and approximately 512 slices in the LatticeECP3 FPGA.
- 128-Tap Long Asymmetrical Filters Using Ladder Architecture: Using the ladder architecture, the FIR filter is split into sections each having the same coefficient set as if it was a single continuous filter chain. Instead of connecting the shifted data and the result outputs from the first section to the corresponding input of the next section, the ladder network connects a delayed version of the first stage input data to the second stage input data and sums a delayed version of the first stage sum output with the second stage sum output.
- 256-Tap Long Symmetrical Filters Using Ladder Architecture: The impulse response for most FIR filters is symmetric. This symmetry can generally be exploited to reduce the arithmetic requirements and produce area-efficient filter realizations. It is possible to use only half the multipliers for symmetric coefficients compared to that used for a similar filter with non-symmetric coefficients. An implementation for symmetric coefficients is shown in the figure below. The 256-tap long symmetrical filter example uses only 32 sysDSP slices, 2EBR and 3.5K slices.
- Polyphase Interpolator FIR Filter Designs: The polyphase interpolation filter implements the computationally efficient 1-to-P interpolation filter where P is an integer greater than 1. The example below shows a design with an interpolation by 16 that uses 128 taps. This requires 8 polyphase filters (sub-filters) with 16 coefficients each.
-
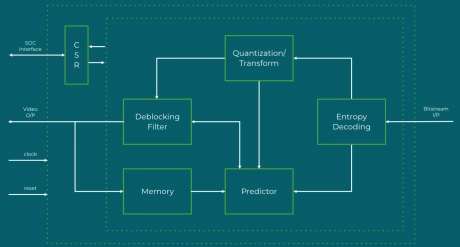
H.264 Decoder
- Thes H.264 Decoder IP Core offers a high-efficiency video decoding solution tailored for a wide range of applications, including multimedia, surveillance, broadcast, and automotive systems.
- Compliant with the ITU-T H.264/AVC standard, it enables real-time decoding of high-definition video streams while maintaining low latency and power consumption.
-
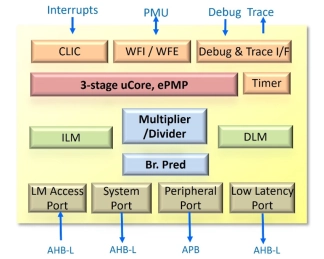
Compact and Performance Efficiency 32-bit RISC-V Core
- The N225 is a 32-bit 3-stage pipeline CPU IP core based on AndeStar™ V5 architecture for embedded applications with small gate count, and some dual-issue ability.
- In addition to commonly used RISC-V IMAC it supports the recently ratified ISA extensions such as B (bit manipulation) and Zce (code size reduction).
-
SATA 6G PHY
- ? 6-Gbps transmission rate through standard SATA cable
- ? Spread-spectrum clock (SSC) generation and absorption
- ? Programmable down-spread (+4,980 ppm through -4,980 ppm)
- ? Fully clock-forwarded transceiver interface, configurable using soft PMA layer above hard macro PHY
-
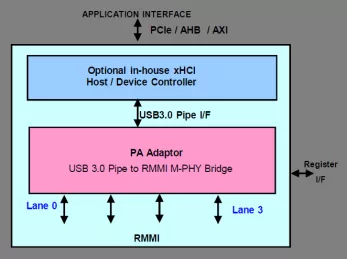
USB 3.0 SSIC Controller
- Compliant with SSIC v1.01
- Compliant with M-PHY Specification v2.0
- Compliant with USB3.0 Pipe Specification
-
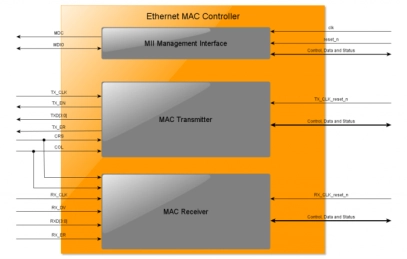
10/100/1000 Ethernet MAC DO-254 IP Core
- The 10/100/1000 Ethernet MAC Controller DO-254 IP Core implements the Media Access Control as specified in the IEEE 802.3-2008 specification.
- The Ethernet MAC Controller has been developed to DAL A according to the DO-254 / ED-80 and is accompanied by a Certification Kit.
-
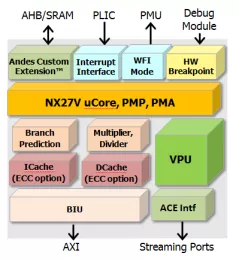
64-bit CPU with RISC-V Vector Extension
- AndeStar™ V5 Instruction Set Architecture (ISA), compliant to RISC-V technology
- RISC-V vector extension
- Vector Processing Unit (VPU) boost the performance of AI, AR/VR, computer vision, cryptography, and multimedia processing
- Andes extensions, architected for performance and functionality enhancements
-
Compact High-Speed 32-bit CPU Core with MemBoost and PMA
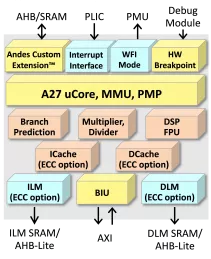
- The 32-bit A27 is a 5-stage processor that supports the latest RISC-V specification, including “G” (“IMAFD”) standard instructions, “C” 16-bit compression instructions, “P” Packed-SIMD/DSP instructions, “N” for user-level interrupts, and Memory Management Unit (MMU) for Linux support.
- A27 features branch prediction, instruction and data caches, local memories, ECC error protection, and Andes Custom Extension™ to add custom instructions to accelerate performance and reduce power consumption.