SHA-3 IP
Filter
Compare
49
IP
from
20
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
SHA3 Cryptographic Hash Cores
- Completely self-contained; does not require external memory
- SHA3-224, SHA3-256, SHA3-384, and SHA3-512 support SHA-3 algorithms per FIPS 202.
- SHAKE128 / SHAKE256 XOF support is included.
- Flow-through design; flexible data bus width
-
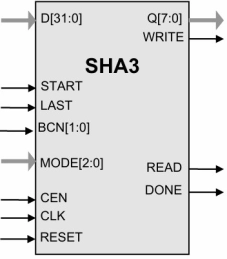
SHA3 IP Core
- SHA3 IP Cores perform cryptographic hashing in compliance with the SHA-3 (Secure Hash Algorithm 3) specifications defined in 'FIPS 202'. This standard specifies methods for generating secure hash values using the SHA-3 algorithm.
- SHA3 IP Cores support the SHA3-224, SHA3-256, SHA3-384, SHA3-512, SHAKE128, and SHAKE256 functions, and are byte-oriented in their implementation.
-
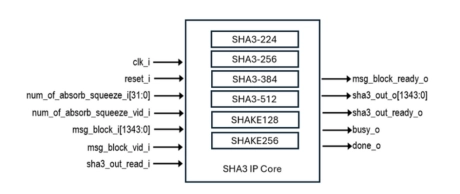
SHA3 core for accelerating NIST FIPS 202 Secure Hash Algorithm
- Supports variable length SHA-3 Hash Functions
- Supports Extendable Output Functions (XOF)
- Configurable architecture for achieving the required performance and silicon area
-
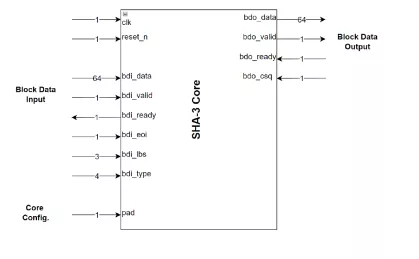
SHA-3 Crypto IP Core
- The SHA-3 – secure hash algorithms – crypto engine is a hardware accelerator for cryptographic hashing functions.
- It is an area efficient and high throughput design and compliant to NIST’s FIPS 202 standard.
- Additionally it supports all SHA-3 hash functions – SHA-3-224, SHA-3-256, SHA-3-384 and SHA-3-512 – as well as extendable output functions (XOF) – SHAKE-128 and SHAKE-256.
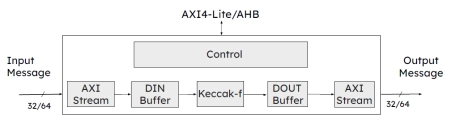
-
Secure Hash Algorithm-3 (SHA-3)
- Support NIST FIPS 202 standard
- Pass NIST FIPS 202 test vectors
- Support four cryptographic hash functions
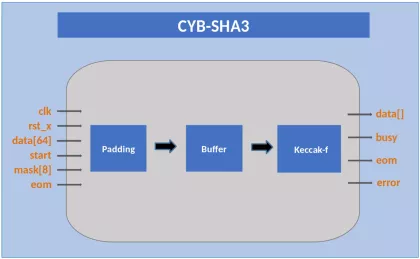
-
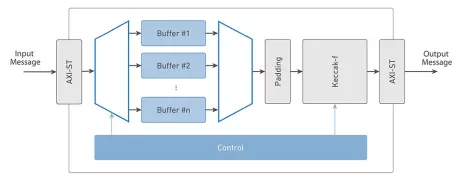
-
SHA-3 Crypto Engine
- The SHA-3 crypto engine has integrated flexibility and scalability to allow for high throughput and a configurable number of hashing rounds per clock cycle to optimize the silicon resource/performance ratio.
- Fixed-length or extendable-output (XOF) functions can simply be chosen per individual message through configuration settings.
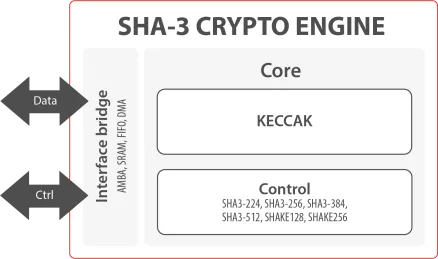
-
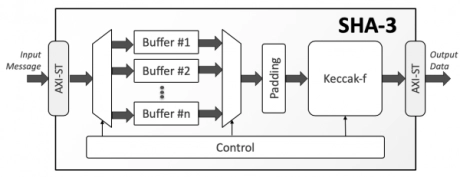
SHA-3 Secure Hash Crypto Engine
- The SHA-3 is a high-throughput, area-efficient hardware accelerator for the SHA-3 cryptographic hashing functions, compliant to NIST’s FIPS 180-4 and FIPS 202 standards.
- The accelerator core requires no assistance from a host processor and uses standard AMBA® AXI4-Stream interfaces for input and output data.
-
SHA-3 (all variants)
- One clock per step algorithm implementation.
- Automatic rate selection.
- Automatic pad insertion.
- Any bit length message, including zero-length, is allowed.
-
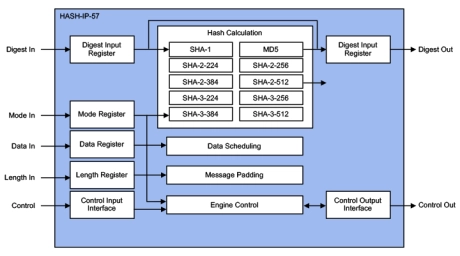
SHA-3, SHA-2, SHA-1, SM3, MD5, Hash Accelerators
- The HASH-IP-57 (EIP-57) is IP for accelerating the various secure hash integrity algorithms like MD5 (RFC1231), SHA-1 (FIPS-180-2), SHA-2 (FIPS-180-3/4) and SHA-3 (FIPS-202), supporting the NIST MAC mode up to 6.4 Gbps @ 450MHz.
- Designed for fast integration, low gate count and full transforms, the HASH-IP-57 accelerators provides a reliable and cost-effective embedded IP solution that is easy to integrate into high-speed crypto pipelines.