ShuffleV: A Microarchitectural Defense Strategy against Electromagnetic Side-Channel Attacks in Microprocessors
By Nuntipat Narkthong ∗, Yukui Luo †, Xiaolin Xu ∗
∗ Northeastern University, Boston, USA
† Binghamton University, New York, USA
Abstract
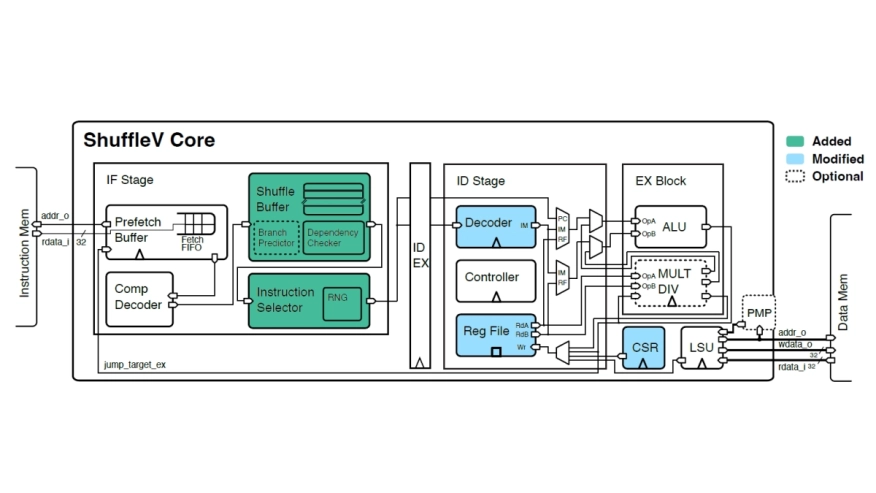
 The run-time electromagnetic (EM) emanation of microprocessors presents a side-channel that leaks the confidentiality of the applications running on them. Many recent works have demonstrated successful attacks leveraging such side-channels to extract the confidentiality of diverse applications, such as the key of cryptographic algorithms and the hyperparameter of neural network models. This paper proposes ShuffleV, a microarchitecture defense strategy against EM Side-Channel Attacks (SCAs). ShuffleV adopts the moving target defense (MTD) philosophy, by integrating hardware units to randomly shuffle the execution order of program instructions and optionally insert dummy instructions, to nullify the statistical observation by attackers across repetitive runs. We build ShuffleV on the open-source RISC-V core and provide six design options, to suit different application scenarios. To enable rapid evaluation, we develop a ShuffleV simulator that can help users to (1) simulate the performance overhead for each design option and (2) generate an execution trace to validate the randomness of execution on their workload. We implement ShuffleV on a Xilinx PYNQ-Z2 FPGA and validate its performance with two representative victim applications against EM SCAs, AES encryption, and neural network inference. The experimental results demonstrate that ShuffleV can provide automatic protection for these applications, without any user intervention or software modification.
The run-time electromagnetic (EM) emanation of microprocessors presents a side-channel that leaks the confidentiality of the applications running on them. Many recent works have demonstrated successful attacks leveraging such side-channels to extract the confidentiality of diverse applications, such as the key of cryptographic algorithms and the hyperparameter of neural network models. This paper proposes ShuffleV, a microarchitecture defense strategy against EM Side-Channel Attacks (SCAs). ShuffleV adopts the moving target defense (MTD) philosophy, by integrating hardware units to randomly shuffle the execution order of program instructions and optionally insert dummy instructions, to nullify the statistical observation by attackers across repetitive runs. We build ShuffleV on the open-source RISC-V core and provide six design options, to suit different application scenarios. To enable rapid evaluation, we develop a ShuffleV simulator that can help users to (1) simulate the performance overhead for each design option and (2) generate an execution trace to validate the randomness of execution on their workload. We implement ShuffleV on a Xilinx PYNQ-Z2 FPGA and validate its performance with two representative victim applications against EM SCAs, AES encryption, and neural network inference. The experimental results demonstrate that ShuffleV can provide automatic protection for these applications, without any user intervention or software modification.
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- RISC-V Debug & Trace IP
- Gen#2 of 64-bit RISC-V core with out-of-order pipeline based complex
- Compact Embedded RISC-V Processor
- Multi-core capable 64-bit RISC-V CPU with vector extensions
- 64 bit RISC-V Multicore Processor with 2048-bit VLEN and AMM
Related Articles
- DRsam: Detection of Fault-Based Microarchitectural Side-Channel Attacks in RISC-V Using Statistical Preprocessing and Association Rule Mining
- Defend encryption systems against side-channel attacks
- How secure is AES against brute force attacks?
- Physical Attacks against Cryptographic Implementations
Latest Articles
- GenAI for Systems: Recurring Challenges and Design Principles from Software to Silicon
- Creating a Frequency Plan for a System using a PLL
- RISCover: Automatic Discovery of User-exploitable Architectural Security Vulnerabilities in Closed-Source RISC-V CPUs
- MING: An Automated CNN-to-Edge MLIR HLS framework
- Fault Tolerant Design of IGZO-based Binary Search ADCs