Sensitivity-Aware Mixed-Precision Quantization for ReRAM-based Computing-in-Memory
By Guan-Cheng Chen 1, Chieh-Lin Tsai 2, Pei-Hsuan Tsai 1, Yuan-Hao Chang 2
1 National Cheng Kung University, Tainan, Taiwan
2 National Taiwan University, Taipei, Taiwan
Abstract
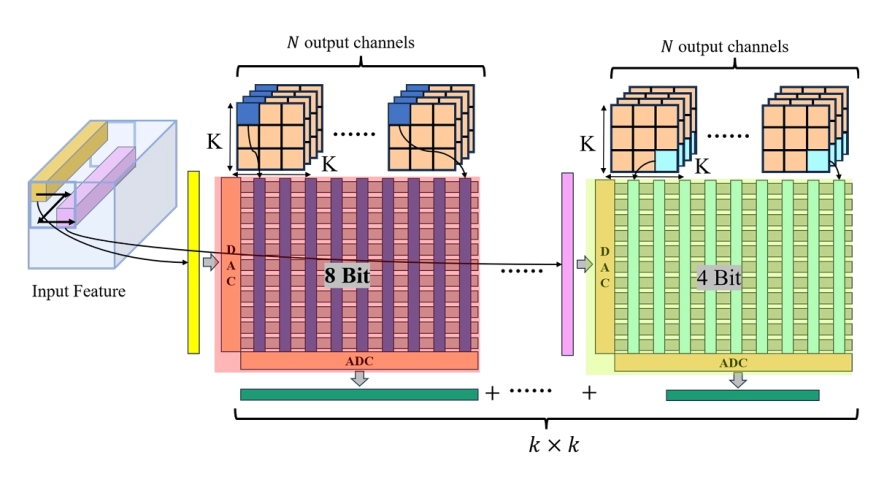
 Compute-In-Memory (CIM) systems, particularly those utilizing ReRAM and memristive technologies, offer a promising path toward energy-efficient neural network computation. However, conventional quantization and compression techniques often fail to fully optimize performance and efficiency in these architectures. In this work, we present a structured quantization method that combines sensitivity analysis with mixed-precision strategies to enhance weight storage and computational performance on ReRAM-based CIM systems. Our approach improves ReRAM Crossbar utilization, significantly reducing power consumption, latency, and computational load, while maintaining high accuracy. Experimental results show 86.33% accuracy at 70% compression, alongside a 40% reduction in power consumption, demonstrating the method's effectiveness for power-constrained applications.
Compute-In-Memory (CIM) systems, particularly those utilizing ReRAM and memristive technologies, offer a promising path toward energy-efficient neural network computation. However, conventional quantization and compression techniques often fail to fully optimize performance and efficiency in these architectures. In this work, we present a structured quantization method that combines sensitivity analysis with mixed-precision strategies to enhance weight storage and computational performance on ReRAM-based CIM systems. Our approach improves ReRAM Crossbar utilization, significantly reducing power consumption, latency, and computational load, while maintaining high accuracy. Experimental results show 86.33% accuracy at 70% compression, alongside a 40% reduction in power consumption, demonstrating the method's effectiveness for power-constrained applications.
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- 5G-NTN Modem IP for Satellite User Terminals
- 14-bit 12.5MSPS SAR ADC - Tower 65nm
- 5G-Advanced Modem IP for Edge and IoT Applications
- TSN Ethernet Endpoint Controller 10Gbps
- 13ns High-Speed Comparator with no Hysteresis
Related Articles
- Pyramid Vector Quantization and Bit Level Sparsity in Weights for Efficient Neural Networks Inference
- The Growing Importance of AI Inference and the Implications for Memory Technology
- CANsec: Security for the Third Generation of the CAN Bus
- Top 5 Reasons why CPU is the Best Processor for AI Inference
Latest Articles
- PDF: PUF-based DNN Fingerprinting for Knowledge Distillation Traceability
- TeraPool: A Physical Design Aware, 1024 RISC-V Cores Shared-L1-Memory Scaled-up Cluster Design with High Bandwidth Main Memory Link
- AutoGNN: End-to-End Hardware-Driven Graph Preprocessing for Enhanced GNN Performance
- LUTstructions: Self-loading FPGA-based Reconfigurable Instructions
- CQ-CiM: Hardware-Aware Embedding Shaping for Robust CiM-Based Retrieval