Leveraging FPGAs for Homomorphic Matrix-Vector Multiplication in Oblivious Message Retrieval
By Grant Bosworth 1, Keewoo Lee 2, and Sunwoong Kim 1
1 Rochester Institute of Technology, Rochester, NY, USA,
2 Ethereum Foundation
Abstract
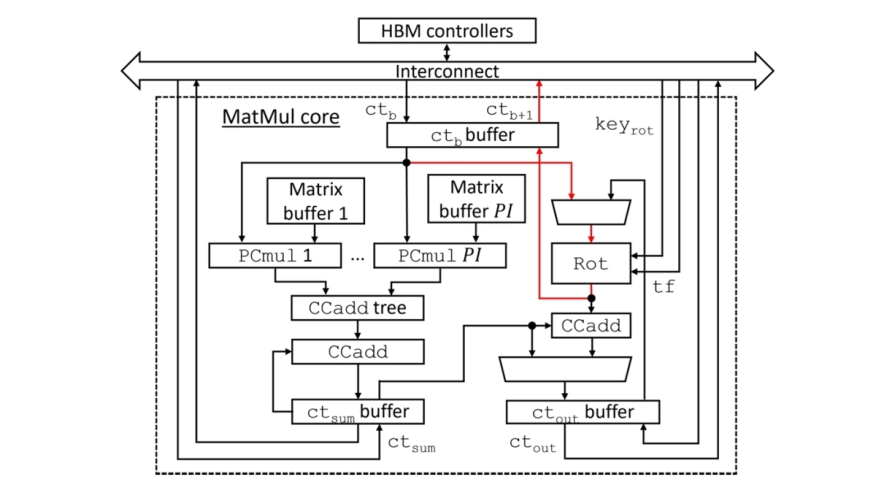
 While end-to-end encryption protects the content of messages, it does not secure metadata, which exposes sender and receiver information through traffic analysis. A plausible approach to protecting this metadata is to have senders post encrypted messages on a public bulletin board and receivers scan it for relevant messages. Oblivious message retrieval (OMR) leverages homomorphic encryption (HE) to improve user expe rience in this solution by delegating the scan to a resource-rich server while preserving privacy. A key process in OMR is the homomorphic detection of pertinent messages for the receiver from the bulletin board. It relies on a specialized matrix-vector multiplication algorithm, which involves extensive multiplications between ciphertext vectors and plaintext matrices, as well as homomorphic rotations. The computationally intensive nature of this process limits the practicality of OMR. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a hardware architecture to accelerate the matrix-vector multiplication algorithm. The building homomorphic operators in this algorithm are implemented using high-level synthesis, with design parameters for different parallelism levels. These operators are then deployed on a field programmable gate array platform using an efficient design space exploration strategy to accelerate homomorphic matrix vector multiplication. Compared to a software implementation, the proposed hardware accelerator achieves a 13.86x speedup.
While end-to-end encryption protects the content of messages, it does not secure metadata, which exposes sender and receiver information through traffic analysis. A plausible approach to protecting this metadata is to have senders post encrypted messages on a public bulletin board and receivers scan it for relevant messages. Oblivious message retrieval (OMR) leverages homomorphic encryption (HE) to improve user expe rience in this solution by delegating the scan to a resource-rich server while preserving privacy. A key process in OMR is the homomorphic detection of pertinent messages for the receiver from the bulletin board. It relies on a specialized matrix-vector multiplication algorithm, which involves extensive multiplications between ciphertext vectors and plaintext matrices, as well as homomorphic rotations. The computationally intensive nature of this process limits the practicality of OMR. To address this challenge, this paper proposes a hardware architecture to accelerate the matrix-vector multiplication algorithm. The building homomorphic operators in this algorithm are implemented using high-level synthesis, with design parameters for different parallelism levels. These operators are then deployed on a field programmable gate array platform using an efficient design space exploration strategy to accelerate homomorphic matrix vector multiplication. Compared to a software implementation, the proposed hardware accelerator achieves a 13.86x speedup.
Index Terms — Design space exploration, field-programmable gate array, high-level synthesis, homomorphic encryption, obliv ious message retrieval
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- JESD204E Controller IP
- eUSB2V2.0 Controller + PHY IP
- I/O Library with LVDS in SkyWater 90nm
- 50G PON LDPC Encoder/Decoder
- UALink Controller
Related Articles
- Growing demand for high-speed data in consumer devices gives rise to new generation of low-end FPGAs
- Leveraging ASIC AI Chips for Homomorphic Encryption
- The Future of Embedded FPGAs - eFPGA: The Proof is in the Tape Out
- Where automotive FPGAs stand in smart car designs
Latest Articles
- Crypto-RV: High-Efficiency FPGA-Based RISC-V Cryptographic Co-Processor for IoT Security
- In-Pipeline Integration of Digital In-Memory-Computing into RISC-V Vector Architecture to Accelerate Deep Learning
- QMC: Efficient SLM Edge Inference via Outlier-Aware Quantization and Emergent Memories Co-Design
- ChipBench: A Next-Step Benchmark for Evaluating LLM Performance in AI-Aided Chip Design
- COVERT: Trojan Detection in COTS Hardware via Statistical Activation of Microarchitectural Events