Advancing Network Packet Management for Converged NIC
Chakra Parvathaneni, V.P. Marketing, Posedge Inc.
S Kesineni, Software Lead, Posedge Inc.
Introduction
In a Data center, with the advent of Virtualization and Virtual Ethernet Bridging, the server to network edge is becoming an increasingly important area of the infrastructure. The most common types of networks used in enterprise Data Centers are Ethernet for LAN and FC for SAN and are converging. Fiber Channel (FC) is a lightweight, high performance protocol usually with in a SAN (limited area), where as iSCSI running over traditional TCP/IP protocols (routable) and existing Ethernet Infrastructure. These have different topologies, administrators, security, and performance requirements.
Converged networking technologies such as iSCSI, Fiber channel over Ethernet (FCoE) and Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) have the potential to simplify the networking infrastructure and help remove some of the problems of each of the technologies. With 10GB Ethernet becoming ubiquitous, the potential for combining multiple network streams over a single fabric becomes more feasible and economical.
However that poses several challenges in the server to network edge, making it increasingly complex due to sprawl of virtual machines. Challenges from VMs include the performance loss and management complexity of integrating software based virtual switches, also referred to as Virtual Ethernet Bridges (VEB).
The remainder of this white paper will focus on a proposed solution to a part of the problem, benefits of that approach and solutions available today from Posedge.
Existing Solutions and Work in Standards
Server edge with many connections, Switches and Ports, is the most complex part of the Data Center Network. It is a performance bottleneck with software based Virtual NICs and variety of protocols for management integration and visibility.
Edge Virtual Bridging
The Edge Virtual Bridging (EVB) work group of IEEE 802.1, which is based on Virtual Ethernet Port Aggregator (VEPA), targets to solve the Management Integration and Visibility.
Converged Enhanced Ethernet
Because FCOE is lightweight encapsulation protocol and lacks the reliable TCP transport layer, it must operate on Converged Enhanced Ethernet (CEE) to eliminate Ethernet frame loss under congestion conditions.
SR-IOV NIC
The HW based SR-IOV specification allows a PCIe device to appear to be multiple separate physical PCIe devices.
Data Center Bridging
Data center bridging (DCB) task group defining the standards could apply to any IEEE 802 MAC layer to provide lossless Ethernet. CEE refers to Ethernet protocols and Ethernet products that are DCB compliant.
There are four technologies defined in the DCB standards are
- Priority based Flow control (PFC), 802.1Qbb
- Enhanced Transmission selection (ETS), 802.1Qaz
- Quantized congestion Notification (QCN), 802.1Qau
- Data center Bridging Exchange protocol (DCBX) 802.1Qaz
- Low Latency Ethernet
Virtual Ethernet Bridge
Virtual Ethernet Bridge (VEB) describes network switches that are implemented within a virtualized server environment and support communications between VMs, the hypervisor and external network switches. In other words VEB is a Virtual Ethernet switch. It can be internal, private, virtual network between VMs within a physical server or it can be used to connect VMs to external network. Today most of the implementations of VEB are software based virtual switches, or “vSwitches” that are incorporated into all modern hypervisors.
This new layer of virtual machines and virtual switches within each virtualized physical interface introduces new complexity at the server edge and impacts the associated network. Posedge devised a potential solution to the above-mentioned problems with an advanced NIC card based Virtual Ethernet Switch architecture.
Advantages and Challenges of NIC based Virtual Ethernet Switch
With ever increasing functionality and complexity, dedicated hardware based Virtual Ethernet Switches provides much superior performance compared to the Software based virtual switches. They also offload the host processor from network functions allowing them to serve compute needs.
The QoS and Firewall requirements for the Virtual Ethernet Switch are extremely demanding. The firewall rules need to be applied on the fly on all the packets at around 40 Gbps (in a typical dual 10Gbps NIC card), and the firewall rules would be changing based on VM motion etc.
An alternative architecture is to send all the data to an external Ethernet switch to make Firewall decisions etc. This solution is sub-optimal as the data bandwidth on the 10Gbps link is not utilized fully and in addition QoS decisions made in the external Ethernet switch will not be applied at the server, which is essential to do achieve end to end QoS.
The solution has to be very latency sensitive and FCoE data needs to hop through minimum number of switches. With an external FCoE switch exclusively for VM switching, it adds to the latency of the FCoE traffic.
As the deployment scenarios and Standards are evolving, it is imperative to have a programmable solution for future upgrades. The planned changes could have quite a significant impact in very common fields like VLAN-ID size etc. So hardware level assumptions would be costly.
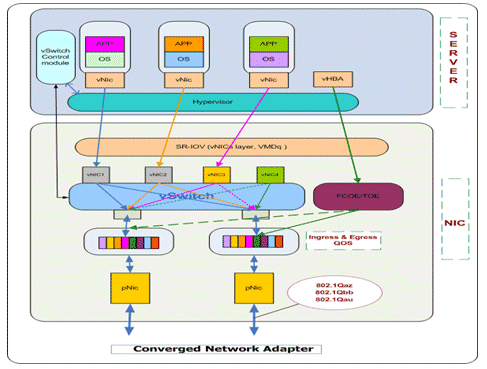
Figure 1: Hardware Architecture
The NIC is one data accumulation point for the Server and is an optimal place for deploying the switch. It eliminates the need for external buffering/buffer copies, and is the confluence point for the various technologies like iSCSI, FCoE.
Posedge Communications Converged NIC Solutions
Posedge Virtual Ethernet switch is hardware based programmable switch for Data Center Servers. In addition to VM level switching, it enables VM-Firewalls, very high levels of QoS (at VM level) and is suited to co-exist and enhance the functionality of FCoE, iSCSI etc. As it is programmable, it is future proof with respect to future standards like Data Centre Exchange Protocol etc.
Posedge Virtual Ethernet switch supports the following features to improve server performance and compatible with evolving Data center Bridging standards.
- PCIe SR-IOV support for max of 1024 VMs
- VEPA, VN-TAG, M-Tag and port extension
- Securing virtual servers
- Monitoring VM traffic using NetFlow or SPAN
- Supporting VM motion
- Low Latency Implementation
- Offloading of the processor,
The solution supports various Network standards like VEB etc, and is programmable for future standard upgrades.
Ingress and Egress QoS
With extensive know-how and deployment experience in QoS in Gateway and Ethernet Switches, Posedge Virtual Ethernet Switch superior QoS with different priority levels per VM. The QoS is applied across 1024 VM’s with 8 priorities per VM. The Ingress QoS is built not to drop sensitive packets (Voice packets) in overloaded conditions, which is essential to augment the Egress QoS.
Firewall and Data Security
With proven track record of handling number of firewall rules in the datapath for Residential and Enterprise Gateways, Posedge’s Fast-Path/Slow-Path offloading helps do efficient Firewall implementation.
Programmable Solution
Posedge Virtual Switch has very high speed parallel Micro-Engines assisted by hardware to perform classification and packet editing functions. The micro-engine based classifier enables programmability for future standards.

Figure 2: Software Architecture
Complete Solution With Software
Posedge solution is complete with hardware, micro-code in firmware and software for handling the Firewall etc. It works with existing standards and is future proof with micro-engines. An FPGA based solution is available now at 2.5 Gbps rates and will be scaled to 20 Gbps rates in an ASIC version.
Future Upgrades
In the market, now there are various NIC solutions for TCP-Offload, FCoE and with Virtual Ethernet Switching coming in, the requirement would be to have a converged Solution addressing all the three protocols in one ASIC.
In addition to these features, it is anticipated to have L2/L3/L4 Security in the NIC card with full offloads. Posedge with its MACSec, IPSEC, DTLS and SSL security solutions is well poised for these upgrades.
Changing Economics Dictates New Approaches
The ever-growing need for cloud computing and data center resources, calls for advanced switching technologies for better management, reliability and re-use. The switching technology needs to provide high throughput, low latency, and scalable with the future data speed requirements in the Data Center Ethernet. Hardware based solutions are essential to achieve the data rates with high levels of QoS, superior functionality and less processor overhead. The solution has to be scalable for future standards as well and hence needs to be programmable and Posedge Virtual Ethernet switch successfully addresses the two problems.
Related Semiconductor IP
- NPU IP Core for Mobile
- MSP7-32 MACsec IP core for FPGA or ASIC
- UHF RFID tag IP with 3.6kBit EEPROM and -18dBm sensitivity
- NPU IP Core for Edge
- Specialized Video Processing NPU IP
Related White Papers
- Advancing Network Packet Management and Security Using Silicon Based Subsystem IP Solutions
- Remote Testing and Diagnosis of system-On-Chips Using Network Management Frameworks
- Floorplan Guidelines for Sub-Micron Technology Node for Networking Chips
- Time Sensitive Networking for Aerospace
Latest White Papers
- Ramping Up Open-Source RISC-V Cores: Assessing the Energy Efficiency of Superscalar, Out-of-Order Execution
- Transition Fixes in 3nm Multi-Voltage SoC Design
- CXL Topology-Aware and Expander-Driven Prefetching: Unlocking SSD Performance
- Breaking the Memory Bandwidth Boundary. GDDR7 IP Design Challenges & Solutions
- Automating NoC Design to Tackle Rising SoC Complexity