Floating-Point FFT IP
Filter
Compare
14
IP
from
6
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
Floating-point (IEEE 754) IP based on Arria 10 and Stratix 10 FPGAs
- FFT size: Any size power-of-two or non-power-of-two
- Dynamic Range: IEEE754 single precision floating point
-
Single precision fixed-size streaming floating-point FFT
- FFT size: Any size power-of-two or non-power-of-two
- Dynamic Range: IEEE754 single precision floating point
-
FFT Intel® FPGA IP Core
- The Fast Fourier transform (FFT) Intel FPGA intellectual property (IP) core is a high-performance, highly parameterizable FFT processor
- The FFT function implements a radix-2/4 decimation-in-frequency (DIF) FFT algorithm for transform lengths of 2m where 6 ≤ m ≤ 14, internally using a block-floating-point architecture to maximize signal dynamic range in the transform calculation.
-
Tensilica FloatingPoint KQ7/KQ8 DSPs
- VLIW parallelism issuing multiple concurrent operations per cycle
- 512-bit and 1024-bit SIMD
- IEEE 754 vector floating-point (HP, SP, DP)
- Performance-optimized fused multiply-add (FMA)
-
Tensilica FloatingPoint KP1/KP6 DSPs
- VLIW parallelism issuing multiple concurrent operations per cycle
- Xtensa LX Secure Mode
- 128-bit and 512-bit SIMD
- IEEE 754 vector floating-point
-
Non-Power-of-Two FFT
- Sample Rates: Very high clock speeds
- FFT size: any size set of transforms (chosen at run-time) factorable into bases up to ~10
-
Fixed-size streaming FFT
- High Throughput: obtained from high clock rates (>500MHz using 65nm technology) and novel algorithms
- FFT size: Any size power-of-two or non-power-of-two
- Dynamic Range: combined block floating point and floating point architecture means smaller word lengths can be used for post processing operations such as equalization (~6db/bit).
- Scalability: array based architecture means higher throughputs are obtained by increasing array size
-
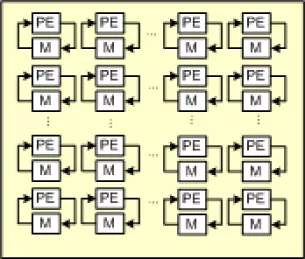
Variable FFT (run time choice of FFT size)
- High Throughput: obtained from high clock rates (>500MHz using 65nm technology) and novel algorithms
- FFT size: any user chosen set of power-of-two or non-power-of-two sizes chosen at run-time (e.g., 128/256/512/1024/2048 points for LTE/WiMax OFDMA)
- Programmability: Simple control circuitry for matching circuit/application functionality and I/O interface.
- Dynamic Range: combined block floating point and floating point architecture means smaller word lengths can be used for post-processing operations such as equalization.
-
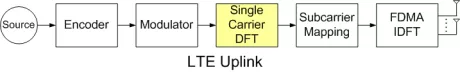
LTE Single Carrier FFT Circuit
- High Throughput: obtained from high clock rates (>400MHz using 65nm technology) and novel algorithms
-
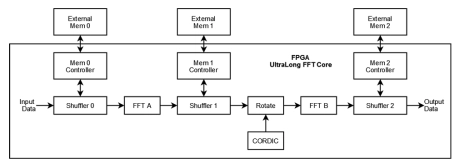
UltraLong FFT
- The UltraLong FFT IP Core uses an efficient Fast Fourier Transform (FFT) algorithm to provide multimillion-point discrete transforms on data frames or continuous data streams.
- This structure utilizes state-of-the-art off-chip memory technology and N1- and N2-length pipelined radix-2 FFT engines with an additional rotation stage to perform N=N1xN2 transform lengths, from 1K to 64M points.