Making Strong Error-Correcting Codes Work Effectively for HBM in AI Inference
By Rui Xie 1, Yunhua Fang 1, Asad Ul Haq 1, Linsen Ma 2, Sanchari Sen 3, Swagath Venkataramani 3, Liu Liu 1, Tong Zhang 1
1 Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute, Troy, New York, USA
2 ScaleFlux, Milpitas, California, USA
3 IBM T.J. Watson Research Center, Yorktown Heights, New York, USA
Abstract
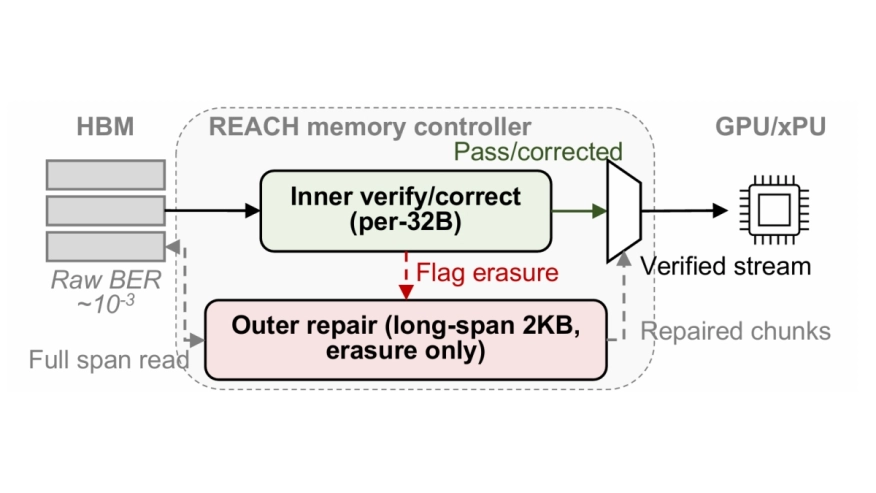
 LLM inference is increasingly memory-bound, and HBM cost per GB now dominates system cost. Today’s HBM stacks include short on-die ECC, which tightens binning, raises price, and locks reliability policy inside the device. This paper asks a simple question: can we tolerate a much higher raw HBM bit error rate (BER) and still keep end-to-end correctness and throughput, without changing the HBM PHY or the fixed 32B transaction size? We propose REACH (Reliability Extension Architecture for Cost-effective HBM), a controller-managed ECC design that keeps the HBM link and 32B transfers unchanged. REACH uses a two-level Reed- Solomon (RS) scheme: each 32B chunk uses an inner RS code to check and correct most faults locally, while chunks that cannot be fixed are marked as erasures. An outer RS code spans kilobytes and runs in erasure-only mode, repairing only the flagged chunks and avoiding the expensive locator step. For small random writes, REACHupdates outer parity with differential parity so it does not recompute parity over the whole span, and an optional importance adaptive bit-plane policy can protect onlycritical fields (for example, BF16 exponents) to reduce ECC work and traffic. On three LLMs at 8K context, REACH keeps ∼79% of the on-die ECC throughput at BER=0 and stays qualified up to raw BER = 10−3, extending toler able device error rates by about three orders of magnitude while keeping tokens/s nearly flat. In ASAP7, a full REACH controller occupies 15.2mm2 and consumes 17.5W at 3.56TB/s (∼4.9pJ/byte), and it reduces ECC area and power by 11.6× and ∼60% compared to a naive long-RS baseline. By moving strong ECC into the controller, REACHturns long-code reliability into a system choice, enabling vendors to trade higher device BER for lower HBM $/GB under the same standard interface.
LLM inference is increasingly memory-bound, and HBM cost per GB now dominates system cost. Today’s HBM stacks include short on-die ECC, which tightens binning, raises price, and locks reliability policy inside the device. This paper asks a simple question: can we tolerate a much higher raw HBM bit error rate (BER) and still keep end-to-end correctness and throughput, without changing the HBM PHY or the fixed 32B transaction size? We propose REACH (Reliability Extension Architecture for Cost-effective HBM), a controller-managed ECC design that keeps the HBM link and 32B transfers unchanged. REACH uses a two-level Reed- Solomon (RS) scheme: each 32B chunk uses an inner RS code to check and correct most faults locally, while chunks that cannot be fixed are marked as erasures. An outer RS code spans kilobytes and runs in erasure-only mode, repairing only the flagged chunks and avoiding the expensive locator step. For small random writes, REACHupdates outer parity with differential parity so it does not recompute parity over the whole span, and an optional importance adaptive bit-plane policy can protect onlycritical fields (for example, BF16 exponents) to reduce ECC work and traffic. On three LLMs at 8K context, REACH keeps ∼79% of the on-die ECC throughput at BER=0 and stays qualified up to raw BER = 10−3, extending toler able device error rates by about three orders of magnitude while keeping tokens/s nearly flat. In ASAP7, a full REACH controller occupies 15.2mm2 and consumes 17.5W at 3.56TB/s (∼4.9pJ/byte), and it reduces ECC area and power by 11.6× and ∼60% compared to a naive long-RS baseline. By moving strong ECC into the controller, REACHturns long-code reliability into a system choice, enabling vendors to trade higher device BER for lower HBM $/GB under the same standard interface.
Keywords: HBM, DRAM,Memory, Error-Correcting Code, Reliability
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- HBM Memory Controller
- HBM 4 Verification IP
- Verification IP for HBM
- TSMC CLN16FFGL+ HBM PHY IP
- Simulation VIP for HBM
Related Articles
- Breaking the HBM Bit Cost Barrier: Domain-Specific ECC for AI Inference Infrastructure
- The Growing Importance of AI Inference and the Implications for Memory Technology
- Top 5 Reasons why CPU is the Best Processor for AI Inference
- RISC-V Based TinyML Accelerator for Depthwise Separable Convolutions in Edge AI
Latest Articles
- GenAI for Systems: Recurring Challenges and Design Principles from Software to Silicon
- Creating a Frequency Plan for a System using a PLL
- RISCover: Automatic Discovery of User-exploitable Architectural Security Vulnerabilities in Closed-Source RISC-V CPUs
- MING: An Automated CNN-to-Edge MLIR HLS framework
- Fault Tolerant Design of IGZO-based Binary Search ADCs