In-Situ Encryption of Single-Transistor Nonvolatile Memories without Density Loss
By Sanwar Ahmed Ovy 1, Jiahui Duan 2, Md Ashraful Islam Romel 1, Franz Muller 3, Thomas Kampfe 3,4, Kai Ni 2, Sumitha George 1
1 North Dakota State University, Fargo, USA;
2 University of Notre Dame, Notre Dame, USA;
3 Fraunhofer IPMS, Dresden, Germany;
4 TU Braunschweig, Braunschweig, Germany
Abstract
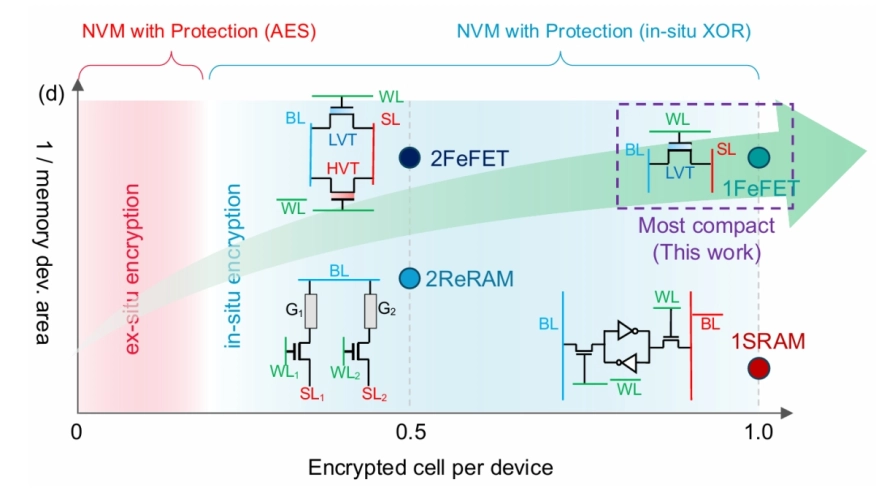
 Non-volatile memories (NVMs) offer negligible leakage power consumption, high integration density, and data retention, but their non-volatility also raises the risk of data exposure. Conventional encryption techniques such as the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) incur large area overheads and performance penalties, motivating lightweight XOR-based in-situ encryption schemes with low area and power requirements. This work proposes an ultra-dense single-transistor encrypted cell using ferroelectric FET (FeFET) devices, which, to our knowledge, is the first to eliminate the two-memory-devices-per-encrypted-cell requirement in XOR-based schemes, enabling encrypted memory arrays to maintain the same number of storage devices as unencrypted arrays. The key idea is an in-memory single-FeFET XOR scheme, where the ciphertext is encoded in the device threshold voltage and leverages the direction-dependent current flow of the FeFET for single-cycle decryption; eliminating complementary bit storage also removes the need for two write cycles, allowing faster encryption. We extend the approach to multi-level-cell (MLC) FeFETs to store multiple bits per transistor. We validate the proposed idea through both simulation and experimental evaluations. Our analysis on a 128x128-bit array shows 2x higher encryption/decryption throughput than prior FeFET work and 45.2x/14.12x improvement over AES, while application-level evaluations using neural-network benchmarks demonstrate average latency reductions of 50% and 95% compared to prior FeFET-based and AES-based schemes, respectively.
Non-volatile memories (NVMs) offer negligible leakage power consumption, high integration density, and data retention, but their non-volatility also raises the risk of data exposure. Conventional encryption techniques such as the Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) incur large area overheads and performance penalties, motivating lightweight XOR-based in-situ encryption schemes with low area and power requirements. This work proposes an ultra-dense single-transistor encrypted cell using ferroelectric FET (FeFET) devices, which, to our knowledge, is the first to eliminate the two-memory-devices-per-encrypted-cell requirement in XOR-based schemes, enabling encrypted memory arrays to maintain the same number of storage devices as unencrypted arrays. The key idea is an in-memory single-FeFET XOR scheme, where the ciphertext is encoded in the device threshold voltage and leverages the direction-dependent current flow of the FeFET for single-cycle decryption; eliminating complementary bit storage also removes the need for two write cycles, allowing faster encryption. We extend the approach to multi-level-cell (MLC) FeFETs to store multiple bits per transistor. We validate the proposed idea through both simulation and experimental evaluations. Our analysis on a 128x128-bit array shows 2x higher encryption/decryption throughput than prior FeFET work and 45.2x/14.12x improvement over AES, while application-level evaluations using neural-network benchmarks demonstrate average latency reductions of 50% and 95% compared to prior FeFET-based and AES-based schemes, respectively.
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- NVM OTP XBC TSMC N7 1.8V
- NVM OTP XBC TSMC N6 1.8V
- NVM OTP XBC TSMC N5A 1.2V Automotive Grade 1 with Functional Safety
- NVM OTP XBC TSMC N5 1.2V
- NVM OTP XBC TSMC N4P 1.2V
Related Articles
- Nonvolatile memories for 90nm SoC and beyond
- How Low Can You Go? Pushing the Limits of Transistors - Deep Low Voltage Enablement of Embedded Memories and Logic Libraries to Achieve Extreme Low Power
- The benefit of non-volatile memory (NVM) for edge AI
- Assessing Design Space for the Device-Circuit Codesign of Nonvolatile Memory-Based Compute-in-Memory Accelerators
Latest Articles
- AutoGNN: End-to-End Hardware-Driven Graph Preprocessing for Enhanced GNN Performance
- LUTstructions: Self-loading FPGA-based Reconfigurable Instructions
- CQ-CiM: Hardware-Aware Embedding Shaping for Robust CiM-Based Retrieval
- GenAI for Systems: Recurring Challenges and Design Principles from Software to Silicon
- Creating a Frequency Plan for a System using a PLL