Handling Asynchronous Clock Groups in SDC
Sanjay Churiwala & Balachander Krishnamurthy, Xilinx
EETimes (11/15/2013 04:40 PM EST)
Introducing CDC
Most SoC designs in today's world employ multiple clocks and commonly have many clock domains. As data crosses from one clock domain to another within the design, the potential for metastability problems arises due to asynchronous clock domain crossings (CDCs).
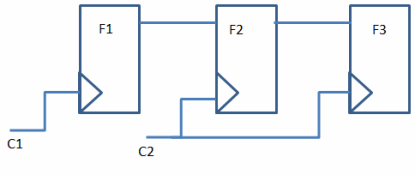
Figure 1: An asynchronous crossing with simple double flop synchronization.
In Figure 1, there is an asynchronous CDC for the data going from flop F1 (clocked by C1) into F2 (clocked by C2), assuming that C1 and C2 are asynchronous with respect to each other.
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- Hardware Security Module (HSM) for AMD Xilinx Versal ACAP device
- Hardware Security Module (HSM) for Xilinx Zynq UltraScale+ MPSoC platform
- ARC4 Core for Xilinx FPG
- Xilinx Virtual Cable
- Xilinx HMC Controller
Related Articles
- Asynchronous Logic: large CMOS devices without a clock tree
- Ultra Low Power Designs Using Asynchronous Design Techniques (Welcome to the World Without Clocks)
- High-Performance DSPs -> DSP performance: Useful work per clock tick
- Keynoter sees asynchronous future for digital designs
Latest Articles
- Crypto-RV: High-Efficiency FPGA-Based RISC-V Cryptographic Co-Processor for IoT Security
- In-Pipeline Integration of Digital In-Memory-Computing into RISC-V Vector Architecture to Accelerate Deep Learning
- QMC: Efficient SLM Edge Inference via Outlier-Aware Quantization and Emergent Memories Co-Design
- ChipBench: A Next-Step Benchmark for Evaluating LLM Performance in AI-Aided Chip Design
- COVERT: Trojan Detection in COTS Hardware via Statistical Activation of Microarchitectural Events