Rapid SoC Proof-Of-Concept For Zero Cost
Jeff Miller, Product Marketing And Strategy, Mentor Graphics
Phil Burr, Senior Product Manager, Arm
THE SCENARIO
Your company provides analog/mixed-signal (AMS) and sensor-based ICs, but your best customer wants you to create a system on a chip (SoC) that includes a digital processor (Figure 1). With little experience with digital processors, you need to quickly provide a proof-of-concept to your customer that shows the viability of this new IC in the next few days. And, you have very little budget.

Figure 1: The scenario – expanding the AMS design to include a processor.
Because of the lack of funding, you need to keep non-recurring engineering (NRE) cost as low as possible. The working definition of NRE in the context of this paper is the cost of IP and EDA tooling. Because your salary is recurring, the time spent proving the concept is not included as NRE, but you only have a few days to complete the proof of concept anyway. How can you show a proof-of-concept to your customer fast and for zero NRE?
ARM® DESIGNSTART™
Recognizing that there are special requirements for sensor and mixed-signal companies, as well as startups or small teams creating custom SoCs, ARM offers the DesignStart portal (Figure 2) that allows designers fast and easy access to a trial selection of ARM products without charge. In addition, Mentor Graphics provides the Tanner EDA design tools for free evaluation and ARM offers approved design partners for SoC development help.
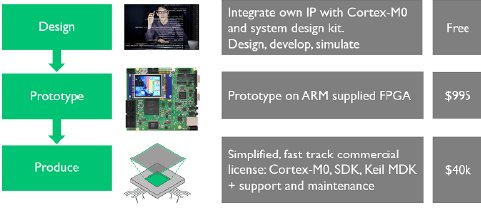
Figure 2: The ARM DesignStart portal (Source: ARM).
For your project, the portal offers the ARM Cortex®-M0 processor that you can download and use for design and simulation without charge. This is the ideal solution to your rapid proof-of-concept project. The ARM Cortex-M0 is a low-power 32-bit processor with a small footprint (Figure 3).

Figure 3: The ARM Cortex-M0 processor (Source: ARM).
This processor is widely-used in the industry for cost-sensitive devices and it has the following key features:
- Built-in low-power features - such as sleep, deep sleep, and state retention low-power modes
- Deterministic instruction execution timing - instructions and interrupts have a fixed timing and interrupt handling is automatic
- Exceptional code density - compact code with smaller code than 8/16-bit devices
- Tiny footprint – only 12k gates, resulting in 32-bit processing with a gate count of an 8-bit processor
- Simple and quick development – with just 56 instructions and one AHB bus interface, it is possible to quickly master the entire Cortex-M0 instruction set and its C-friendly architecture
Related Semiconductor IP
- HBM4 PHY IP
- Ultra-Low-Power LPDDR3/LPDDR2/DDR3L Combo Subsystem
- HBM4 Controller IP
- IPSEC AES-256-GCM (Standalone IPsec)
- Parameterizable compact BCH codec
Related Articles
- An Efficient Device for Forward Collision Warning Using Low Cost Stereo Camera & Embedded SoC
- EDA in the Cloud Will be Key to Rapid Innovative SoC Design
- Accelerating SoC Evolution With NoC Innovations Using NoC Tiling for AI and Machine Learning
- Early Interactive Short Isolation for Faster SoC Verification
Latest Articles
- Pipeline Stage Resolved Timing Characterization of FPGA and ASIC Implementations of a RISC V Processor
- Lyra: A Hardware-Accelerated RISC-V Verification Framework with Generative Model-Based Processor Fuzzing
- Leveraging FPGAs for Homomorphic Matrix-Vector Multiplication in Oblivious Message Retrieval
- Extending and Accelerating Inner Product Masking with Fault Detection via Instruction Set Extension
- ioPUF+: A PUF Based on I/O Pull-Up/Down Resistors for Secret Key Generation in IoT Nodes