Artificial Intelligence and Machine Learning based Image Processing
By V Srinivas Durga Prasad, Softnautics
Image processing is the process of converting an image to a digital format and then performing various operations on it to gather useful information. Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) has had a huge influence on various fields of technology in recent years. Computer vision, the ability for computers to understand images and videos on their own, is one of the top trends in this industry. The popularity of computer vision is growing like never before and its application is spanning across industries like automobiles, consumer electronics, retail, manufacturing and many more. Image processing can be done in two ways: Physical photographs, printouts, and other hard copies of images being processed using analogue image processing and digital image processing is the use of computer algorithms to manipulate digital images. The input in both cases is an image. The output of analogue image processing is always an image. However, the output of digital image processing may be an image or information associated with that image, such as data on features, attributes, and bounding boxes. According to a report published by Data Bridge Market Research analyses, the Image processing systems market is expected to grow at a CAGR of 21.8% registering a market value of USD 151,632.6 million by 2029. Image processing is used in a variety of use cases today, including visualisation, pattern recognition, segmentation, image information extraction, classification, and many others.
Image processing working mechanism
Artificial intelligence and Machine Learning algorithms usually use a workflow to learn from data. Consider a generic model of a working algorithm for an Image Processing use case. To start, AI algorithms require a large amount of high-quality data to learn and predict highly accurate results. As a result, we must ensure that the images are well-processed, annotated, and generic for AIML image processing. This is where computer vision (CV) comes in; it is a field concerned with machines understanding image data. We can use CV to process, load, transform, and manipulate images to create an ideal dataset for the AI algorithm.
Let’s understand the workflow of a basic image processing system
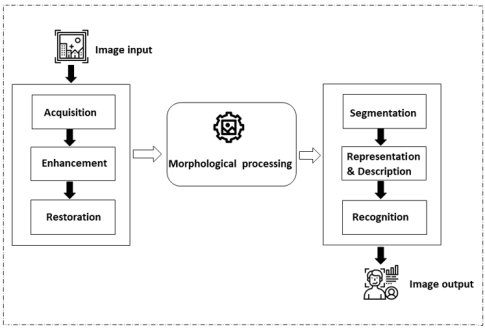
An Overview of Image Processing System
Acquisition of image
The initial level begins with image pre-processing which uses a sensor to capture the image and transform it into a usable format.
Enhancement of image
Image enhancement is the technique of bringing out and emphasising specific interesting characteristics which are hidden in an image.
Restoration of image
Image restoration is the process of enhancing an image's look. Picture restoration, as opposed to image augmentation, is carried out utilising specific mathematical or probabilistic models.
Colour image processing
A variety of digital colour modelling approaches such as HSI (Hue-Saturation-Intensity), CMY (Cyan-Magenta-Yellow) and RGB (Red-Green-Blue) etc. are used in colour picture processing.
Compression and decompression of image
This enables adjustments to image resolution and size, whether for image reduction or restoration depending on the situation, without lowering image quality below a desirable level. Lossy and lossless compression techniques are the two main types of image file compression which are being employed in this stage.
Morphological processing
Digital images are processed depending on their shapes using an image processing technique known as morphological operations. The operations depend on the pixel values rather than their numerical values, and well suited for the processing of binary images. It aids in removing imperfections for structure of the image.
Segmentation, representation and description
The segmentation process divides a picture into segments, and each segment is represented and described in such a way that it can be processed further by a computer. The image's quality and regional characteristics are covered by representation. The description's job is to extract quantitative data that helps distinguish one class of items from another.
Recognition of image
A label is given to an object through recognition based on its description. Some of the often-employed algorithms in the process of recognising images include the Scale-invariant Feature Transform (SIFT), the Speeded Up Robust Features (SURF), and the PCA (Principal Component Analysis).
Frameworks for AI image processing
- Open CV
OpenCV is a well-known computer vision library that provides numerous algorithms and utilities to support the algorithms. The modules for object detection, machine learning, and image processing are only a few of the many that it includes. With the help of this programme, you may do picture processing tasks like data extraction, restoration, and compression.
- TensorFlow
TensorFlow, created by Google, is one of the most well-known end-to-end machine learning programming frameworks for tackling the challenges of building and training a neural network to automatically locate and categorise images to a level of human perception. It offers functionalities like work on multiple parallel processors, cross platform, GPU configuration, support for a wide range of neural network algorithms, etc.
- PyTorch
Intended to shorten the time it takes to get from a research prototype to commercial development, it includes features like a tool and library ecosystem, support for popular cloud platforms, a simple transition from development to production, distribution training, etc.
- Caffe
It is a deep learning framework intended for image classification and segmentation. It has features like simple CPU and GPU switching, optimised model definition and configuration, computation utilising blobs, etc.
Applications
- Machine vision
The ability of a computer to comprehend the world is known as machine vision. Digital signal processing and analogue-to-digital conversion are combined with one or more video cameras. The image data is transmitted to a robot controller or computer. This technology aids companies in improving automated processes through automated analysis. For instance, specialised machine vision image processing methods can frequently sort parts more efficiently when tactile methods are insufficient for robotic systems to sort through various shapes and sizes of parts. These methods use very specific algorithms that consider the parameters of the colours or greyscale values in the image to accurately define outlines or sizing for an object.
- Pattern recognition
The technique of identifying patterns with the aid of a machine learning system is called pattern recognition. The classification of data generally takes place based on previously acquired knowledge or statistical data extrapolated from patterns and/or their representation. Image processing is used in pattern recognition to identify the items in an image, and machine learning is then used to train the system to recognise changes in patterns. Pattern recognition is utilised in computer assisted diagnosis, handwriting recognition, image identification, character recognition etc.
- Digital video processing
A video is nothing more than just a series of images that move quickly. The number of frames or photos per minute and the calibre of each frame employed determine the video's quality. Noise reduction, detail improvement, motion detection, frame rate conversion, aspect ratio conversion, colour space conversion, etc. are all aspects of video processing. Televisions, VCRs, DVD players, video codecs, and other devices all use video processing techniques.
- Transmission and encoding
Today, thanks to technological advancements, we can instantly view live CCTV footage or video feeds from anywhere in the world. This indicates that image transmission and encoding have both advanced significantly. Progressive image transmission is a technique of encoding and decoding digital information representing an image in a way that the image's main features, like outlines, can be presented at low resolution initially and then refined to greater resolutions. An image is encoded by an electronic analogue to multiple scans of the exact image at different resolutions in progressive transmission. Progressive image decoding results in a preliminary approximate reconstruction of the image, followed by successively better images whose adherence is gradually built up from succeeding scan results at the receiver side. Additionally, image compression reduces the amount of data needed to describe a digital image by eliminating extra data, ensuring that the image processing is finished and that it is suitable for transmission.
- Image sharpening and restoration
Here, the terms "image sharpening" and "restoration" refer to the processes used to enhance or edit photographs taken with a modern camera to produce desired results. Zooming, blurring, sharpening, converting from grayscale to colour, identifying edges and vice versa, image retrieval, and image recognition are included. Recovering lost resolution and reducing noise are the goals of picture restoration techniques. Either the frequency domain or the image domain is used for image processing techniques. Deconvolution, which is carried out in the frequency domain, is the easiest and most used technique for image restoration.
Image processing can be employed to enhance an image's quality, remove unwanted artefacts from an image, or even create new images completely from scratch. Nowadays, image processing is one of the fastest-growing technologies, and it has a huge potential for future wide adoption in areas such as video and 3D graphics, statistical image processing, recognising, and tracking people and things, diagnosing medical conditions, PCB inspection, robotic guidance and control, and automatic driving in all modes of transportation.
At Softnautics, we help industries to design Vision based AI solutions such as image classification & tagging, visual content analysis, object tracking, identification, anomaly detection, face detection and pattern recognition. Our team of experts have experience in developing vision solutions based on Optical Character Recognition, NLP, Text Analytics, Cognitive Computing, etc. involving various FPGA platforms.
Author: V Srinivas Durga Prasad
Srinivas is a Marketing professional at Softnautics working on techno-commercial write-ups, marketing research and trend analysis. He is a marketing enthusiast with 7+ years of experience belonging to diversified industries. He loves to travel and is fond of adventures.
Related Semiconductor IP
- NPU IP Core for Mobile
- NPU IP Core for Edge
- Specialized Video Processing NPU IP
- HYPERBUS™ Memory Controller
- AV1 Video Encoder IP
Related White Papers
- Generic and Automatic Specman based Verification Environment for Image Signal Processing IPs
- Multimedia Intelligence: Confluence of Multimedia and Artificial Intelligence
- An overview of Machine Learning pipeline and its importance
- Artificial Intelligence (AI) utilizing deep learning techniques to enhance ADAS
Latest White Papers
- Transition Fixes in 3nm Multi-Voltage SoC Design
- CXL Topology-Aware and Expander-Driven Prefetching: Unlocking SSD Performance
- Breaking the Memory Bandwidth Boundary. GDDR7 IP Design Challenges & Solutions
- Automating NoC Design to Tackle Rising SoC Complexity
- Memory Prefetching Evaluation of Scientific Applications on a Modern HPC Arm-Based Processor