HBM IP
Filter
Compare
416
IP
from
38
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
HBM 4 Verification IP
- The HBM4 Verification IP provides an effective & efficient way to verify the components interfacing with HBM interface of an ASIC/FPGA or SoC.
- The HBM4 VIP is fully compliant with Standard HBM Version JESD270-4 specifications from JEDEC.
- This VIP is a light weight VIP with easy plug-and-play interface so that there is no hit on the design time and the simulation time.
-
Verification IP for HBM
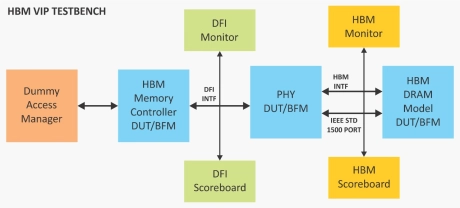
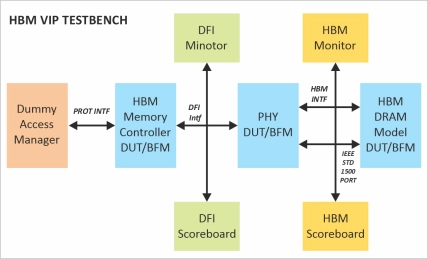
- HBM VIP is a comprehensive memory VIP solution portfolio for high bandwidth memory (HBM), targeting a new standard in memory performance, density, power consumption, and cost.
- HBM VIP is intended for SoC and memory control ler designers who employ external HBM modules and PHY developers to ensure both comprehensive verification and protocol and timing compliance.
-
Simulation VIP for HBM
- Speed (MHz)
- 1800MHz (3.6 Gbps/pin)
- Device Density
- Supports a wide range of device densities from 1Gb to 24Gb
-
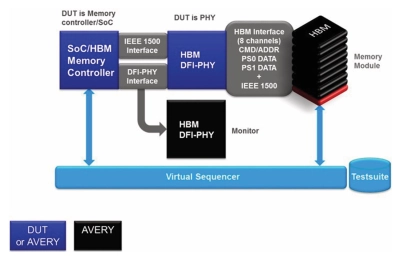
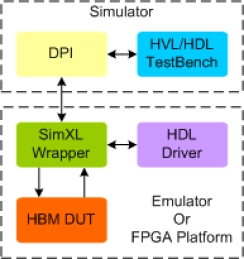
HBM Synthesizable Transactor
- Supports 100% of HBM protocol standard JESD235, JESD235A, JESD235B, JESD235C and JESD235D.
- Supports all the HBM commands as per the specs
- Supports all types of timing and protocol violation detection
- Supports burst length of 2 and 4
-
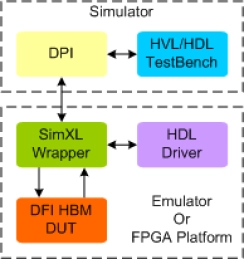
HBM DFI Synthesizable Transactor
- Compliant with DFI version 4.0 or 5.0 Specifications.
- Supports HBM devices compliant with JEDEC HBM DRAM Standard JESD235, JESD235A, JESD235B and JESD235C.
- Supports all Interface Groups.
- Supports Write Transactions with Data mask
-
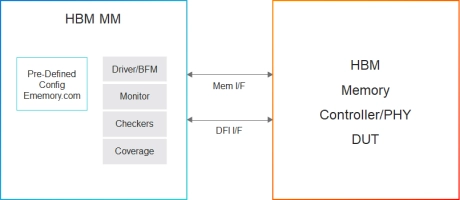
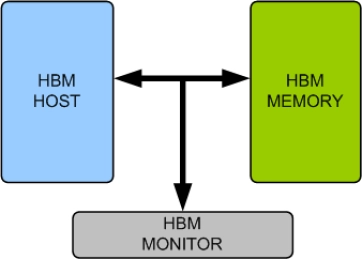
HBM Memory Model
- Supports HBM memory devices from all leading vendors.
- Supports 100% of HBM protocol standard JESD235, JESD235A, JESD235B, JESD235C and JESD235D.
- Supports all the HBM commands as per the specs.
- Supports programmable clock frequency of operation.
-
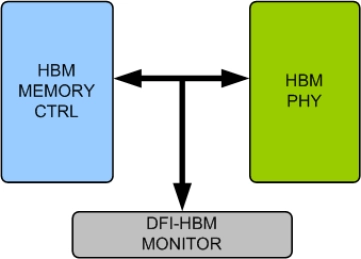
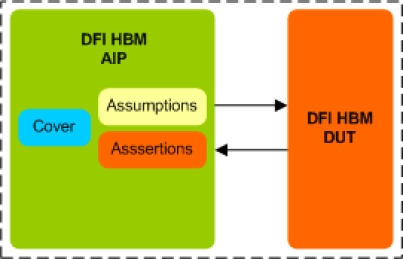
HBM DFI Verification IP
- Compliant with DFI version 4.0 or 5.0 Specifications.
- Supports HBM devices compliant with JEDEC HBM DRAM Standard JESD235, JESD235A, JESD235B and JESD235C.
- Supports all Interface Groups.
- Supports Write Transactions with Data mask
-
HBM DFI Assertion IP
- Specification Compliance
- Compliant with DFI version 4.0 or 5.0 Specifications.
- Supports HBM devices compliant with JEDEC HBM DRAM Standard JESD235, JESD235A, JESD235B and JESD235C.
- Supports all Interface Groups.
-
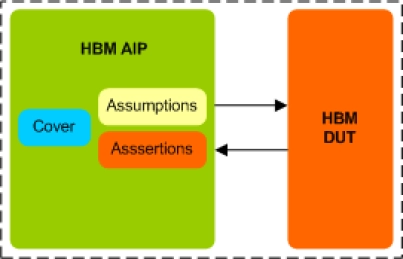
HBM Assertion IP
- Specification Compliance
- Supports HBM memory devices from all leading vendors.
- Supports 100% of HBM protocol standard JESD235, JESD235A, JESD235B, JESD235C and JESD235D.
- Supports all the HBM commands as per the specs.
-
HBM 3 Verification IP
- Compliant to JEDEC HBM SDRAM Specification versionJESD235A.
- Supports Legacy and Pseudo Channel Mode.
- Supports connection to any HBM Memory Controller IPcommunicating with a JESD235A compliant HBM Memory Model.
- Available in all Stack memory size from 8 Gb to 32 Gb (8Channels/Stack).