The Advancements of DDR5: How it Stacks Up Against DDR4
The first generation of Synchronous DRAM (SDRAM) is SDR, which stands for Single Data Rate SDRAM. SDR can transfer only one instruction per clock cycle, which limits the speed and efficiency of data transfer. Double Data Rate SDRAM (DDR-SDRAM) is the new version of SDRAM in which data transfer is possible through both the clock edges (rising and falling edge), making it twice as fast as SDR SDRAM. Data transfer on both the clock edges is common in all generations of DDR, but each new generation brings features that make them technically very different.
Given below is a figure showing SDR vs DDR data transfer per clock.
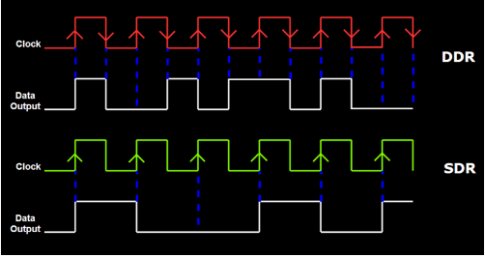
Figure.1 SDR vs DDR data transfer
As SoCs are getting more complex with the addition of more cores and functionality, low power and high performance become vital goals. DDR SDRAMs meet these memory requirements by offering high-performance, greater-density, and low-power memory solutions. DDR has improved over the years as the industry has progressed from DDR to DDR2, DDR3, DDR4, and now DDR5 SDRAM.
DDR5 is the latest and fifth generation of DDR SDRAM. This standard is able to achieve a higher data transfer rate (speed), more bandwidth, reduced operating voltage, and better efficiency. DDR5 maintains the same pin configuration as its predecessor DDR4, unlike the last transition from DDR3 to DDR4 in which the DDR3 module uses 240 pins and DDR4 uses 288 pins.
Let us see, “Why DDR5 is becoming the preferred choice?”.
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- LPDDR6/5X/5 PHY V2 - Intel 18A-P
- MIPI SoundWire I3S Peripheral IP
- LPDDR6/5X/5 Controller IP
- Post-Quantum ML-KEM IP Core
- MIPI SoundWire I3S Manager IP
Related Blogs
- Cowan LRA model's 2010 semicon sales growth forecast estimate: How does it "stack up" against other prognosticators?
- Announcing the launch of CHERI Alliance: A unified front against digital threats
- Guarding against the threat of clock attacks with analog IP
- LPDDR6: The Next-Generation LPDDR Device Standard and How It Differs from LPDDR5
Latest Blogs
- ML-DSA explained: Quantum-Safe digital Signatures for secure embedded Systems
- Efficiency Defines The Future Of Data Movement
- Why Standard-Cell Architecture Matters for Adaptable ASIC Designs
- ML-KEM explained: Quantum-safe Key Exchange for secure embedded Hardware
- Rivos Collaborates to Complete Secure Provisioning of Integrated OpenTitan Root of Trust During SoC Production
