High-Bandwidth Core Access to Accelerators: Enabling Optimized Data Transfers with RISC-V
Domain-specific accelerators (DSAs) are becoming increasingly common in SoCs. A DSA provides higher performance per watt by optimizing the specialized function it implements. Examples of DSAs include compression/decompression units, random number generators and network packet processors. A DSA is typically connected to the core complex using a standard IO interconnect, such as an AXI bus (Figure 1).
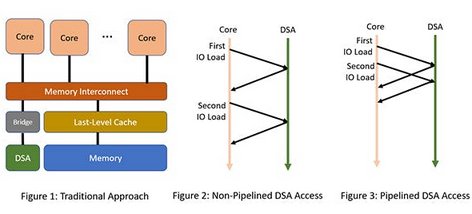
RISC-V offers a unique opportunity to optimize high-bandwidth communication between cores and DSAs. Cores often issue fine-grain load and store instructions in the IO space to access DSA memory. The problem, however, is that these loads and stores to DSA memory might have side effects. For example, a load to a specific DSA memory address might trigger a network message as a side effect of the load. Typically, because of such side effects, loads and stores from a core to an IO device are required to be observed by the IO device in order. This is also known as point-to-point ordering.
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- RISC-V Debug & Trace IP
- Gen#2 of 64-bit RISC-V core with out-of-order pipeline based complex
- Compact Embedded RISC-V Processor
- Multi-core capable 64-bit RISC-V CPU with vector extensions
- 64 bit RISC-V Multicore Processor with 2048-bit VLEN and AMM
Related Blogs
- Part 1: Fast Access to Accelerators: Enabling Optimized Data Transfer with RISC-V
- High-Bandwidth Accelerator Access to Memory: Enabling Optimized Data Transfers with RISC-V
- Fast Access to Accelerators: Enabling Optimized Data Transfer with RISC-V
- Part 3: High-Bandwidth Accelerator Access to Memory: Enabling Optimized Data Transfers with RISC-V
Latest Blogs
- Embedded Security explained: Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) for embedded Systems
- Accreditation Without Compromise: Making eFPGA Assurable for Decades
- Synopsys Delivers First Complete UFS 5.0 and M‑PHY v6.0 IP Solution for Next‑Gen Storage
- World First: Synopsys MACsec IP Receives ISO/PAS 8800 Certification for Automotive and Physical AI Security
- Last-level cache has become a critical SoC design element
