Public Key Accelerator IP
Public key cryptography, or asymmetric cryptography, uses mathematical functions to create codes that are exceptionally difficult to crack, enabling designers to protect sensitive data and systems. Common public key algorithms include RSA, Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA), and Diffie-Hellman (DH), which require the calculation of complex modular exponentiation operations to encrypt, decrypt, sign, and verify data used in data encryption, digital signatures, and key exchanges. Similarly, the Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC) based algorithms require complex mathematical operations, such as point multiplications, and are designed to support devices with limited computing power or memory to encrypt internet traffic.
All offers in
Public Key Accelerator IP
Filter
Compare
90
Public Key Accelerator IP
from
20
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
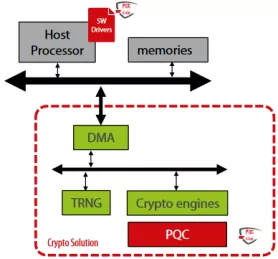
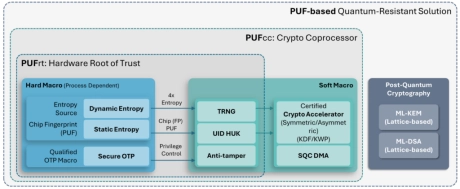
PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Solution
- PUFsecurity is proud to pioneer the world’s first PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) solution, delivering cutting-edge, hardware-level security that sets a new standard.
- Our innovative solution integrates PUF technology with quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, ensuring robust key protection and seamless transition to a quantum-secure future.
-
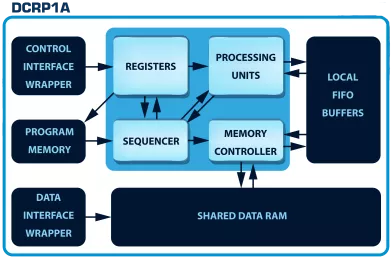
100% Secure Cryptographic System for RSA, Diffie-Hellman and ECC with AMBA AHB, AXI4 and APB
- The DCRP1A - CryptOne IP is a 100% secure cryptographic system
- CryptOne is a fully scalable, hardware-accelerated cryptographic system
- Designed for next-generation SoCs, FPGAs, and secure embedded systems, it delivers 100% secure asymmetric cryptography acceleration for demanding applications.
-
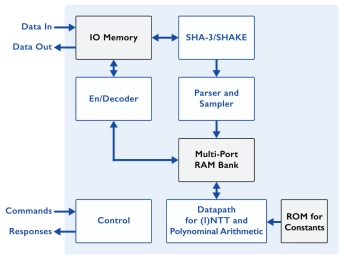
xQlave® ML-KEM (Kyber) Key Encapsulation Mechanism IP core
- Quantum-resistant key exchange for future-proof security
- Compliant with NIST's ML-KEM standard
- Pure RTL without hidden CPU or software components
- Optimised architecture with constant-time execution
-
Highly-optimized PQC implementations, capable of running PQC in under 15kb RAM
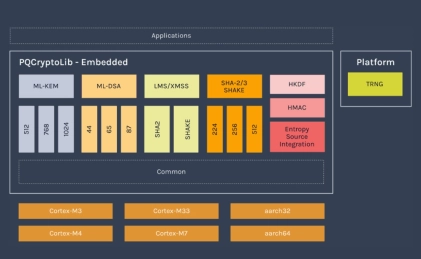
- PQCryptoLib-Emebedded is a versatile, CAVP-ready cryptography library designed and optimized for embedded devices.
- With its design focused on ultra-small memory footprint, PQCryptoLib-Embedded solutions have been specically designed for embedded systems, microcontrollers and memory-constrained devices. It provides a PQC integration to devices already in the field.
-
Post-Quantum Key Encapsulation IP Core
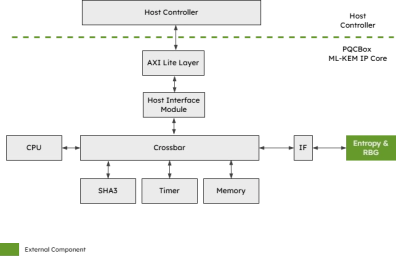
- The PQC-KEM is an IP Core for ML-KEM Key Encapsulation that supports key generation, encapsulation, and decapsulation operations for all ML-KEM variants standardized by NIST in FIPS 203.
- ML-KEM is a post-quantum cryptographic (PQC) algorithm, designed to be robust against a quantum computer attack.
-
ASCON Authenticated Encryption & Hashing Engine
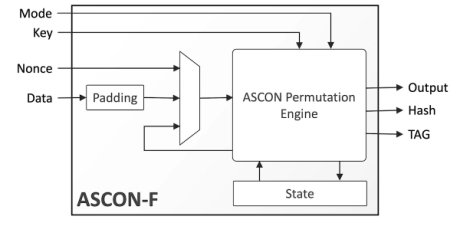
- The ASCON-F IP core is a compact, high-throughput hardware engine implementing the lightweight authenticated encryption with associated data (AEAD) and hashing algorithms described in the Ascon v1.2 specification.
- A single instance of the ASCON-F IP core can encrypt or decrypt data using the Ascon-128 and Ascon-128a functions or perform Cryptographic hashing Hash per the Ascon-Hash and Ascon-Hasha functions.
-
ML-DSA Digital Signature Engine
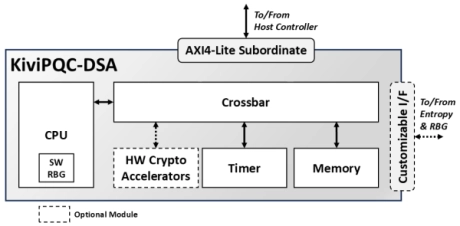
- The KiviPQC™-DSA is a hardware accelerator for post-quantum cryptographic operations.
- It implements the Module Lattice-based Digital Signature Algorithm (ML-DSA), standardized by NIST in FIPS 204.
- This mechanism realizes the appropriate procedures for securely generating a private/public key pair, digitally signing a message or a data block, and performing digital signature verification.
-
ML-KEM Key Encapsulation & ML-DSA Digital Signature Engine
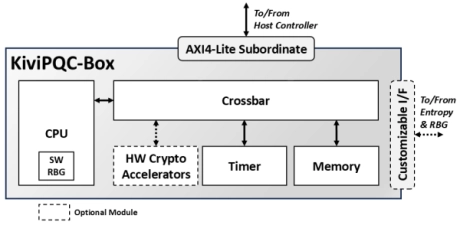
- The KiviPQC™-Box is a hardware accelerator for post-quantum cryptographic operations.
- It implements both the Module Lattice-based Key Encapsulation Mechanism (ML-KEM) and the Module Lattice-based Digital Signature Algorithm (ML-DSA), standardized by NIST in FIPS 203 and FIPS 204, respectively.
-
ML-KEM Key Encapsulation IP Core
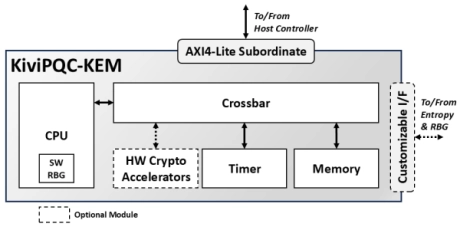
- The KiviPQC™-KEM is a hardware accelerator for post-quantum cryptographic operations.
- It implements the Module Lattice-based Key Encapsulation Mechanism (ML-KEM), standardized by NIST in FIPS 203.
- This mechanism realizes the appropriate procedures for securely exchanging a shared secret key between two parties that communicate over a public channel using a defined set of rules and parameters.
-
Crypto Coprocessor with integrated Post-Quantum Cryptography IPs
- The Crypto Coprocessors are a hardware IP core platform that accelerates cryptographic operations in System-on-Chip (SoC) environment on FPGA or ASIC.
- Symmetric operations are offloaded very efficiently as it has a built-in scatter/gather DMA. The coprocessors can be used to accelerate/offload IPsec, VPN, TLS/SSL, disk encryption, or any custom application requiring cryptography algorithms.