Hash and HMAC Accelerator IP
Welcome to the ultimate Hash and HMAC Accelerator IP hub! Explore our vast directory of Hash and HMAC Accelerator IP
All offers in
Hash and HMAC Accelerator IP
Filter
Compare
72
Hash and HMAC Accelerator IP
from
33
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
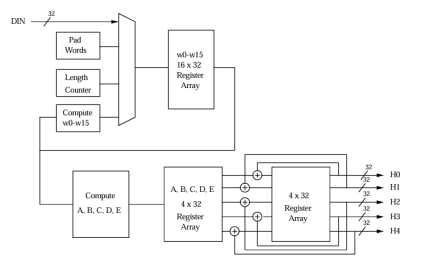
SHA-3 Crypto IP Core
- The SHA-3 – secure hash algorithms – crypto engine is a hardware accelerator for cryptographic hashing functions.
- It is an area efficient and high throughput design and compliant to NIST’s FIPS 202 standard.
- Additionally it supports all SHA-3 hash functions – SHA-3-224, SHA-3-256, SHA-3-384 and SHA-3-512 – as well as extendable output functions (XOF) – SHAKE-128 and SHAKE-256.
-
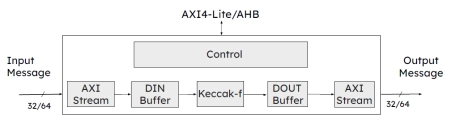
SHA-3 Crypto Engine
- The SHA-3 crypto engine has integrated flexibility and scalability to allow for high throughput and a configurable number of hashing rounds per clock cycle to optimize the silicon resource/performance ratio.
- Fixed-length or extendable-output (XOF) functions can simply be chosen per individual message through configuration settings.
-
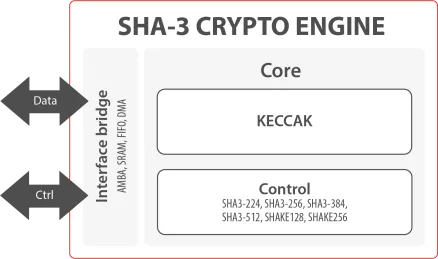
Hash Crypto Engine
- The Hash Crypto Engine is flexible and optimized hash IP core compliant with FIPS 180-3 (HASH functions), FIPS 198 (HMAC function) and OSCCA (SM3).
- With a flexible wrapper supporting a wide selection of programmable hashing modes (SHA-1, SHA-224, SHA-256, SHA-384, SHA-512, SM3 and MD5) with HMAC and several options of data interface, the Hash Crypto Engine is an easy-to-use solution with predictable resources and performances on ASIC and FPGA.
-
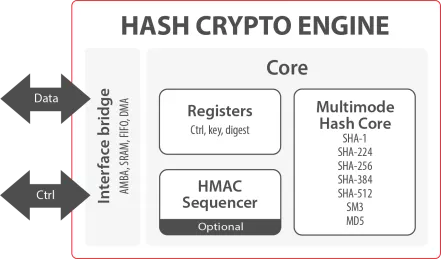
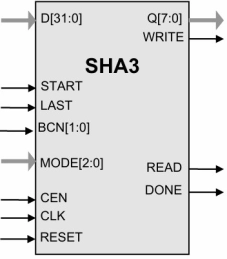
SHA3 Cryptographic Hash Cores
- Completely self-contained; does not require external memory
- SHA3-224, SHA3-256, SHA3-384, and SHA3-512 support SHA-3 algorithms per FIPS 202.
- SHAKE128 / SHAKE256 XOF support is included.
- Flow-through design; flexible data bus width
-
HMAC-SHA256 cryptographic accelerator
- Hardware Root of Trust
- Widely used password hash algorithm
- Security Critical HTTP, SSL, TLS
- Key storage in Private memory

-
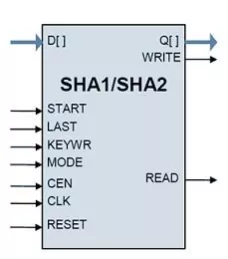
SHA1, SHA2 Cryptographic Hash Cores
- Completely self-contained; does not require external memory
- SHA1 supports SHA-1 per FIPS 180-1, SHA2-256 and SHA2-512 support SHA-2 per FIPS 180-2.
- HMAC option is available with flow-through and microprocessor-friendly (-SK) interfaces for the key input.
- Flow-through design; flexible data bus width
-
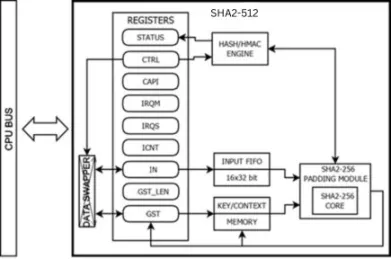
Secure Hash Algorithm 512 IP Core
- FIPS PUB 180-4 compliant SHA2-512 function
- RFC 2104 compliant HMAC mode native support
- SHA2 224, 256, 384, 512-bit modes support
- Secure storage for precomputed HMAC keys
-
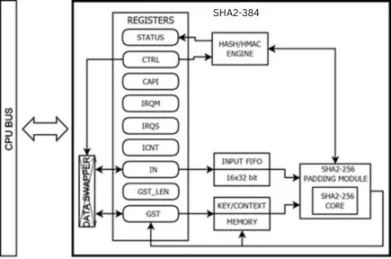
Secure Hash Algorithm 384 IP Core
- FIPS PUB 180-4 compliant SHA2-384 function
- RFC 2104 compliant HMAC mode native support
- SHA2 224, 256, 384-bit modes support
- Secure storage for precomputed HMAC keys
-
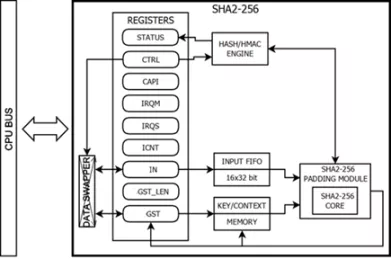
Secure Hash Algorithm 256 IP Core
- FIPS PUB 180-4 compliant SHA2-256 function
- RFC 2104 compliant HMAC mode native support
- SHA2 224 and 256 bit modes support
- Secure storage for precomputed HMAC keys
-
SHA-1 Processor
- Suitable for data authentication applications.
- Fully synchronous design.
- Available as fully functional and synthesizable VHDL or Verilog soft-core.
- Xilinx and Altera netlist available for various devices.