demodulator IP
Filter
Compare
61
IP
from
18
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
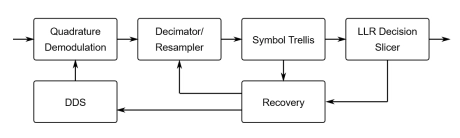
SOQPSK-TG Demodulator IP Core
- Shaped Offset Quadrature Phase Shift Keying - Telemetry Group (SOQPSK-TG) is a type of QPSK/OQPSK modulation. SOQPSK-TG provides constant-envelope modulation with continuous phase.
- This minimizes spectral occupancy and improves resistance to interference and nonlinear amplification.
-
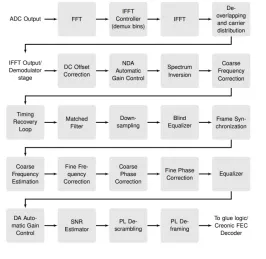
DVB-S2X Multi-Carrier Demodulator
- Supports CCM, ACM and VCM
- Supports roll-off factors 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% to 35%
- Support for short and normal blocks (16,200 bits and 64,800 bits) with pilots only
- Support for QPSK to 256-APSK
-
DVB-C Demodulator
- The demodulator is designed to be used together with a cable tuner and an analog to digital converter (ADC).
- The system has an internal state machine to control the operation, which can be externally configured via the SPI interface.
- This DVB-C QAM demodulator is supplied as a portable and synthesizable Verilog-2001 IP.
-
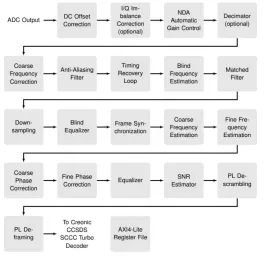
CCSDS 131.2 Wideband Demodulator
- Compliant with CCSDS 131.2-B-1
- Supports ACM mode
- Supports roll-off factors 5%, 10%, 15%, 20%, 25% and 35%
- Support for blocks with pilots only
-
DVB-T2 Demodulator and LDPC/ BCH Decoder
- DVB-T2 EN302 755 V1.2.1, Rev.9 compliant
- Supports IF input
- Single input – Single output (SISO)
- Sampling frequency offset (SFO) tracking and compensation
- Carrier frequency offset (CFO) detection and correction
-
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation: Modulator and Demodulator
- 1. Quadrature amplitude modulation Aside from increased channel capacity, QAM has various other advantages, which are stated below.
- 2. One of the most significant advantages of QAM is its ability to sustain a high data rate. As a result, the carrier signal can carry a certain amount of bits. Because of these benefits, it is preferred in wireless communication networks.
- 3. The noise immunity of QAM is quite strong. Noise interference is a bit low as a result of this.
- 4. It has a low mistake probability value.
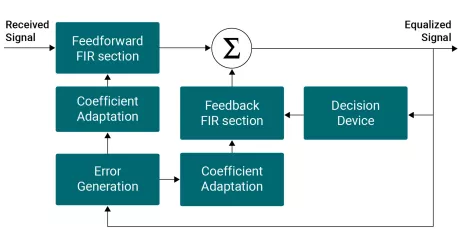
-
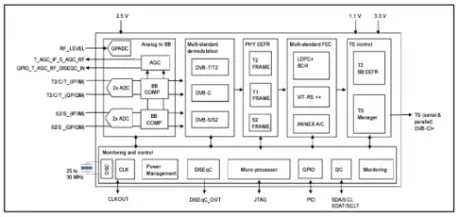
DVB-S2/S/T2/T/C Combo Demodulator IP (Silicon Proven)
- Combines a configurable DVB-T2/T/C/S/S2 demodulator.
- AGC derived from IF
- Low-power process, design and architecture
- Includes full suite of low-level drivers and application software, detailed user manuals and reference design schematics
-
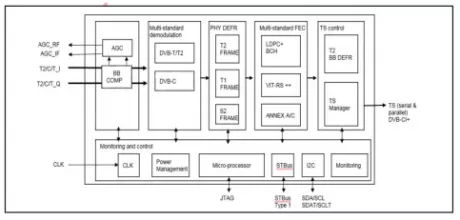
DVB-C Demodulator IP (Silicon Proven)
- QAM and FEC solution
- ITU-T J.83 Annexes A/B/C, DVB-C specification (ETSI 300 429)
- Nordig Unified v2.4 and SARFT compliant
- Up to 7.2 Ms/s symbol rate
-
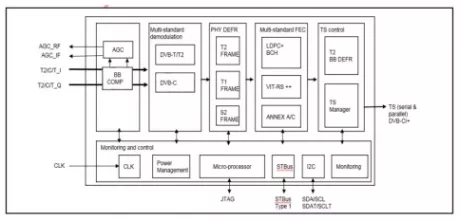
DVB-T2/T Demodulator and Decoder IP (Silicon Proven)
- DVB-T2 with T2-base profile of ETSI EN- 302755 v1.3.1,DTG7 v3 and Nordig Unified v2.4 compliant, 1.7-5-6-7 and 8 MHz normal and extended BW signals supported, GS streams, FEF and MISO supported
- DVB-T demodulator: Compliant with ETSI EN-300744 v1.5.1, DTG7 v3 and Nordig Unified v2.4 compliant, 6-7 and 8 MHz BW supported
- DVB-T/T2 compatible with zero-high- and legacy-IF tuners (CAN or silicon)
- Embedded microcontroller (DVB-T2 task sequencing by firmware and monitoring)
-
DVB-S2X NarrowBand Demodulator & Decoder IP (Silicon Proven)
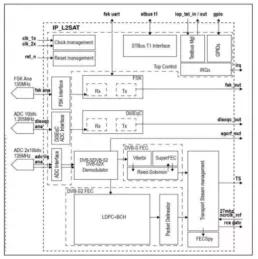
- This is single demodulator subsystem compliant DVB-S/S2/S2X satellite standards.
- It is meant to be integrated in the L2A/L2B SOCs. The single demodulator subsystem is made of several blocks.
- 1 narrow-band demodulator DVB-S / DVBS2 / DVB-S2X up to 65 Msymb/s.
- 1 DVB-S FEC (Viterbi, Reed-Solomon, Super FEC)