Embedded FPGA IP
Filter
Compare
254
IP
from
69
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
Embedded FPGA
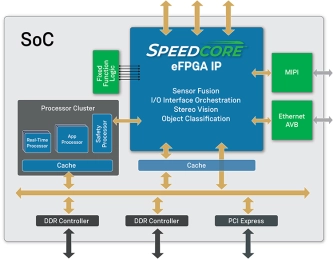
- Speedcore embedded FPGA (eFPGA) IP has brought the performance and flexibility of programmable logic to ASICs and SoCs.
- Customers can integrate a Speedcore eFPGA IP into an ASIC or SoC for high-performance, compute-intensive and real-time processing applications such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), 5G wireless, networking, storage and automotive.
-
Embedded FPGA
- Fully integrated into RTL SOC design flow
- Highly scalable and customizable
- Technology independent
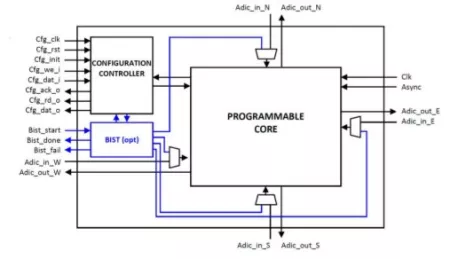
-
Tiny, Ultra-Low-Power Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The BA5x-TN is a compact, ultra-low power, 32-bit, deeply embedded processor IP core.
- With a two-stage execution pipeline, the processor implements the Embedded variant of the base RV32 ISA (RV32E).
- It uses just 16 general-purpose compressed instructions and omits other resource-demanding extensions.
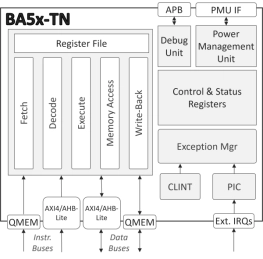
-
Low-Power Embedded RISC-V Processor
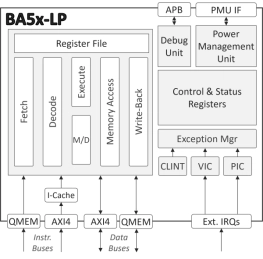
- The BA5x-LP is a highly efficient, low-power, 32-bit, deeply embedded processor IP core.
- The two-stage pipeline processor implements either the RV32I or RV32E instruction set.
- It comes pre-configured with the Multiply/Divide (M) and Compressed Instruction (C) extensions, providing a more flexible and capable platform without a significant increase in area or power.
-
Enhanced-Processing Embedded RISC-V Processor
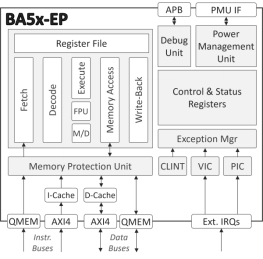
- The BA5x-EP is a highly-featured 32-bit RISC-V embedded processor IP core optimized for complex, processing-demanding applications.
- It is equipped with a floating-point unit and cache memories, supports hardware-level virtualization, and is suitable for concurrent execution in a multi-processor environment.
-
Vector-Capable Embedded RISC-V Processor
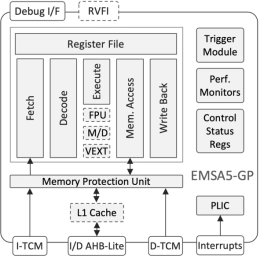
- The EMSA5-GP is a highly-featured 32-bit RISC-V embedded processor IP core optimized for processing-demanding applications.
- It is equipped with floating-point and vector-processing units, cache memories, and is suitable for concurrent execution in a multi-processor environment.
-
Compact Embedded RISC-V Processor
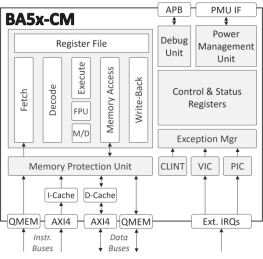
- The BA5x-CM is a feature-rich 32-bit deeply embedded processor.
- Equipped with a floating-point unit and an instruction cache memory and supporting concurrent execution in a multiprocessor environment, it is well-suited to a wide range of edge IoT and similar applications.
-
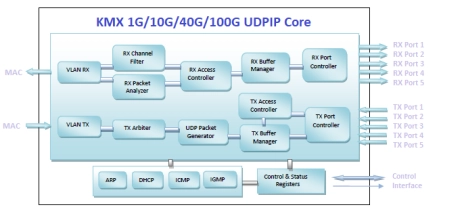
100G UDP/IP Hardware Protocol Stack Core
- The core Implements a UDP/IP hardware protocol stack that enables high-speed communication over a LAN or a point-to-point connection.
- It is ideal to offload systems from demanding tasks of UDP/IP and to enable media streaming in both FPGA and RISC designs.
- The core supports ARP request, reply and manages 32-entry ARP cache. ICMP ping reply is included.
-
DDR5/DDR4 and LPDDR5/LPDDR4 EMIF FPGA IP
- DDR4 and DDR5 offer higher bandwidth and improved performance over previous generations, with DDR5 providing further enhancements in speed and power efficiency
- LPDDR4 and LPDDR5 are optimized for low power consumption, making them ideal for embedded applications, with LPDDR5 offering even faster data rates and improved energy management
- When integrated with Altera FPGAs these memory technologies enable faster data processing and more efficient power usage for a wide range of applications including networking, cloud and edge.
-
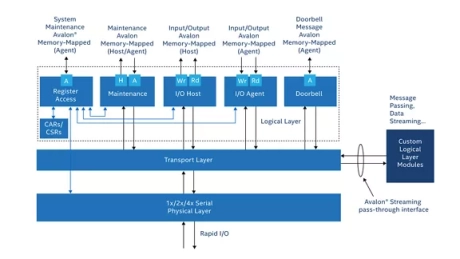
RapidIO Intel® FPGA IP
- Intel is discontinuing the intellectual property (IP) for RapidIO I and RapidIO II, more information can be found in the product discontinuance notification (PDN2025).