Combating the Memory Walls: Optimization Pathways for Long-Context Agentic LLM Inference
By Haoran Wu 1, Can Xiao 2, Jiayi Nie 1, Xuan Guo 1, Binglei Lou 2, Jeffrey T. H. Wong 2, Zhiwen Mo 2, Cheng Zhang 2, Przemyslaw Forys 2, Wayne Luk 2, Hongxiang Fan 2, Jianyi Cheng 3, Timothy M. Jones 1, Rika Antonova 1, Robert Mullins 1, Aaron Zhao 2
1 University of Cambridge
2 Imperial College London
3 University of Edinburgh
Abstract
 LLMs now form the backbone of AI agents for a diverse array of applications, including tool use, command-line agents, and web or computer use agents. These agentic LLM inference tasks are fundamentally different from chatbot-focused inference -- they often have much larger context lengths to capture complex, prolonged inputs, such as entire webpage DOMs or complicated tool call trajectories. This, in turn, generates significant off-chip memory traffic for the underlying hardware at the inference stage and causes the workload to be constrained by two memory walls, namely the bandwidth and capacity memory walls, preventing the on-chip compute units from achieving high utilization.
LLMs now form the backbone of AI agents for a diverse array of applications, including tool use, command-line agents, and web or computer use agents. These agentic LLM inference tasks are fundamentally different from chatbot-focused inference -- they often have much larger context lengths to capture complex, prolonged inputs, such as entire webpage DOMs or complicated tool call trajectories. This, in turn, generates significant off-chip memory traffic for the underlying hardware at the inference stage and causes the workload to be constrained by two memory walls, namely the bandwidth and capacity memory walls, preventing the on-chip compute units from achieving high utilization.
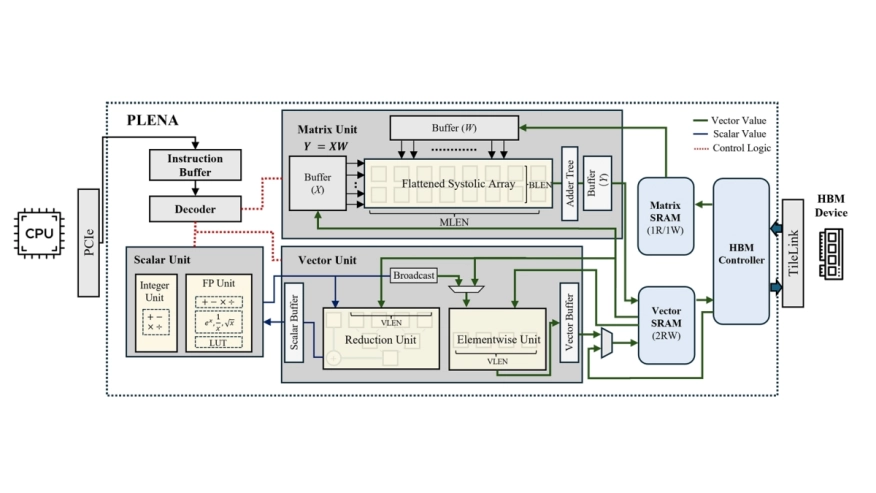
In this paper, we introduce PLENA, a hardware-software co-designed system that applies three core optimization pathways to tackle these challenges. PLENA includes an efficient hardware implementation of compute and memory units supporting an asymmetric quantization scheme. PLENA also features a novel flattened systolic array architecture that has native support for FlashAttention to tackle these memory walls in the scenario of inference serving for long-context LLMs. Additionally, PLENA is developed with a complete stack, including a custom ISA, a compiler, a cycle-emulated simulator, and an automated design space exploration flow. The simulated results show that PLENA achieves up to 8.5x higher utilization than existing accelerators, and delivers 2.24x higher throughput than the A100 GPU and 3.85x higher throughput than the TPU v6e, under the same multiplier count and memory settings. The full PLENA system will also be open-sourced.
To read the full article, click here
Related Semiconductor IP
- Multi-channel Ultra Ethernet TSS Transform Engine
- Configurable CPU tailored precisely to your needs
- Ultra high-performance low-power ADC
- HiFi iQ DSP
- CXL 4 Verification IP
Related Articles
- Pie: Pooling CPU Memory for LLM Inference
- SPAD: Specialized Prefill and Decode Hardware for Disaggregated LLM Inference
- AnaFlow: Agentic LLM-based Workflow for Reasoning-Driven Explainable and Sample-Efficient Analog Circuit Sizing
- The Growing Importance of AI Inference and the Implications for Memory Technology
Latest Articles
- GenAI for Systems: Recurring Challenges and Design Principles from Software to Silicon
- Creating a Frequency Plan for a System using a PLL
- RISCover: Automatic Discovery of User-exploitable Architectural Security Vulnerabilities in Closed-Source RISC-V CPUs
- MING: An Automated CNN-to-Edge MLIR HLS framework
- Fault Tolerant Design of IGZO-based Binary Search ADCs