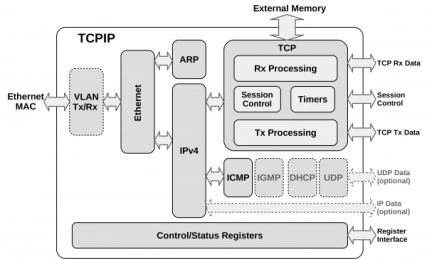
UDP TCP IP
Filter
Compare
35
IP
from
14
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
100G bps Full TCP & UDP Offload Engine
- Increase your TCP and UDP Network actual performance by up to 600%
- Built around Proven and Mature TCP and UDP technology since 2009.
- 40G: In production. Performed Live demo of 40G at Super Computing 2015
- Qualified on Altera/Intel and Xilinx. FPGA Subsystems Solutions available now
- First company to implement and deliver Full TCP Stack in High performance FPGA in 2009.
-
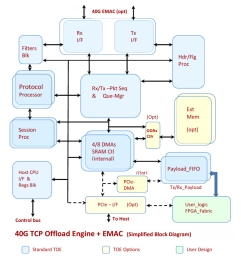
40G-1K Sess. TCP + UDP Offload Engine
- Highly customizable hardware IP block. Easily portable to ASIC flow, Xilinx/Altera FPGAs or Structured/ASIC flow.
- Eighth Generation TOE and System Solutions provide ‘Ultra-Low Latency’ and Ultra-High Performance with highest TCP bandwidth in Full Duplex. Network Tested and mature TCP protocol offload implementation
- All stages of Full TCP stack implemented in High performance hardware
-
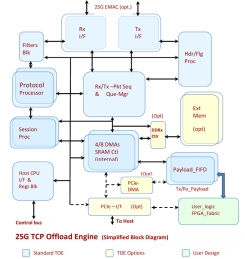
25G-1K Sess. TCP + UDP Offload Engine
- Highly customizable hardware IP block. Easily portable to ASIC flow, Xilinx/Altera
- FPGAs or Structured/ASIC flow.
- Eighth Generation TOE and System Solutions provide ‘Ultra-Low Latency’ and Ultra-High Performance with highest TCP bandwidth in Full Duplex. Network Tested and mature TCP protocol offload implementation
- All stages of Full TCP stack implemented in High performance hardware
-
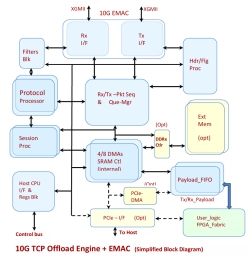
10G-16K Sess. TCP + UDP Offload engine (INT-20011-16K)
- Highly customizable hardware IP block. Easily portable to ASIC flow, Xilinx/Altera FPGAs or Structured/ASIC flow.
- Seventh Generation TOE and System Solutions provide ‘Ultra-Low Latency’ and Ultra-High Performance with highest TCP bandwidth in Full Duplex. Network Tested and mature TCP protocol offload implementation
- All stages of Full TCP stack implemented in High performance hardware
-
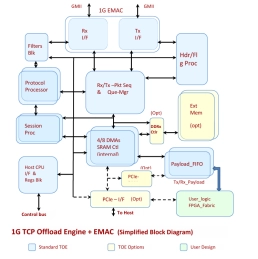
1G TCP Offload Engine TOE Very Low Latency (TOE)
- Ideal for high performance and mid performance specialized, differentiable ASICs or FPGAs for Network security or Network infrastructure applications
- Less than 4000 Xilinx slices, Altera ALMs or 150,000 ASIC gates + on-chip memory
- Fully integrated 100 M bit/1-G bit high performance EMAC.
- Scalable MAC Rx FIFOs and Tx FIFOs make it ideal for optimizing system performance.
-
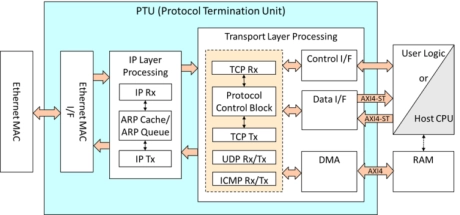
TCP/UDP Offload Engine
- Full hardware TCP/UDP protocol stack realize both high performance and guaranteed delivery
- The TCP/UDP offload engine supports simultaneous connection of more than 10,000 sessions on a single core, which is a feature of our IP along with its high quality and performance.
-
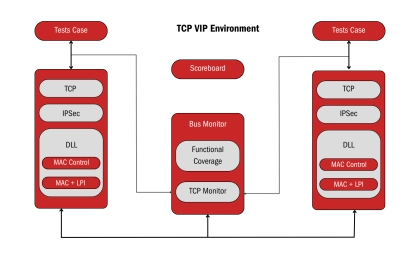
100G TCP/IP Offload Engine - Validates high-speed network traffic, optimizing flow and reliability
- The 100G TCP/IP Offload Engine is a cutting-edge Verification IP designed to streamline the testing of high-speed networking interfaces. It supports high-performance, real-world simulations of network traffic, flow control, and buffer management for seamless data integrity at 100G rates.
- With its extensive debugging and protocol compliance features, the Offload Engine aids in reducing validation time while ensuring system reliability. It integrates easily with modern verification frameworks, optimizing performance across diverse network topologies
-
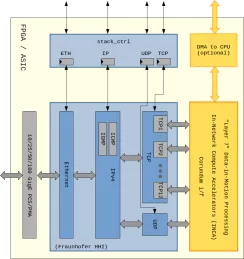
TCP/UDP/IP Network Protocol Accelerator Platform
- Highly modular TCP/UDP/IP stack implementation in synthesizable HDL
- Full line rate of 70 Gbps or more in FPGA, 100 Gbps or more in ASIC
- 128-bit wide bi-directional data paths with streaming interfaces
- Multiple, parallel TCP engines for scalable processing
-
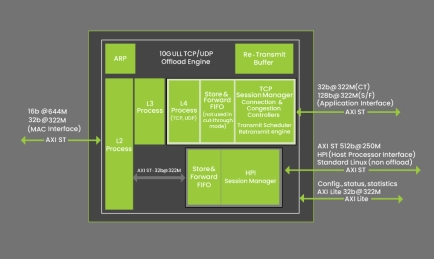
ULL TCP/IP, UDP/IP Offload Engine
- High-performance TCP and UDP IP offload engine cores offer a reliable, ultra-low-latency solution for financial and network applications.
- They address the data center industry’s growing need for throughput and hardware acceleration and provide network protocol offload for applications such as financial data processing, reprogrammable Smart NICs, and high-performance computing.
-
1G/10G TCP/IP Hardware Stack
- The TCPIP-1G/10G core implements a complete TCP/IP Hardware Protocol Stack.
- More capable than many offloading engines, it allows systems to connect to an Internet Protocol (IP) network and exchange data using the TCP protocol without requiring assistance from — or even the presence of — a system processor.