FFT IP
Filter
Compare
55
IP
from
23
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
FFT Algorithm Accelerator
- Support transform point sizes n = 2^m, m = 4 ~ 12
- Support 16-bit and 32-bit fixed-point data formats
- Support bus max transmission width 64bit
- Support Radix-2 Decimation-In-Time (DIT) and Decimation-In-Frequency (DIF) FFT, IFFT algorithms
-
FFT Intel® FPGA IP Core
- The Fast Fourier transform (FFT) Intel FPGA intellectual property (IP) core is a high-performance, highly parameterizable FFT processor
- The FFT function implements a radix-2/4 decimation-in-frequency (DIF) FFT algorithm for transform lengths of 2m where 6 ≤ m ≤ 14, internally using a block-floating-point architecture to maximize signal dynamic range in the transform calculation.
-
High performance FFT with Gsps throughput
- Throughput of greater than 8Gsps with 1GHz core clock frequency
- Architecture can be scaled to support higher throughput per clock cycle
- Configurable to supports large transform sizes i.e >8k
-
High performance FFT optimised for Radar
- 1 clock cycle per point, no gap required between packets
- Run-time selection of any power of 2 FFT points
- Run-time selection of froward or inverse transform
-
Fast Fourier Transformation
- The FFT is a fully customizable FFT. The key features are free choose of the FFT dimension, data width and an additional output with the absolute value of the spectrum.
-
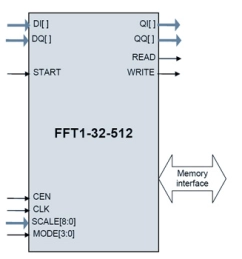
32-512 Point Streaming FFT Core
- Supports 32/64/128/256/512-point complex FFT and IFFT and can switch dynamically
- Inputs and outputs data in the natural order
- Throughput of 1 sample (In-phase I + quadrature Q) per 4 clocks; no-gap processing of the input data
- Parameterized bit width.
-
Floating-point (IEEE 754) IP based on Arria 10 and Stratix 10 FPGAs
- FFT size: Any size power-of-two or non-power-of-two
- Dynamic Range: IEEE754 single precision floating point
-
FFT - Streaming Mixed-Radix Architecture
- Complex FFT/IFFT operation, run-time configurable on a per-frame basis
- Configurable transform sizes:
-
Single precision fixed-size streaming floating-point FFT
- FFT size: Any size power-of-two or non-power-of-two
- Dynamic Range: IEEE754 single precision floating point
-
Non-Power-of-Two FFT
- Sample Rates: Very high clock speeds
- FFT size: any size set of transforms (chosen at run-time) factorable into bases up to ~10