USB OTG controller IP
Filter
Compare
195
IP
from
17
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
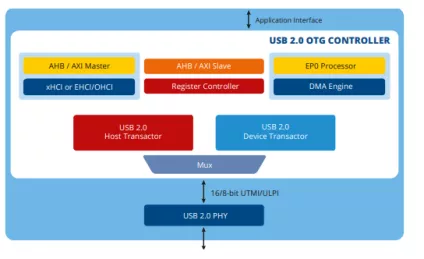
USB 2.0 OTG High / Full / Low- Speed Dual Role IP Core
- Support SW controlled host/device role switching.
- Support Fullspeed and Lowspeed
- Support Control, Bulk, Interrupt and Isochronous Transfer Types
- Support L1/L2 power saving modes for USB 2.0 port
-
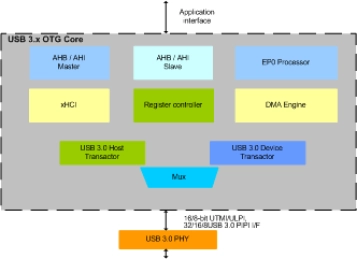
USB 3.0 OTG High / Full / Low- Speed Dual Role IP Core
- Support SW controlled host/device role switching.
- Support Superspeed, Highspeed and Fullspeed
- Support Control, Bulk, Interrupt and Isochronous Transfer Types
- Support U1/U2/U3 power saving modes for USB 3.x port
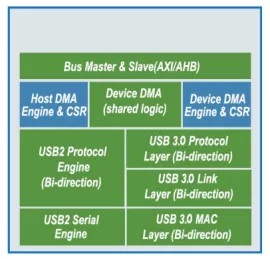
-
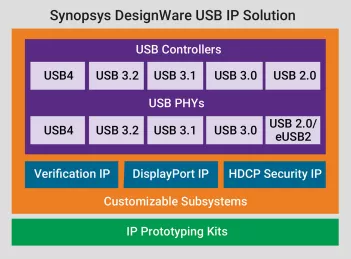
USB 2.0 Hi-Speed OTG Controller version 4 with Active Clock Gating to save active power
- Configuration options to maximize performance and minimize CPU interrupts
- Flexible parameters enable easy integration into low and high-latency systems
- Transfer- or transaction-based processing of USB data based on system requirements
- Configurable data buffering options to fine-tune performance/ area trade-offs
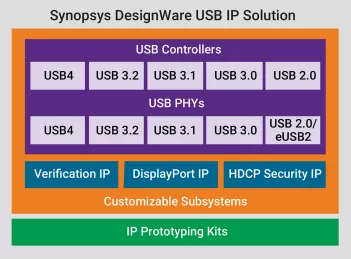
-
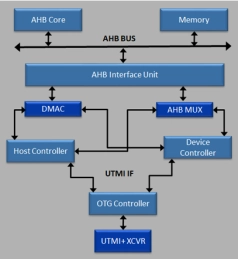
USB 2.0 Hi-Speed OTG Controller Subsystem w/AHB Interface Supporting HSIC (config. as Device only or Full Speed only)
- Configuration options to maximize performance and minimize CPU interrupts
- Flexible parameters enable easy integration into low and high-latency systems
- Transfer- or transaction-based processing of USB data based on system requirements
- Configurable data buffering options to fine-tune performance/ area trade-offs
-
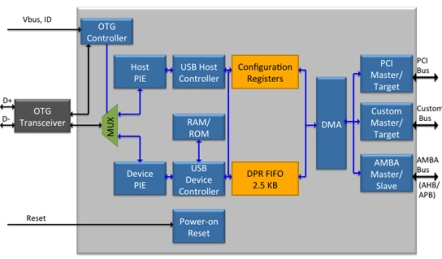
USB 2.0 OTG Dual Role Device (DRD) Controller
- Compliant with OTG Supplement Rev. 1.0a
- USB 2.0 Compliant
- Supports 480 Mbit/s (HS), 12 Mbit/s (FS), and 1.5 Mbit/s (LS)
- Supports Session Request Protocol (SRP) and Host Negotiation Protocol (HNP)
-
USB 2.0 OTG IP Core
- High speed support: 480 Mbit/s
- Full speed support: 12 Mbit/s
- USB 2.0 Compliant
- High/Full speed support using 8/16 bit UTMI/ULPI interface
-
USB3.x OTG IIP
- USB 3.0/3.1/3.2 Common support
- Compliant with USB 3.0/3.1/3.2 specification
- Supports Superspeed USB 3.0, SuperSpeedPlus 3.1, 3.2
- Configurable number of Configurations, Interfaces, Alternative Interfaces and Endpoints