QAM Modulator IP
Filter
Compare
15
IP
from
6
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
ISDB-T Modulator
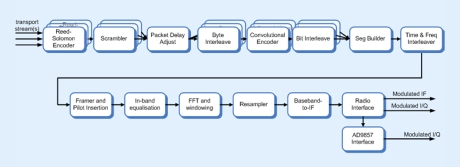
- The CMS0045 ISDB-T Modulator provides all the necessary processing steps to modulate one, two or three transport stream into a complex I/Q signal for input to a pair of DACs, or an interpolating DAC device such as the AD9857/9957 or AD9789. Optionally the output can be selected as an IF to supply a single DAC.
- The design has been optimised to provide excellent performance in low cost FPGA devices such as the Cyclone range from Altera or the Spartan range from Xilinx
-
Quadrature Amplitude Modulation: Modulator and Demodulator
- 1. Quadrature amplitude modulation Aside from increased channel capacity, QAM has various other advantages, which are stated below.
- 2. One of the most significant advantages of QAM is its ability to sustain a high data rate. As a result, the carrier signal can carry a certain amount of bits. Because of these benefits, it is preferred in wireless communication networks.
- 3. The noise immunity of QAM is quite strong. Noise interference is a bit low as a result of this.
- 4. It has a low mistake probability value.
-
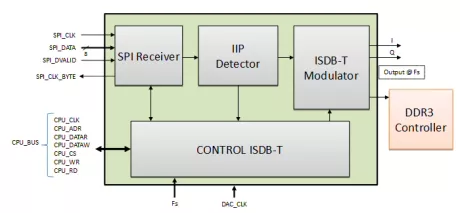
ISDB-T Modulator
- ARIB STD-B31 compliant operation, supporting one, two or three-layers
- Drop-in module for Spartan-6™, Virtex-6™, Artix-7™, Kintex-7™, Virtex-7™ FPGAs and Zynq™
-
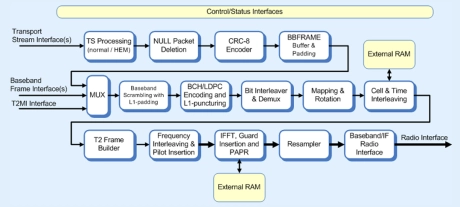
DVB-T2 modulator
- 1k, 2k, 4k, 8k, 16k and 32k OFDM.
- BPSK, QPSK, QAM-16, QAM-64 and QAM-256 support.
- Variable 1·7-10MHz bandwidth interpolation.
- Automatic L1 field padding and puncturing.
-
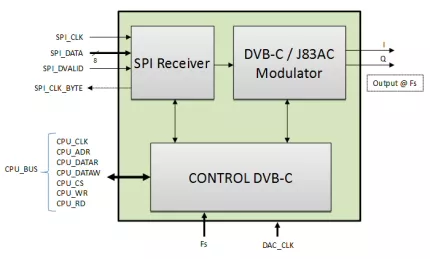
DVB-C Modulator J.83 Annex A/C Core
- ITU-T J.83 Annex A/C, DVB-C (ETS 300 429) Compliant baseband transmitter for Cable Modem Termination Systems (CMTS)
- Drop-in module for Spartan-6™, Virtex-6™, Artix-7™, Kintex-7™, Virtex-7™ FPGAs and Zynq™
- Single clock (up to 160 MHz)
- Robust SPI input (discarding incorrect input packets)
-
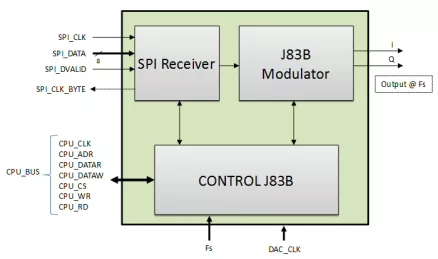
Cable Modulator J.83 Annex B
- ITU-T J.83 Annex B Compliant baseband transmitter for Cable Modem Termination Systems (CMTS)
- Drop-in module for Spartan-6™, Virtex-6™, Artix-7™, intex-7™, Virtex-7™ FPGAs and Zynq™
- Single clock (up to 160 MHz)
- Robust SPI input (discarding incorrect input packets)
-
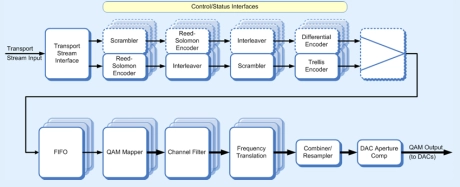
Multi-channel Cable Modulator
- The CMS0024 Multi-channel Cable Modulator encodes up to four separate transport streams for J83 or DVB-C.
- The resulting QAM symbols are filtered and up-converted, each channel to its own frequency division multiplex (FDM) sub channel.
- The IF channels are then combined output to the radio interface as a single I/Q sample stream for translation to the final RF frequency.
-
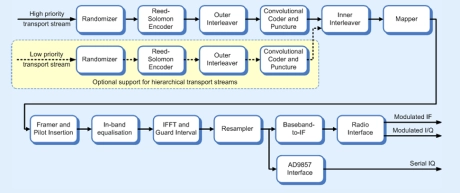
DVB-T/DVB-H modulator
- Fully compliant with ETSI EN 300 744 V1.5.1.
- Extension core available for DVB-T(H) support.
- Enables rapid development of audio/visual systems using commodity Free-to-Air set-top-box technology and low-cost FPGAs.
- Configurable support for 2K and 8K OFDM modes and hierarchical transmission. (4k for DVB-T(H))
-
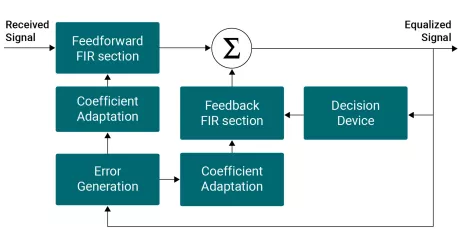
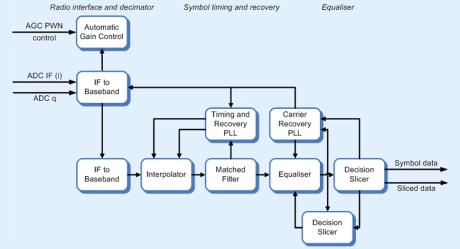
Multi-mode QAM Demodulator
- IF sub-sampling or I/Q baseband interface.
- Variable ADC width support.
- Single external clock source required.
- Single external analogue loop for AGC.
-
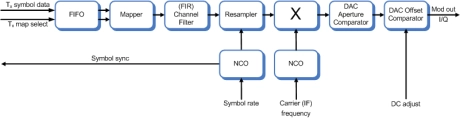
Universal QAM/PSK Modulator
- The CMS0004 Universal QAM/PSK Modulator is a flexible, high-performance, linear modulator core designed for a wide range of broadband applications including point-to-point and point-to-multipoint terrestrial, satellite and wireline transceiver systems.
- It supports both continuous and burst-mode operation and its synchronous control interface readily accommodates physical-layer protocols that employ variable-rate frame structures.