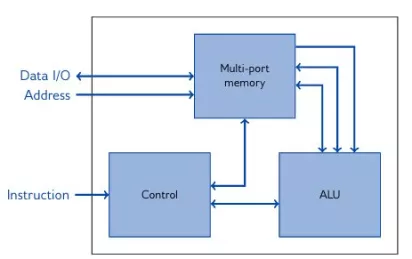
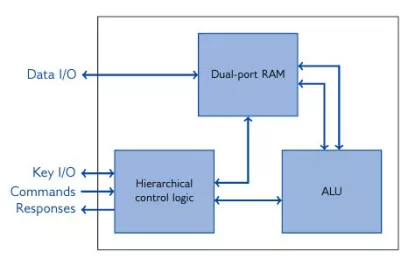
Signature IP IP
Filter
Compare
90
IP
from
24
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
ECDSA (Elliptic Curve Digital Signature) IP Core
- Full ECDSA implementation adhering to Standards for Efficient Cryptography (SEC)
- Bitcoin algorithm support
- Technology-independent HDL model
- Simple external interface for easy adaptation
-
Post-Quantum Key Encapsulation and Digital Signature IP Core
- The KiviPQC-Box is an IP core that combines the algorithms ML-DSA and ML-KEM into one single package.
- ML-DSA and ML-KEM are algorithms that are standardized by NIST as post-quantum algorithms defined in NIST FIPS 204 and NIST FIPS 203 and provide cyber secure protection against the threat of quantum computers.
-
Post-Quantum Digital Signature IP Core
- The KiviPQC-DSA is an IP core implementing the ML-DSA (Module-Lattice-based Digital Signature Algorithm) a post-quantum cryptographic standard defined by NIST FIPS 204.
- Designed to withstand both classical and quantum computer attacks, ML-DSA ensures the authenticity and integrity of signed data far into the future.
-
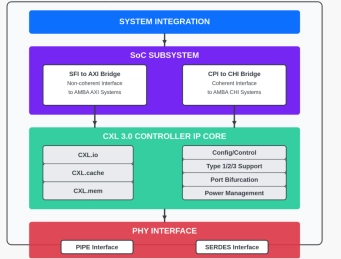
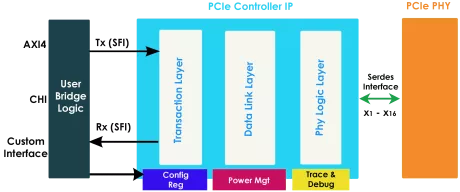
CXL 3.0 Controller
- The CXL Controller IP is micro-architected with power, performance, and area optimization for high bandwidth, minimum latency, and low power applications.
- The CXL IP supports seamless transition from FPGA prototyping to production silicon implementation.
- Featuring native integration with SignatureIP's Coherent and Non-coherent Network-on-Chip (NoC) IPs, this controller enables robust SoC subsystems and complete platform solutions
-
-
Curve25519 Key Exchange and Digital Signature IP Core
- Minimal Resource Requirements: The entire XIP4003C requires less than 800 ALMs (Cyclone® 5) and uses only 1-2 multipliers/DSP Blocks2 and 1-2 internal memory block in a typical FPGA implementation.
- Constant Latency: The execution time of XIP4003C is independent of the key value, and consequently provides protection against timing-based side-channel attacks.
- Performance: Despite its small size, XIP4003C can support more than 100 key exchange or digital signature operations per second.
- Standard Compliance: XIP4003C is compliant with RFC7748, RFC8032, and the draft version of FIPS 186-5. XIP4003C can be used as a part of many public-key protocols including IKEv2 (RFC 8031) and TLS 1.3 (RFC 8446).
-
Cloud-active NOC configuration tool for generating and simulating Coherent and Non-Coherent NoCs
- Drag & Drop Graphical User Interface
- Unified configuration tree view
- Intelligent routing path calculation
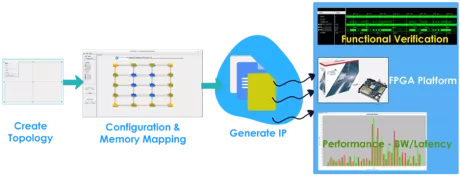
-
Coherent Network-on-chip (NoC) IP
- Layered, scalable, configurable, and physically aware configurable NoC
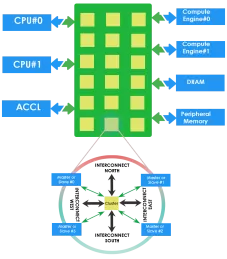
-
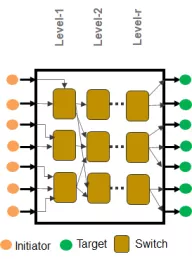
-
RSA Signature Verification IP Core
- Minimal Resource Requirements: The entire XIP5012C requires less than 280 LUTs (lookup tables) and 2 internal memory blocks (Xilinx® Zynq®-7000).
- Performance: Despite its small size, XIP5012C can support more than 10 digital signature verification operations per second.
- Standard Compliance: XIP5012C is compliant with FIPS 186-4.