Managed Ethernet Switch IP
Filter
Compare
13
IP
from
4
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
100M/1G/2.5G/5G/10G Managed Ethernet Switch
- Full-duplex 100M/1G/2.5G/5G/10G Ethernet Interfaces
- Configurable from 3 up-to 32 Ethernet ports
-
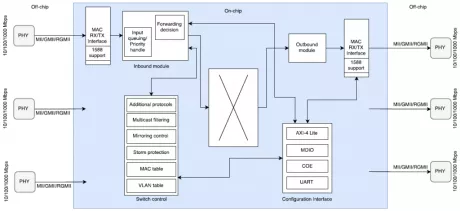
Managed Ethernet Switch
- Full-Duplex Ethernet 10/100/1000.
- Half-Duplex Ethernet 10/100.
- Configurable 3 to 16 Ethernet ports.
- MII/GMII/RGMII interfaces for attaching to an external Physical Layer device (PHY).
-
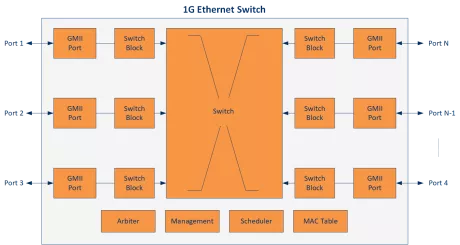
1G Ethernet Switch IP Core
- Up to 16 ports configurable at compile time
- Configurable queuing behavior (round-robin, fair queuing)
- Supports Ethernet Multicast
- Ultra compact size
-
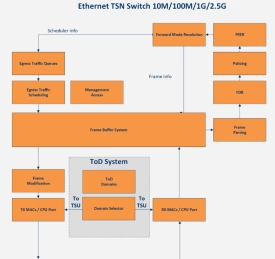
10M/100M/1G/2.5G Compact Ethernet TSN Switch
- The 10M/100M/1G/2.5G compact Ethernet TSN Switch IP core is an advanced managed switch targeting automotive, avionics, and industrial applications.
- It is providing cut-through and supporting the TSN family of standards. It is compliant to several TSN profiles as defined by IEEE while offering the ultimately lowest gate count on the market.
-
Managed Redundant Switch
- Full-Duplex Ethernet 10/100/1000.
- Half-Duplex Ethernet 10/100.
- Configurable 3 to 16 Ethernet ports.
- MII/GMII/RGMII interfaces for attaching to an external Physical Layer device (PHY).
-
25G Ultra Low latency, 64-bit Ethernet MAC + PCS Solution (64-bit and 128-bit UI)
- MAC Core Features
- PCS Core Features
-
100G Only 320-bit Ethernet MAC + PCS @ 312.5MHz Solution; 4x25
- MAC Core Features
- PCS Core Features (Common)
- PCS Core Features (CAUI-4 Option)
- PCS Core Features (CAUI-10 Option)
-
100G Only 320-bit Ethernet MAC + PCS @ 312.5MHz Solution; 10x10
- MAC Core Features
- PCS Core Features (Common)
- PCS Core Features (CAUI-4 Option)
- PCS Core Features (CAUI-10 Option)
-
Tri-Mode Ethernet Media Access Controller (TEMAC)
- Designed to IEEE 802.3-2012 specification
- Supports 10/100/1000/2500 Mbps Ethernet
- Configurable half-duplex and full-duplex operation
- Configured and monitored through an optional independent microprocessor-neutral interface