I2C IP
Filter
Compare
436
IP
from
69
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
Intel 18A 1.2V/1.5V I2C
- Synopsys Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) IO library is used for two wire interfaces to connect low-speed devices like EEPROM, A/D, and D/A converters and microcontrollers on the same bus
- It is designed for higher IO voltage supply with support for low core voltage and includes fail-safe and fail-tolerance options
- The following operating modes are supported: * Standard Mode: 100 kHz * Fast Mode: 400 kHz * Fast-Plus Mode: 1 MHz * High-Speed Mode: 3.4 MHz
-
Intel 16 1.8V I2C with 3.3V Fail-safe & Fail-tolerant
- Synopsys Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) IO library is used for two wire interfaces to connect low-speed devices like EEPROM, A/D, and D/A converters and microcontrollers on the same bus
- It is designed for higher IO voltage supply with support for low core voltage and includes fail-safe and fail-tolerance options
- The following operating modes are supported: * Standard Mode: 100 kHz * Fast Mode: 400 kHz * Fast-Plus Mode: 1 MHz * High-Speed Mode: 3.4 MHz
-
GF 22FDX 1.8V/3.3V I2C with 5V Fail-Safe and Fail-Tolerant Library
- Synopsys Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) IO library is used for two wire interfaces to connect low-speed devices like EEPROM, A/D, and D/A converters and microcontrollers on the same bus
- It is designed for higher IO voltage supply with support for low core voltage and includes fail-safe and fail-tolerance options
- The following operating modes are supported: * Standard Mode: 100 kHz * Fast Mode: 400 kHz * Fast-Plus Mode: 1 MHz * High-Speed Mode: 3.4 MHz
-
GF 22FDX 1.8V/3.3V I2C with 5V Fail-Safe and Fail-Tolerant Library
- Synopsys Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) IO library is used for two wire interfaces to connect low-speed devices like EEPROM, A/D, and D/A converters and microcontrollers on the same bus
- It is designed for higher IO voltage supply with support for low core voltage and includes fail-safe and fail-tolerance options
- The following operating modes are supported: * Standard Mode: 100 kHz * Fast Mode: 400 kHz * Fast-Plus Mode: 1 MHz * High-Speed Mode: 3.4 MHz
-
GF 22FDX 1.8V/3.3V I2C with 5V Fail-safe & Fail-tolerant Auto Grade 1 Library
- Synopsys Inter-Integrated Circuit (I2C) IO library is used for two wire interfaces to connect low-speed devices like EEPROM, A/D, and D/A converters and microcontrollers on the same bus
- It is designed for higher IO voltage supply with support for low core voltage and includes fail-safe and fail-tolerance options
- The following operating modes are supported: * Standard Mode: 100 kHz * Fast Mode: 400 kHz * Fast-Plus Mode: 1 MHz * High-Speed Mode: 3.4 MHz
-
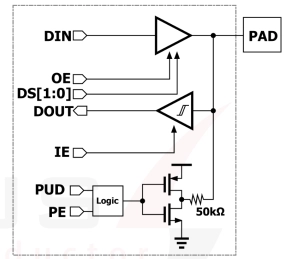
1.8V/3.3V GPIO With I2C Compliant ODIO in GF 55nm
- This I/O Library, developed on GlobalFoundries 55nm CMOS, delivers a complete suite of digital and analog I/O solutions with robust 2 kV HBM / 500 V CDM ESD protection and latch-up immunity.
- The library includes 1.8/3.3 V GPIOs supporting GMII and LVCMOS standards, I2C-compliant ODIOs, and flexible analog I/Os (ANA/DANA) with integrated ESD.
-
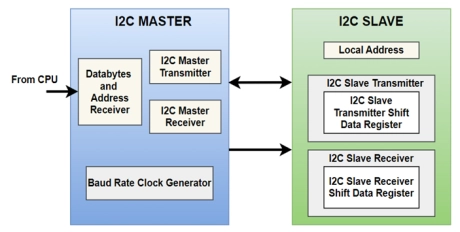
I2C protocol Controller
- I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) bus Interface serves as an interface between the microcontroller and the serial I2C bus.
- It provides multimaster capability, and controls all I2C bus-specific sequencing, protocol, arbitration and timing.
- It supports the standard mode (Sm, up to 100 kHz), Fast mode (Fm, up to 400 kHz), Fast mode plus mode (Fm+, up to 1MHz) and High-speed mode (Hs-mode, up to 3.4MHz).
-
I2C - Function Controller
- The I2C (Inter - Integrated Circuit) protocol is a widely used serial communication protocol for transferring data between electronic devices. It was developed by Philips in the 1980s and is now owned by NXP Semiconductors. I2C uses two bidirectional data lines called SDA (Serial Data) and SCL (Serial Clock) for communication between devices.
- It allows multiple devices to be connected to the same bus, and each device can be identified by a unique address. The protocol supports data transfer rates ranging from a few kilobits per second to several hundred kilobits per second.
-
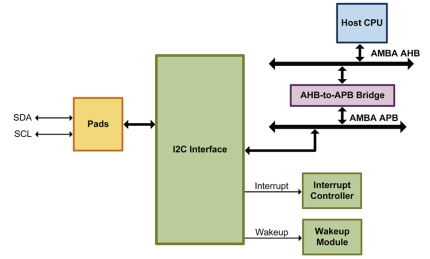
APB I2C Master/Slave Controller
- The I2C Interface provides full support for the two-wire I2C synchronous serial interface, compatible with the ACCESS.
- Bus physical layer, with additional support for the SMBus protocol, including Packet Error Checking (PEC).
- Through its I2C compatibility, it provides a simple interface to a wide range of low-cost memories and I/O devices, including: EEPROMs, SRAMs, timers, A/D converters, D/A converters, clock chips, and peripheral drivers.
-
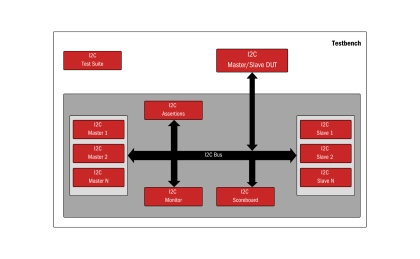
I2C - Verifies I2C communication, ensuring protocol compliance and error-free data transfer
- I2C (Inter-Integrated Circuit) is a low-speed communication protocol designed for embedded systems. As a Verification IP (VIP), it simulates and validates I2C interfaces, ensuring accurate data transmission, addressing, and error handling.
- This VIP supports various device roles, data rates, and stress-testing scenarios, such as clock stretching and multi-master configurations, ensuring reliable communication in applications like sensor interfacing and memory device validation