ML-KEM
ML-KEM IP cores (Modular Lattice-based Key Encapsulation Mechanism IP cores) deliver post-quantum secure key exchange and encryption acceleration for next-generation embedded systems, ASICs, and FPGAs. Based on the NIST-approved ML-KEM standard—formerly known as Kyber—these IP cores provide robust protection against quantum attacks, ensuring long-term confidentiality for data transmission and device communications.
Explore our vast directory of ML-KEM IP cores below.
All offers in
ML-KEM
Filter
Compare
28
ML-KEM
from
13
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
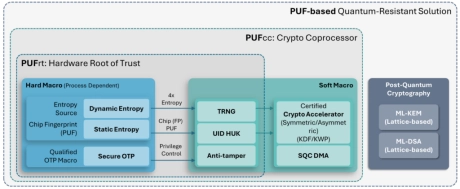
PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Solution
- PUFsecurity is proud to pioneer the world’s first PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) solution, delivering cutting-edge, hardware-level security that sets a new standard.
- Our innovative solution integrates PUF technology with quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, ensuring robust key protection and seamless transition to a quantum-secure future.
-
xQlave® ML-KEM (Kyber) Key Encapsulation Mechanism IP core
- Quantum-resistant key exchange for future-proof security
- Compliant with NIST's ML-KEM standard
- Pure RTL without hidden CPU or software components
- Optimised architecture with constant-time execution
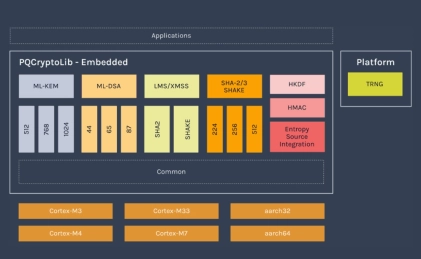
-
Highly-optimized PQC implementations, capable of running PQC in under 15kb RAM
- PQCryptoLib-Emebedded is a versatile, CAVP-ready cryptography library designed and optimized for embedded devices.
- With its design focused on ultra-small memory footprint, PQCryptoLib-Embedded solutions have been specically designed for embedded systems, microcontrollers and memory-constrained devices. It provides a PQC integration to devices already in the field.
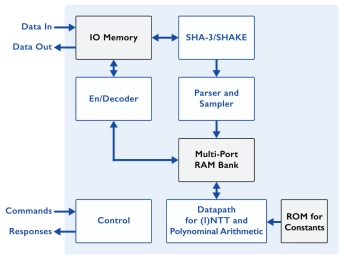
-
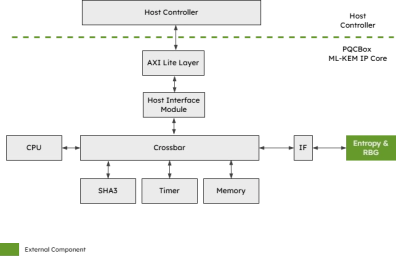
Post-Quantum Key Encapsulation IP Core
- The PQC-KEM is an IP Core for ML-KEM Key Encapsulation that supports key generation, encapsulation, and decapsulation operations for all ML-KEM variants standardized by NIST in FIPS 203.
- ML-KEM is a post-quantum cryptographic (PQC) algorithm, designed to be robust against a quantum computer attack.
-
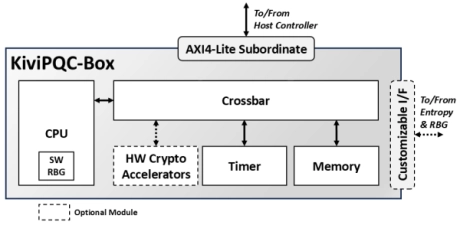
ML-KEM Key Encapsulation & ML-DSA Digital Signature Engine
- The KiviPQC™-Box is a hardware accelerator for post-quantum cryptographic operations.
- It implements both the Module Lattice-based Key Encapsulation Mechanism (ML-KEM) and the Module Lattice-based Digital Signature Algorithm (ML-DSA), standardized by NIST in FIPS 203 and FIPS 204, respectively.
-
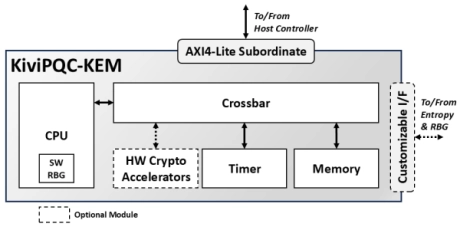
ML-KEM Key Encapsulation IP Core
- The KiviPQC™-KEM is a hardware accelerator for post-quantum cryptographic operations.
- It implements the Module Lattice-based Key Encapsulation Mechanism (ML-KEM), standardized by NIST in FIPS 203.
- This mechanism realizes the appropriate procedures for securely exchanging a shared secret key between two parties that communicate over a public channel using a defined set of rules and parameters.
-
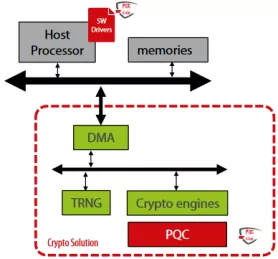
Crypto Coprocessor with integrated Post-Quantum Cryptography IPs
- The Crypto Coprocessors are a hardware IP core platform that accelerates cryptographic operations in System-on-Chip (SoC) environment on FPGA or ASIC.
- Symmetric operations are offloaded very efficiently as it has a built-in scatter/gather DMA. The coprocessors can be used to accelerate/offload IPsec, VPN, TLS/SSL, disk encryption, or any custom application requiring cryptography algorithms.
-
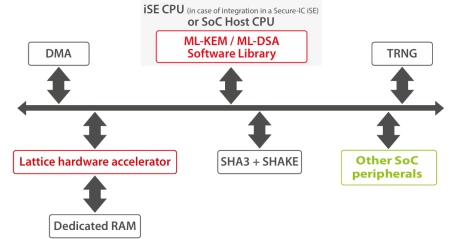
ML-KEM / ML-DSA Post-Quantum Cryptography IP
- ML-KEM (Crystals-Kyber) and ML-DSA (Crystals-Dilithium) are Post-Quantum Cryptographic (PQC) algorithms, meaning they are mathematically designed to be robust against a cryptanalytic attack using a quantum computer.
- Both have been standardized by the NIST in it post-quantum cryptography project.
-
Single instance HW Lattice PQC ultra accelerator
- PQPerform-Flare is a powerful hardware-based FIPS 140-3 CAVP-certified product, designed for high throughput and low latency PQC.
- It adds PQC for applications that typically handle a large number of transactions, such as high-capacity network hardware applications and secure key management HSMs.
-
Highly configurable HW Lattice PQC ultra acceleration in AXI4 & PCIe systems
- PQPerform-Inferno is a powerful, scalable hardware solution engineered for unparalleled performance in the post-quantum era.
- As a FIPS 140-3 CAVP-certified product, it provides a trusted foundation for next-generation security.