Memory Compiler IP
Filter
Compare
556
IP
from
44
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
Single Port High-Speed Multi Bank SRAM Memory Compiler on GF 22FDX+
- Ultra-Low Leakage - GLOBALFOUNDRIES low-leakage 6T L110 bit cells with High Vt and low leakage periphery to ensure minimal leakage and high yield.
- Multi-Bank Architecture - Memory split into 1 to 4 banks for reduced bit line length and enhanced timing.
- Ultra Low Power Standby - Built-in source biasing trims standby current to a minimum for data retention.
-
Single Port Low Leakage SRAM Memory Compiler on GF 22FDX+
- Ultra-Low Leakage: High VT (HVT) and low leakage (LLHVT) devices are used with source biasing to minimize standby currents while operating at low voltage
- Bit Cell: Utilizes GlobalFoundries® Ultra-Low Leakage, 6T(L110) bit cells to ensure high manufacturing yields
- Five Power Modes: High Performance, Low Leakage, Standby, Retention, and Power Off modes provide flexibility for power optimization
-
Single Port Low Leakage SRAM Memory Compiler on GF 22FDX+
- Ultra-Low Leakage: High VT (HVT) and low leakage (LLHVT) devices are used with source biasing to minimize standby currents while operating at low voltage
- Bit Cell: Utilizes GlobalFoundries® Ultra-Low Leakage 6T (P110UL) bit cells to ensure high manufacturing yields
- Five Power Modes: High Performance, Low Leakage, Standby, Retention, and Power Off modes provide flexibility for power optimization
- Speed Grades: Three options to adjust the speed/leakage balance and optimize for high speed or low power operation
-
sROMet compiler - Memory optimized for high density and low power - Dual Voltage - compiler range up to 1M
- Foundry sponsored - sROMet compiler - TSMC 55 nm uLPeFlash - Non volatile memory optimized for high density and low power - Dual Voltage - compiler range up to 1M
-
Memory Compiler
- High-Density Memory Compilers
- Ultra-High-Speed Memory Compilers
- Low-Power Memory Compilers
-
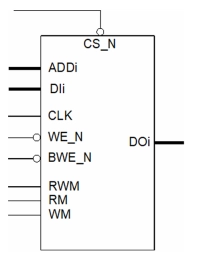
Single Port High Speed SRAM Memory Compiler on N22ULL
- Ultra low power data retention. Memory instances generated by the Bulk 22ULL go into a deep sleep mode that retains data at minimal power consumption.
- Self biasing. The SP SRAM 22ULL internal self-biasing capabilities provide ease of IP integration.
- High yield. To ensure high manufacturing yield, bulk 22ULL uses low leakage 6T (0.110µ2) bit cells and is consistent with Design for Manufacturing (DFM) guidelines for the Bulk 22ULL process.
- High usability. All signal and power pins are available on metal 4 while maintaining routing porosity in metal 4. Power pins can optionally be made available on metal 5 to simplify the power connections at the chip level.
-
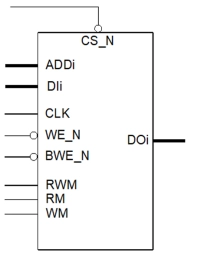
Single Port Low Voltage SRAM Memory Compiler on N22ULL - Low Power Retention and Column Repair
- Ultra-Low Leakage: High VT (HVT) are used to minimize leakage performance
- Bit Cell: Utilizes Low Leakage 6T bit cells to ensure high manufacturing yields
- Ultra Low Power Standby: Internally generated bias voltage for low leakage data retention
- Isolated Array and Periphery supplies: Periphery voltage can be shut off to further reduce standby power
-
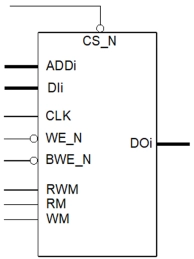
Single Port Low Voltage SRAM Memory Compiler on N22ULL
- Ultra-Low Leakage: High VT (HVT) are used to minimize leakage performance
- Bit Cell: Utilizes Low Leakage 6T bit cells to ensure high manufacturing yields
- Ultra Low Power Standby: Internally generated bias voltage for low leakage data retention
-
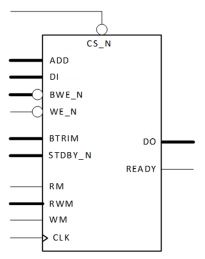
Single Port Low Leakage SRAM Memory Compiler on GF 22FDX
- Ultra-Low Leakage: High VT (HVT) and low leakage (LLHVT) devices are used with source biasing to minimize standby currents while operating at low voltage
- Bit Cell: Utilizes GlobalFoundries® Ultra-Low Leakage 6T (P110UL) bit cells to ensure high manufacturing yields
- Five Power Modes: High Performance, Low Leakage, Standby, Retention, and Power Off modes provide flexibility for power optimization
- Speed Grades: Three options to adjust the speed/leakage balance and optimize for high speed or low power operation
-
Ultra High-Speed Cache Memory Compiler - 2-Port Register File - TSMC N3P
- The Ultra High-Speed cache memory is an adaptable, independent, non-coherent cache Intellectual Property (IP) featuring an advanced cache architecture.
- This architecture enhances system performance, scalability, power efficiency, data locality, application responsiveness, cost optimization, and market competitiveness, providing a distinctive business value.