ML-KEM IP
Filter
Compare
31
IP
from
12
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
ML-KEM Key Encapsulation & ML-DSA Digital Signature Engine
- The KiviPQC™-Box is a hardware accelerator for post-quantum cryptographic operations.
- It implements both the Module Lattice-based Key Encapsulation Mechanism (ML-KEM) and the Module Lattice-based Digital Signature Algorithm (ML-DSA), standardized by NIST in FIPS 203 and FIPS 204, respectively.
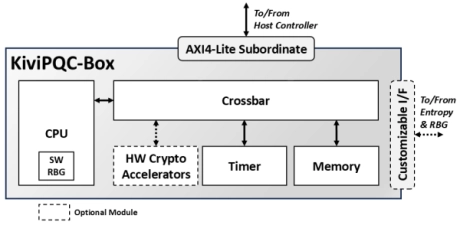
-
Post-Quantum ML-KEM IP Core
- Efficient Performance
- SCA/FIA Protections
- Patented High-Performance Modulo Multiplication
- Flexible Interfaces
-
ML-KEM Key Encapsulation IP Core
- The KiviPQC™-KEM is a hardware accelerator for post-quantum cryptographic operations.
- It implements the Module Lattice-based Key Encapsulation Mechanism (ML-KEM), standardized by NIST in FIPS 203.
- This mechanism realizes the appropriate procedures for securely exchanging a shared secret key between two parties that communicate over a public channel using a defined set of rules and parameters.
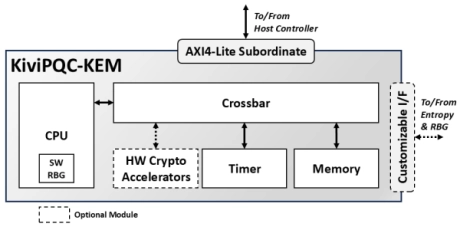
-
Fast Quantum Safe Engine for ML-KEM (CRYSTALS-Kyber) and ML-DSA (CRYSTALS-Dilithium)
- The Quantum Safe Engine (QSE) IP provides Quantum Safe Cryptography acceleration for ASIC, SoC and FPGA devices.
- The QSE-IP-86 core is typically integrated in a hardware Root of Trust or embedded secure element in chip designs together with a PKE-IP-85 core that accelerates classic public key cryptography and a TRNG-IP-76 core that generates true random numbers.
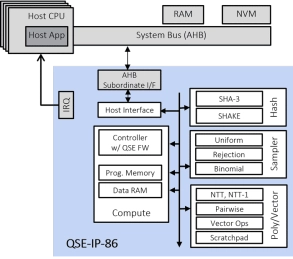
-
Fast Quantum Safe Engine for ML-KEM (CRYSTALS-Kyber) and ML-DSA (CRYSTALS-Dilithium) with DPA
- Compliant with FIPS 203 ML-KEM and FIPS 204 ML-DSA standards
- Uses CRYSTALS-Kyber, CRYSTALS-Dilithium quantum-resistant algorithms
- Includes SHA-3, SHAKE-128 and SHAKE-256 acceleration
- The embedded QSE CPU combined with Rambus-supplied firmware implements the full FIPS 203/204 protocols
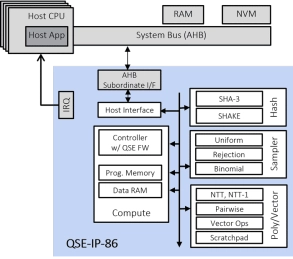
-
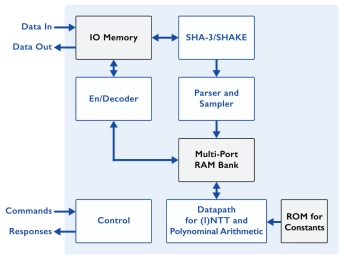
xQlave® ML-KEM (Kyber) Key Encapsulation Mechanism IP core
- Quantum-resistant key exchange for future-proof security
- Compliant with NIST's ML-KEM standard
- Pure RTL without hidden CPU or software components
- Optimised architecture with constant-time execution
-
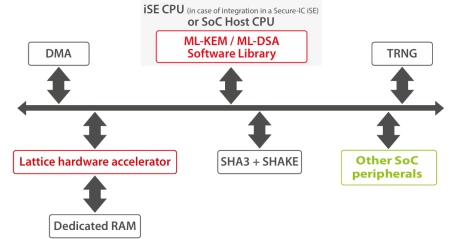
ML-KEM / ML-DSA Post-Quantum Cryptography IP
- ML-KEM (Crystals-Kyber) and ML-DSA (Crystals-Dilithium) are Post-Quantum Cryptographic (PQC) algorithms, meaning they are mathematically designed to be robust against a cryptanalytic attack using a quantum computer.
- Both have been standardized by the NIST in it post-quantum cryptography project.
-
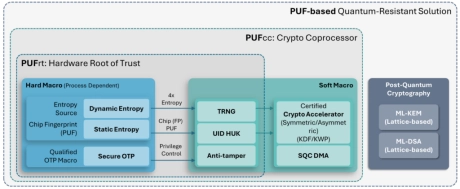
PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Solution
- PUFsecurity is proud to pioneer the world’s first PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) solution, delivering cutting-edge, hardware-level security that sets a new standard.
- Our innovative solution integrates PUF technology with quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, ensuring robust key protection and seamless transition to a quantum-secure future.
-
Post-Quantum Key Encapsulation and Digital Signature IP Core
- The KiviPQC-Box is an IP core that combines the algorithms ML-DSA and ML-KEM into one single package.
- ML-DSA and ML-KEM are algorithms that are standardized by NIST as post-quantum algorithms defined in NIST FIPS 204 and NIST FIPS 203 and provide cyber secure protection against the threat of quantum computers.