FIR IP
Filter
Compare
953
IP
from
143
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
FIR II Intel® FPGA IP Core
- The FIR II Intel IP core provides a fully-integrated finite impulse response (FIR) filter function optimized for use with Intel FPGA devices
- The FIR II IP core has an interactive parameter editor that allows you to easily create custom FIR filters
- The parameter editor outputs IP functional simulation model files for use with Verilog HDL and VHDL simulators
- You can use the parameter editor to implement a variety of filter types, including single rate, decimation, interpolation, and fractional rate filters.
-
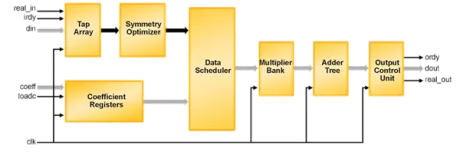
Serial FIR Filter
- Serial Arithmetic for Reduced Resource Utilization
- Variable Number of Taps up to 64
- Data and Coefficients up to 32 Bits
- Output Size Consistent with Data Size
-
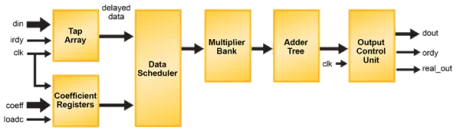
Parallel FIR Filter
- Variable number of taps up to 64
- Data and coefficients up to 32 bits
- Output size consistent with data size
- Zero-latency operation
-
FIR Filter Generator
- Direct Form 64-Tap FIR Filter: In the direct form FIR filter, the input samples are shifted into a shift register queue and each shift register is connected to a multiplier. The products from the multipliers are added together to get the FIR filter’s output sample. This example shows a 64-tap FIR filter using 16 sysDSP blocks and approximately 512 slices in the LatticeECP3 FPGA.
- 128-Tap Long Asymmetrical Filters Using Ladder Architecture: Using the ladder architecture, the FIR filter is split into sections each having the same coefficient set as if it was a single continuous filter chain. Instead of connecting the shifted data and the result outputs from the first section to the corresponding input of the next section, the ladder network connects a delayed version of the first stage input data to the second stage input data and sums a delayed version of the first stage sum output with the second stage sum output.
- 256-Tap Long Symmetrical Filters Using Ladder Architecture: The impulse response for most FIR filters is symmetric. This symmetry can generally be exploited to reduce the arithmetic requirements and produce area-efficient filter realizations. It is possible to use only half the multipliers for symmetric coefficients compared to that used for a similar filter with non-symmetric coefficients. An implementation for symmetric coefficients is shown in the figure below. The 256-tap long symmetrical filter example uses only 32 sysDSP slices, 2EBR and 3.5K slices.
- Polyphase Interpolator FIR Filter Designs: The polyphase interpolation filter implements the computationally efficient 1-to-P interpolation filter where P is an integer greater than 1. The example below shows a design with an interpolation by 16 that uses 128 taps. This requires 8 polyphase filters (sub-filters) with 16 coefficients each.
-
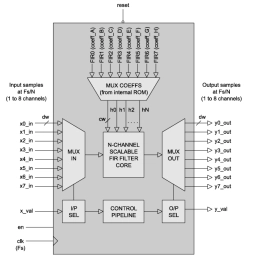
N-channel Multiplexed FIR Filter
- FIR_NTAP_MUX is an N-channel multiplexed FIR filter designed for high sample rate applications where hardware resources are limited.
- The main filter core is organized as a scalable systolic array permitting the user to specify large order filters without compromising maximum attainable clock-speed.
-
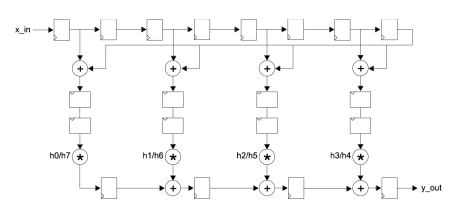
Generic high-speed FIR Filter with symmetry
- FIR filter designed for high sample rate applications with symmetrical coefficients and an even or odd number of taps.
- Features configurable coefficients and data width. Design uses only half the number of multipliers compared to a normal FIR implementation.
- Matlab®, FDAtool and Simulink® compatible.
-
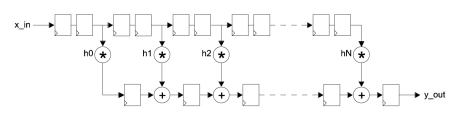
Generic ultra-speed FIR Filter
- FIR filter designed for very high sample rate applications up to 600 MHz.
- Organized as a systolic array, the filter is modular and scalable, permitting the user to specify large order filters without compromising maximum attainable clock-speed. Matlab®, FDAtool and Simulink® compatible.
-
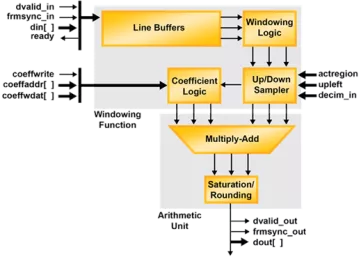
2D FIR Filter
- Single color plane
- Single-rate, interpolating, and decimating filter configurations
- Input frame size set at compile-time
- Static or dynamic zoom and pan
-
FIR Compiler
- Delivers VHDL demonstration testbench with CORE Generator
- Supports Pipelined Direct-Form based Multiply Accumulate (MAC) FIR and Transposed Direct-Form based MACFIR
- High-performance finite impulse response (FIR), polyphase decimator, polyphase interpolator, half-band, half-band decimator and half-band interpolator, Hilbert transform, and interpolated filter implementations
- Advanced interleaved channels to enable implementation of configurable bandwidth feature for advanced systems
-
TX & RX FIR Filter specifically to support DSP Application
- Synthesizable, technology-independent IP Core for FPGA/ASIC and SoC
- Coded with Verilog
- It support 2 type of filters, Equiripple and Root Rise Cosine (RRC)
- 16/12-bit Fixed-Point Representation/Operation (Imaginary and Real Number)
