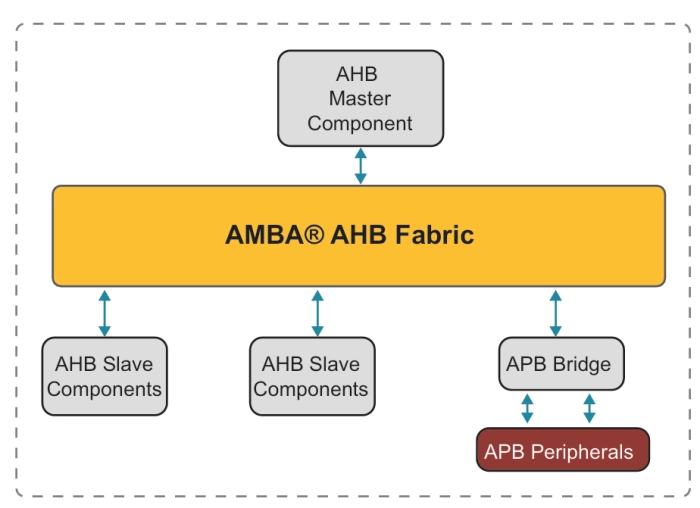
The AHB Channel provides the necessary infrastructure to connect as many as 7 AHB Slaves (numbered 1-7) to an AHB bus Master. The AHB Channel performs a combinational decode on the incoming AHB address to produce the block selects for the various AHB Slaves. The address decoder contained in the AHB Channel has one area of memory reserved for a configurable remap application.
Typically, the AHB Channel is connected as in the following description. Each of the AHB Channel’s 7 Mirrored Slave Ports is connected to an AHB Slave module (e.g. External Bus Interface, Memory Controller, AHB-to-APB Bridge.) On the Master side, the AHB Channel’s Mirrored Master Port is connected either to an AHB Arbiter (in an AHB system with multiple bus Masters) or directly to an AHB Master such as a micro-processor (in an AHB system with a single bus Master.)
AHB Channel with Decoder and Data Mux IP Core
Overview
Key Features
- AMBA® 2.0 Compatible
- Simple AHB Infrastructure for up to 7 AHB Slaves
- Multiple Masters can be easily accommodated using AHB Arbiter
- Includes Address Decoding
- Includes Read Data Muxing
- Remap to assist boot loading and debug
Block Diagram
Deliverables
- Verilog Source
- Complete Test Environment
- AHB Bus Functional Model
Technical Specifications
Short description
AHB Channel with Decoder and Data Mux IP Core
Vendor
Vendor Name
Maturity
Silicon Proven
Availability
Now
Related IPs
- APB Channel with Decoder and Data Mux
- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES-128) core with AMBA AHB interface
- RSA/ECC Public Key Accelerator Farm with TRNG and AHB
- RSA/ECC Public Key Accelerators with TRNG and AHB
- AHB Octal SPI Controller with PSRAM and XIP Support
- High Channel Count DMA IP Core for PCI-Express