ESIstream IP
Filter
Compare
45
IP
from
15
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
UDP Offload Engine for IPv6
- Full IPv6 support including Echo, NDP, MLD
- Line-rate UDP/IPv6 transmit and receive
- RFC 768 & RFC 8200 compliant
- Packet parsing and header synthesis in hardware
-
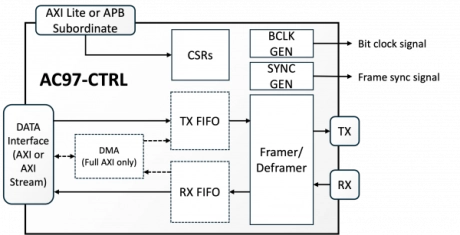
AC'97 Audio Controller
- The AC97-CTRL Audio Controller is a configurable IP block designed to simplify the integration of the AC'97 audio interface into ASIC and FPGA designs.
- Fully compliant with the Intel Audio Codec '97 (AC’97) Revision 2.3 specification, this controller facilitates reliable transmission and reception of stereo or multi-channel audio streams using the well-established AC-Link interface.
- With support for a single codec operating at a standard 48 kHz sample rate, the core is ideal for embedded applications that demand proven audio infrastructure with a compact silicon footprint and efficient data handling.
-
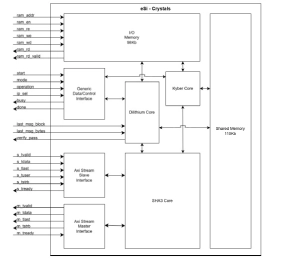
PQC CRYSTALS core for accelerating NIST FIPS 202 FIPS 203 and FIPS 204
- eSi-Crystals is a hardware core for accelerating the high-level operations specified in the NIST FIPS 202, FIPS 203 and FIPS 204 standards.
- It supports the Cryptographic Suite for Algebraic Lattices (CRYSTALS), it is lattice-based digital signature algorithm designed to withstand attacks from quantum computers, placing it in the category of post-quantum cryptography (PQC).
-
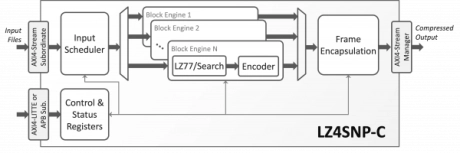
LZ4/Snappy Data Compressor
- LZ4SNP-C is a custom hardware implementation of a lossless data compression engine that complies with the LZ4 and Snappy compression standards.
- The core receives uncompressed input files and produces compressed files. No post-processing of the compressed files is required, as the core encapsulates the compressed data payload with the proper headers and footers.
-
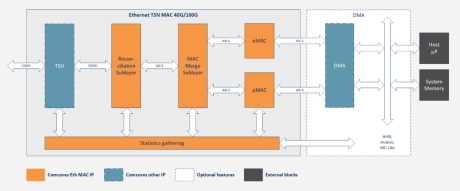
Ethernet TSN MAC 40G/100G
- Silicon agnostic Ethernet TSN MAC IP with speeds of 40G and 100G, based IEEE 802.3 Ethernet Layer 2 solution with support for key TSN features
-
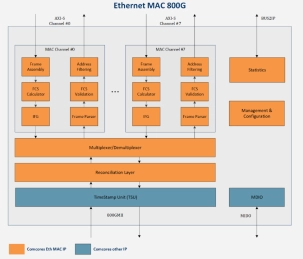
Ethernet MAC 800G
- The 800G Ethernet Media Access Control (MAC) IP core provides a comprehensive and flexible solution for implementing the IEEE 802.3 MAC layer for high-speed Ethernet required in demanding applications such as hyperscale data centers, high-performance computing (HPC), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) / Machine Learning (ML) clusters.
-
R-Tile PCIe Hard IP
- R-Tile is a FPGA companion tile that supports configurations up to PCIe 5.0 x16 in Endpoint (EP), Root Port (RP), and Transaction Layer (TL) Bypass modes
- PCIe 3.0, 4.0, and 5.0 configurations are natively supported
- R-Tile also supports up to 16 SerDes channels through a PHY Interface for PCIe (PIPE) 5.1.1 in SerDes Architecture mode.
-
Intel® FPGA IP for PCIe
- PCI Express (PCIe*) protocol is a high-performance, scalable, and feature-rich serial protocol with data transfer rates from 2.5 gigatransfers per second (GT/s) to 32 GT/s and beyond
- Intel® FPGA Intellectual Property (IP) for PCIe continues to scale as the PCI-SIG organization delivers next-generation specifications
- Intel has been a member of PCI-SIG since 1992, and with each new generation of silicon, Intel continues to participate in PCI-SIG Compliance Workshops to ensure interoperability and conformance with current industry standards.
-
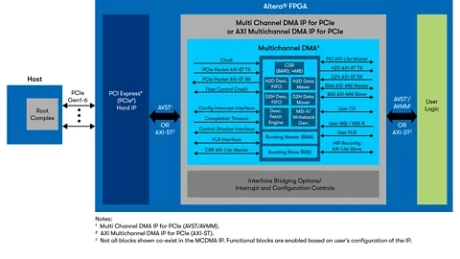
Multichannel DMA Intel FPGA IP for PCI Express*
- The Multichannel DMA IP for PCI Express provides high efficiency, speed, and configuration flexibility to support various applications from HPC, cloud, networking, to embedded
- With support for up to 2048 channels and Linux-based PCIe drivers provided, this low latency, low resource utilization solution is essential in handling movements of large volumes of data to optimize system performance.
-
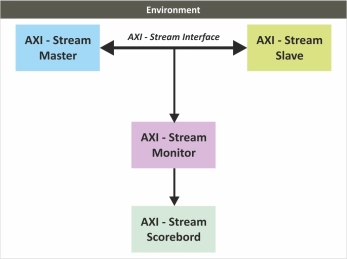
AMBA AXI STREAM Verification IP
- Compliant with AMBA® AXI5- Stream and AXI4-Stream.
- Support for all types of AMBA AXI5-Stream and AXI4-STREAM components.
- Supports parameterized data widths.
- Supports byte stream transmission number of data and null bytes.