SPI IP
Filter
Compare
471
IP
from
96
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
Quad SPI Controller
- The SPI controller support master/slave operation over the single-lane, dual-lane,quad-lane and half duplex singlelane protocols
- Programmable clock polarity and phase (CPOL/CPHA)
- Configurable MSB First or LSB First
- Master/Slave mode configurable frequency (FPCLK/2 max)
- SPI bus busy status flag
-
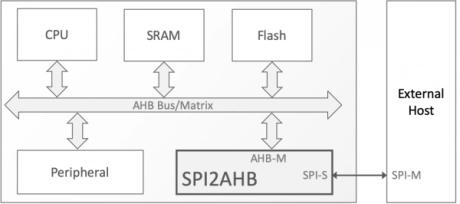
SPI to AHB Bridge
- The SPI to AHB bridge is an SPI slave that provides a link between a SPI bus (that consists of two data signals, one clock signal and one select signal) and AMBA AHB.
- On the SPI bus the slave acts as an SPI memory device where accesses to the slave are translated to AMBA accesses.
- The core can translate SPI accesses to AMBA byte, half-word or word accesses. The access size to use is configurable via the SPI bus.
-
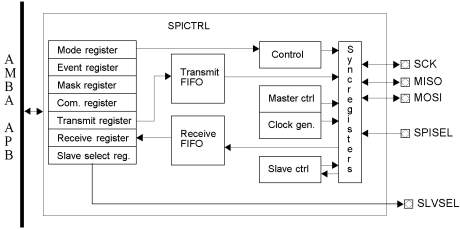
SPI Controller
- The SPICTRL provides a link between the AMBA APB bus and the Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) bus.
- Through registers mapped into APB address space the core can be configured to work either as a master or a slave.
-
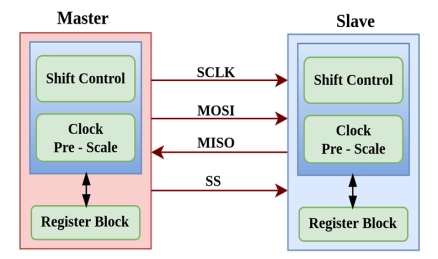
SPI - Function Controller
- The SPI protocol specification supports high speed data transfer as per the peripheral specification, making it ideal for high - performance applications that require fast data transfer rates.
-
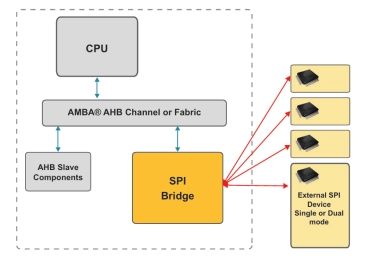
AHB-Lite Slave to SPI Master
- The AHB-Lite to SPI Bridge is used to translate 32-bit AHB-Lite Writes and Reads to Writes and Reads over a SPI interface. A custom 32-bit protocol is implemented on the SPI bus.
- The AHB-Lite to SPI Bridge has two AHB-Lite Slave component interfaces; one for access to the control/status registers (Register Interface), and another for access to the external SPI device (External Interface).
- The Bridge also has a SPI interface that operates exclusively as a SPI Master component device.
-
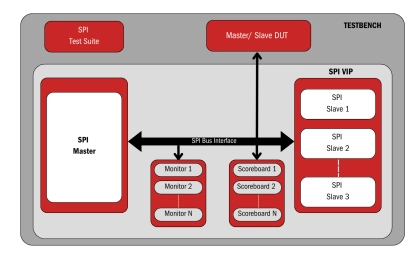
SPI - Verifies reliable data transfer and protocol compliance in SPI systems
- SPI (Serial Peripheral Interface) is a high-speed, synchronous communication protocol that ensures reliable data transfer between microcontrollers and peripherals. It verifies correct data transmission, signal timing, and error handling in SoC designs.
- This versatile Verification IP (VIP) supports various SPI modes and clock configurations, enabling robust testing of master-slave communication, data integrity, and error conditions across multiple applications in embedded systems, automotive, IoT, and more
-
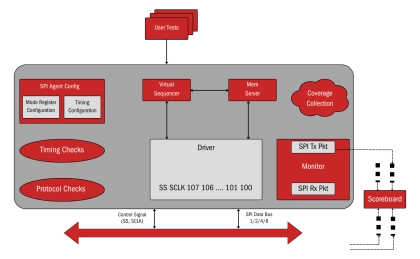
SPI Flash Controller - Ensures reliable validation of SPI Flash memory controllers
- The SPI Flash Controller Verification IP (VIP) is a powerful tool for verifying and simulating SPI Flash memory controllers in SoCs. It supports single, dual, and quad SPI modes, enabling seamless validation of read, write, erase, and advanced operations.
- This VIP is designed for diverse applications, including IoT devices, automotive systems, consumer electronics, and aerospace. It ensures efficient performance, low power usage, and reliable integration of SPI Flash memory in mission-critical and everyday devices
-
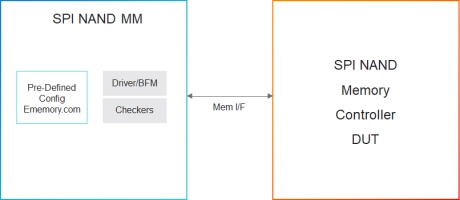
Simulation VIP for SPI NAND
- Operation Modes
- Single I/O, Dual I/O, and Quad I/O (Q-SPI and QSPI) and serial mode 0 and mode 3
- Pins
- HOLD# and WP# Pins functionalities
-
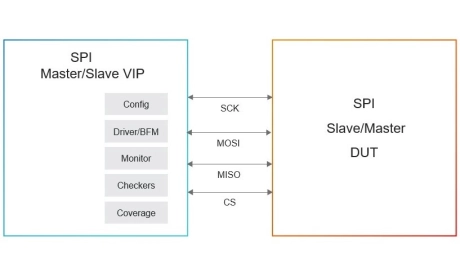
Simulation VIP for SPI
- Full Duplex
- Simultaneous transfer from Manager and Subordinate
- Variable Size Shift Registers
- 8, 16, and 32-bit shift register for Tx and Rx
-
SPI to AHB-Lite Bridge
- The SPI2AHB core implements an SPI slave to AHB-Lite master bridge. It allows an external SPI master to perform read or write access to any memory-mapped device on the internal AHB bus.
- The core implements a simple over-SPI protocol to convert SPI transactions into AHB Read or Write instructions.