Post-Quantum IP
Filter
Compare
42
IP
from
15
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) Solution
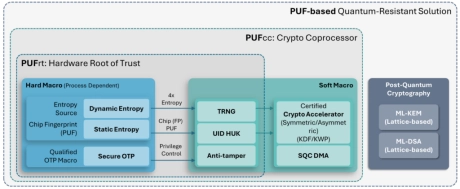
- PUFsecurity is proud to pioneer the world’s first PUF-based Post-Quantum Cryptography (PQC) solution, delivering cutting-edge, hardware-level security that sets a new standard.
- Our innovative solution integrates PUF technology with quantum-resistant cryptographic algorithms, ensuring robust key protection and seamless transition to a quantum-secure future.
-
Post-Quantum Key Encapsulation and Digital Signature IP Core
- The KiviPQC-Box is an IP core that combines the algorithms ML-DSA and ML-KEM into one single package.
- ML-DSA and ML-KEM are algorithms that are standardized by NIST as post-quantum algorithms defined in NIST FIPS 204 and NIST FIPS 203 and provide cyber secure protection against the threat of quantum computers.
-
High-Performance Hybrid Classical and Post-Quantum Cryptography
- The High-Performance Hybrid Cryptography IP core delivers accelerated support for both classical (RSA, ECC) and post-quantum (ML-KEM, ML-DSA) algorithms in a unified architecture optimized for maximum throughput.
-
Hybrid Classical and Post-Quantum Cryptography
- The Hybrid Cryptography IP core combines traditional asymmetric algorithms—such as RSA and ECC—with post-quantum standards including ML-KEM (Kyber) and ML-DSA (Dilithium)—in a single, efficient hardware module.
-
Post-Quantum Accelerator
- The Post-Quantum Cryptography IP core provides a high-efficiency hardware solution supporting ML-KEM (Kyber) and ML-DSA (Dilithium) as standardized in FIPS 203 and 204, along with additional hash-based signature schemes including SPHINCS+, XMSS, and LMS.
-
Post-Quantum ML-DSA IP Core
- Efficient Performance
- SCA/FIA Protections
- Patented High-Performance Modular Multiplication
- Flexible Interfaces
- RAM/ROM Firmware Support
-
Post-Quantum ML-KEM IP Core
- Efficient Performance
- SCA/FIA Protections
- Patented High-Performance Modulo Multiplication
- Flexible Interfaces
-
Post-Quantum Digital Signature IP Core
- The KiviPQC-DSA is an IP core implementing the ML-DSA (Module-Lattice-based Digital Signature Algorithm) a post-quantum cryptographic standard defined by NIST FIPS 204.
- Designed to withstand both classical and quantum computer attacks, ML-DSA ensures the authenticity and integrity of signed data far into the future.
-
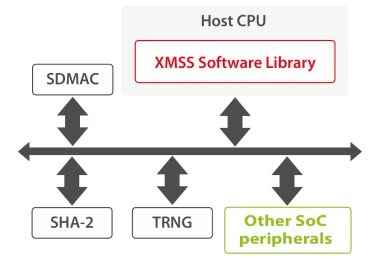
XMSS Post-Quantum Cryptography IP
- XMSS is a Post-Quantum Cryptographic (PQC) algorithm, meaning it is mathematically designed to be robust against a cryptanalytic attack using a quantum computer.
- XMSS is a stateful Hash-Based Signature Scheme that has been recommended by NIST in 2020.
-
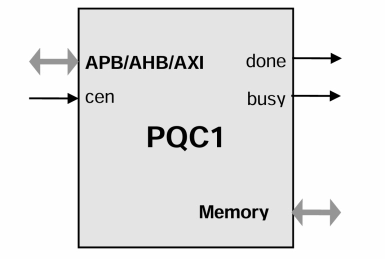
APB Post-Quantum Cryptography Accelerator IP Core
- Implements ML-KEM and ML-DSA post-quantum cryptography digital signature standards. The system interface is an microprocessor slave bus (APB, AHB, AXI options are available).
- The design is fully synchronous and requires only minimal CPU intervention due to internal microprogramming sequencer.