FPU IP
Filter
Compare
91
IP
from
19
vendors
(1
-
10)
-
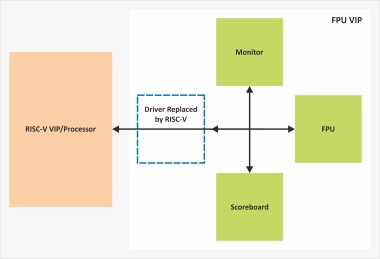
FPU Verification IP
- Compliant to RISC-V Specification and IEEE 754 floating point standard.
- Configurable bits (half, single, double and quad precision).
- Supports all RISC-V Floating point instructions (ADD, SUB, MUL, DIV, SQRT, comparison, and conversion between float and int).
- Supports the rounding modes defined by RISC-V.
-
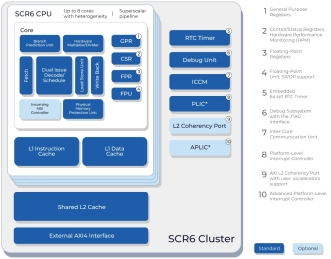
High-performance microcontroller core with a 12-stage dual-issue out-of-order pipeline and a high performance FPU
- SCR6 is a high-performance, silicon-proven, 64-bit RISC-V processor core. It is optimized for embedded RTOS-based applications, that require considerable computational power.
- The SCR6 core supports RISC-V standard "I" Integer, "M" Integer Multiplication and Division, "A" Atomic, "C" 16-bit compressed, "F" Single-Precision Floating-Point, "D" Double-Precision Floating-Point, "B" Bit Manipulation, and "K" Scalar Cryptography extensions.
-
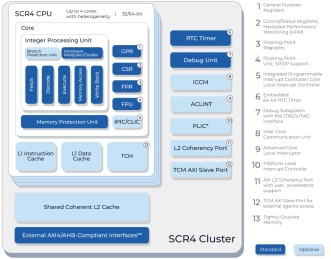
Efficient microcontroller core with a 5-stage in-order pipeline, privilege modes, an FPU, an MPU, L1 and L2 caches
- SCR4 is a 32/64-bit RISC-V low-power, high-performance, area-optimized processor core with floating-point arithmetic functionality.
- The SCR4 core fully supports RISC-V standard "I" Integer, "M" Integer Multiplication and Division, "A" Atomic, "C" 16-bit Compressed, "F" Single-Precision Floating-Point, "D" Double-Precision Floating-Point, “B” Bit Manipulation, and “K” Scalar Cryptography extensions.
-
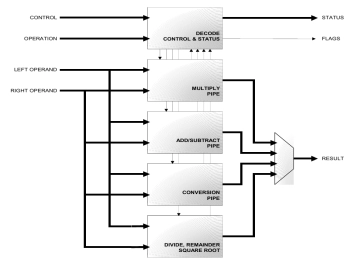
Double & Single Precision IEEE-754 complete FPU
- The A2FD is a fully synthesizable module implemented in Verilog RTL.
- It is a co-processor unit providing floating-point computation compliant with the ANSI/IEEE Std 754-1985, IEEE Standard for Binary Floating-Point Arithmetic (IEEE Standard).
- It is designed to provide high performance floating-point computation while minimizing die size and power. Pipelined, single-cycle throughput operation is available for all operations except Divide, Remainder and Square Root operations.
-
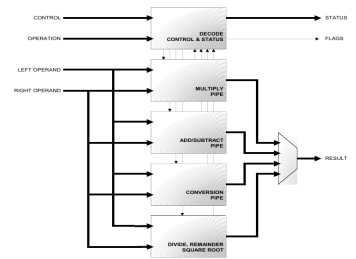
Half Precision IEEE-754R complete FPU for graphics processing
- The A2FH is a co-processor unit providing floating-point computation compliant with the ANSI/IEEE Std 754-2008, IEEE Standard for Binary Floating-Point Arithmetic (IEEE-754R Standard).
- It is designed to provide a powerful floating-point functionality for low-power, low frequency applications.
-
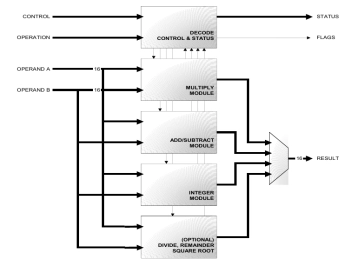
Single Precision IEEE-754 complete FPU
- The A2F is a fully synthesizable module implemented in Verilog RTL.
- It is a co-processor unit providing floating-point computation compliant with the ANSI/IEEE Std 754-1985, IEEE Standard for Binary Floating-Point Arithmetic (IEEE Standard).
- It is designed to provide high performance floating-point computation while minimizing die size and power.
-
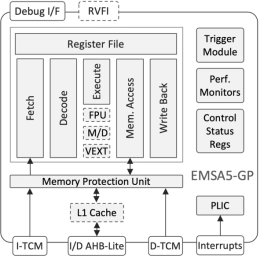
Vector-Capable Embedded RISC-V Processor
- The EMSA5-GP is a highly-featured 32-bit RISC-V embedded processor IP core optimized for processing-demanding applications.
- It is equipped with floating-point and vector-processing units, cache memories, and is suitable for concurrent execution in a multi-processor environment.
-
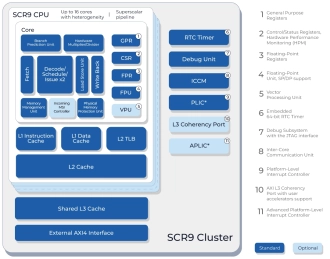
High-performance Linux-capable application core with a 12-stage dual-issue out-of-order pipeline, a VPU, cache coherency, and a hypervisor
- SCR9 is a high-performance, silicon-proven, Linux-capable 64-bit RISC-V processor core for entry-level server-class applications and personal computing devices.
- The SCR9 core supports RISC-V standard "I" Integer, "M" Integer Multiplication and Division, "A" Atomic, "C" 16-bit Compressed, "F" Single-Precision Floating-Point, "D" Double-Precision Floating-Point, "V" Vector Operations, "B" Bit Manipulation, and "K" Scalar Cryptography extensions.
-
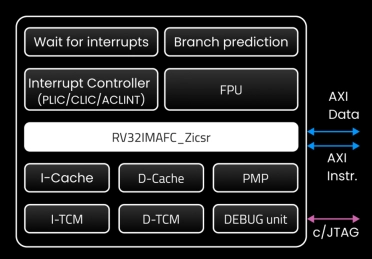
Custom RISC-V Processor
- Traditional processors no longer strike the right balance between high performance, energy consumption, and cost.
- Keysom processors deliver powerful capabilities, optimizing IoT and AI workflows with energy-efficient, small-footprint solutions.
-
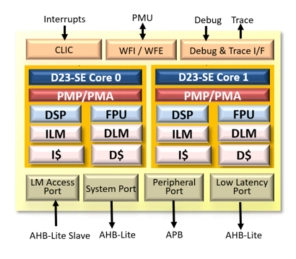
ISO26262 ASIL-B/D Compliant 32-bit RISC-V Core
- The AndesCore™ D23-SE is a 32-bit 3-stage pipeline CPU IP core based on AndeStar™ V5 architecture for embedded applications with small gate count, and some dual-issue ability.
- In addition to commonly used RISC-V IMAC, single/double precision FPU and DSP extensions, it supports the recently ratified ISA extensions such as B (bit manipulation), K (scalar cryptography), CMO (cache management operations) as well as Zce (code size reduction), plus Andes Custom Extension™ (ACE) for user-defined instructions.